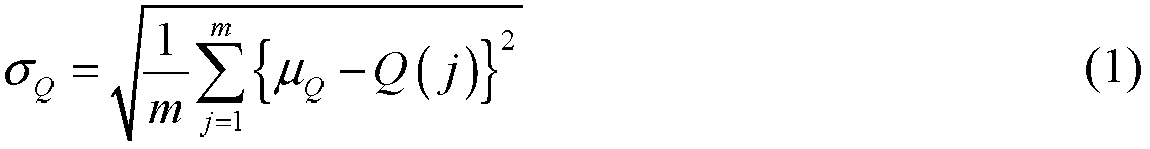Energy consumption balancing and coverage keeping method for underwater wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and network technology, applied in the direction of network topology, wireless communication, energy consumption reduction, etc., can solve the problems that the cluster head node contains many cluster members, local network interruption, and needs to be further improved, so as to maintain network coverage, The effect of reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
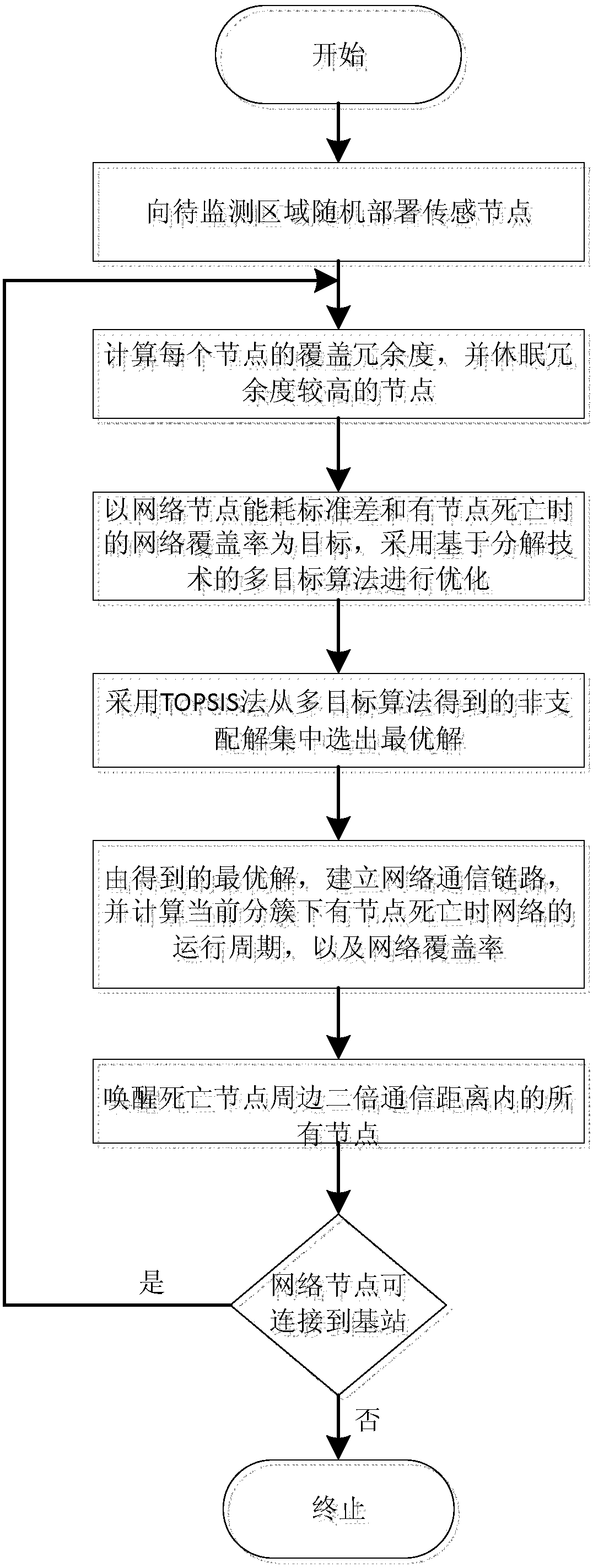
[0030] The implementation of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments, so as to fully understand how the present invention applies technical means to solve technical problems and achieve the realization process of technical effects and implement them accordingly. It should be noted that, as long as there is no conflict, each embodiment of the present invention and each feature in each embodiment can be combined with each other, and the technical solutions formed are all within the protection scope of the present invention.
[0031] The present invention first calculates the degree of influence of the network node on the coverage rate when the network node is dormant, and executes the dormancy strategy for the node with less impact, that is, the node with high coverage redundancy, and then calculates the standard deviation of the network coverage rate and the energy consumption of the network node As the goa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com