Electric railway auto-transformer (AT) traction network fault positioning method
A technology for electrified railway and fault location, which is applied to the fault location, fault detection according to the conductor type, and electrical measurement. It can solve the problems of impact, short-circuit data limited, poor positioning accuracy, etc., and achieve the effect of less investment and easy implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
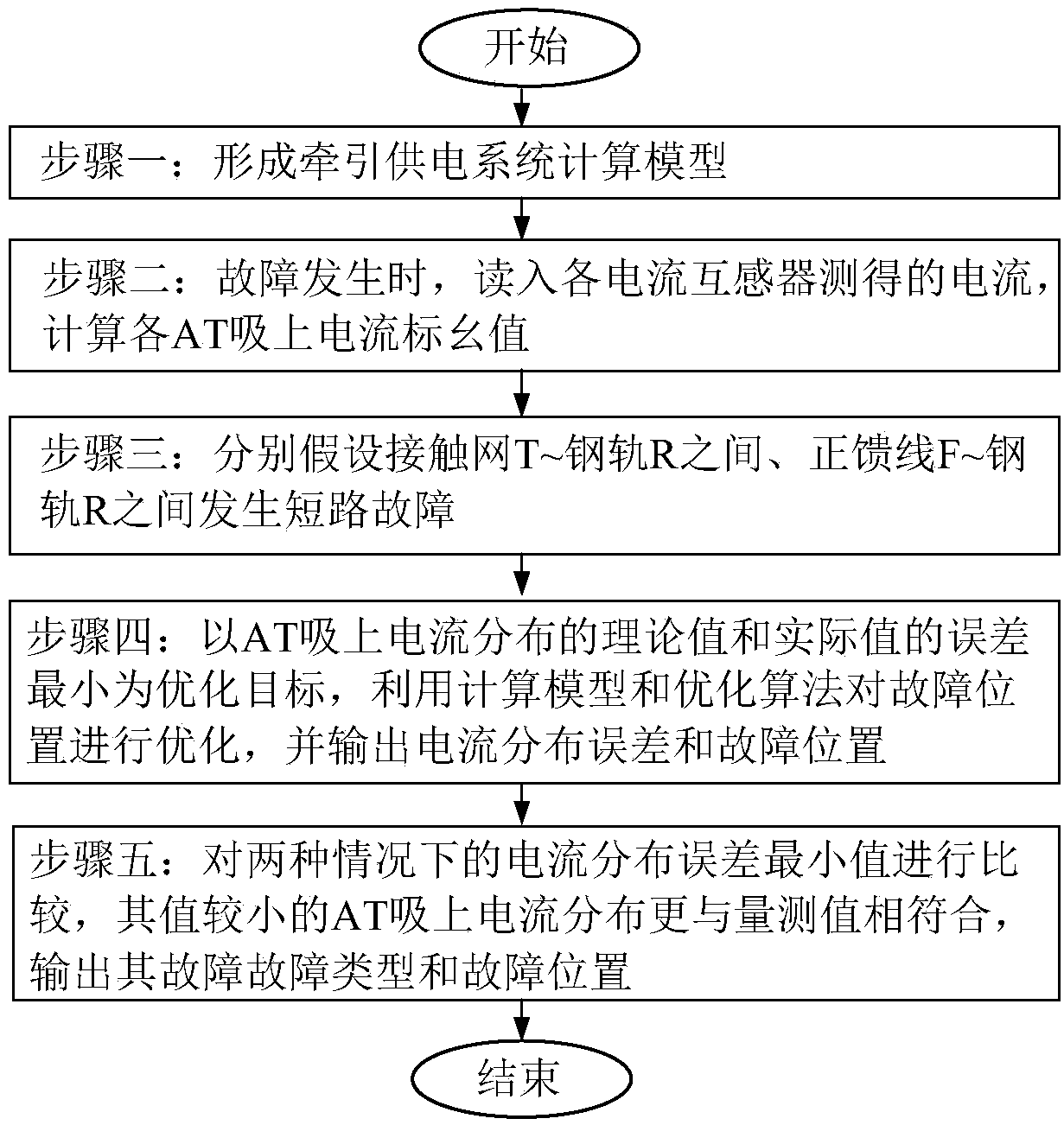
[0044] The implementation steps of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings and specific embodiments.
[0045] The implementation steps of this method are as follows: figure 1 shown and explained as follows:
[0046] Step 1. Forming the traction power supply system model:
[0047] The calculation model of AT traction network is established based on multi-conductor transmission line theory or generalized symmetric component method. When the power supply line is long, in order to improve the accuracy of fault location, the influence of power supply line should be considered when modeling.
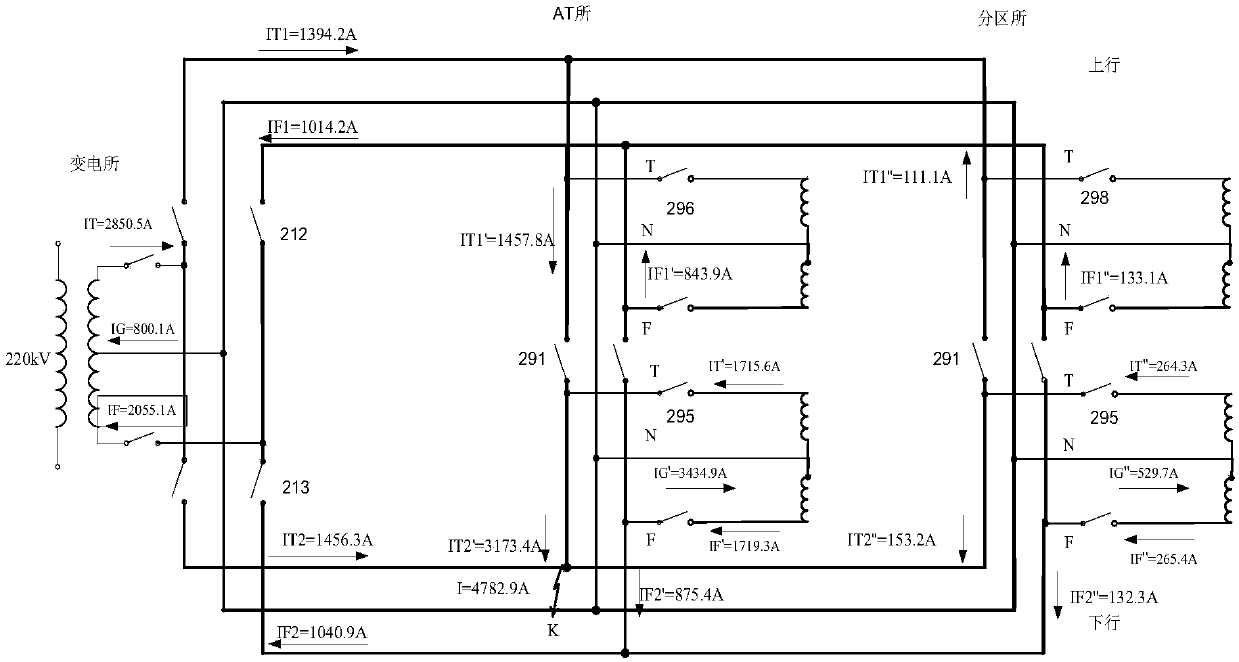
[0048] Step 2. When a fault occurs, read in the current measured by each current transformer, and calculate the per unit value of the current absorbed by each AT:
[0049] When the AT traction network fails, the actual short-circuit current can be obtained by the generalized symmetrical component method according to the measured current of the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com