Driving destination recommendation method and device
A destination and data technology, applied in the field of information processing, can solve the problem that the driving destination recommendation method cannot be recommended
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0066] The technical solutions of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Apparently, the described embodiments are some of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all of them. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
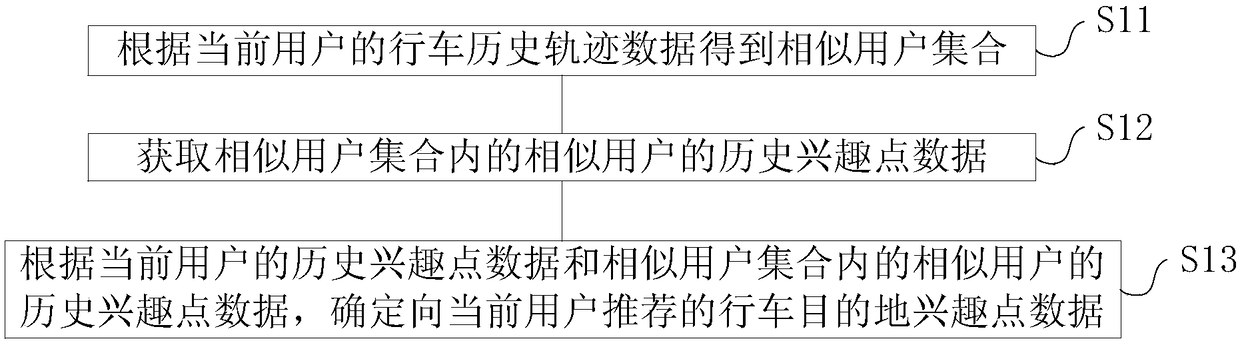
[0067] An embodiment of the present invention provides a driving destination recommendation method, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0068] S11. Obtain a set of similar users according to the current user's driving history trajectory data; wherein, through matching the current user's driving history trajectory data with the navigation electronic map, the user's driving history trajectory record database Da is obtained, and the driving history trajectory record database Da includes but It is not limited to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com