Method for improving in vitro fertilizable competence of vitrification freezing oocyte
A technology of vitrification and oocytes, which is applied in the field of artificial in vitro fertilization, can solve the problems of decreased fertilization ability of vitrified oocytes, solve the problem of decreased fertilization ability, increase cleavage rate and blastocyst rate, and be widely used foreground effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
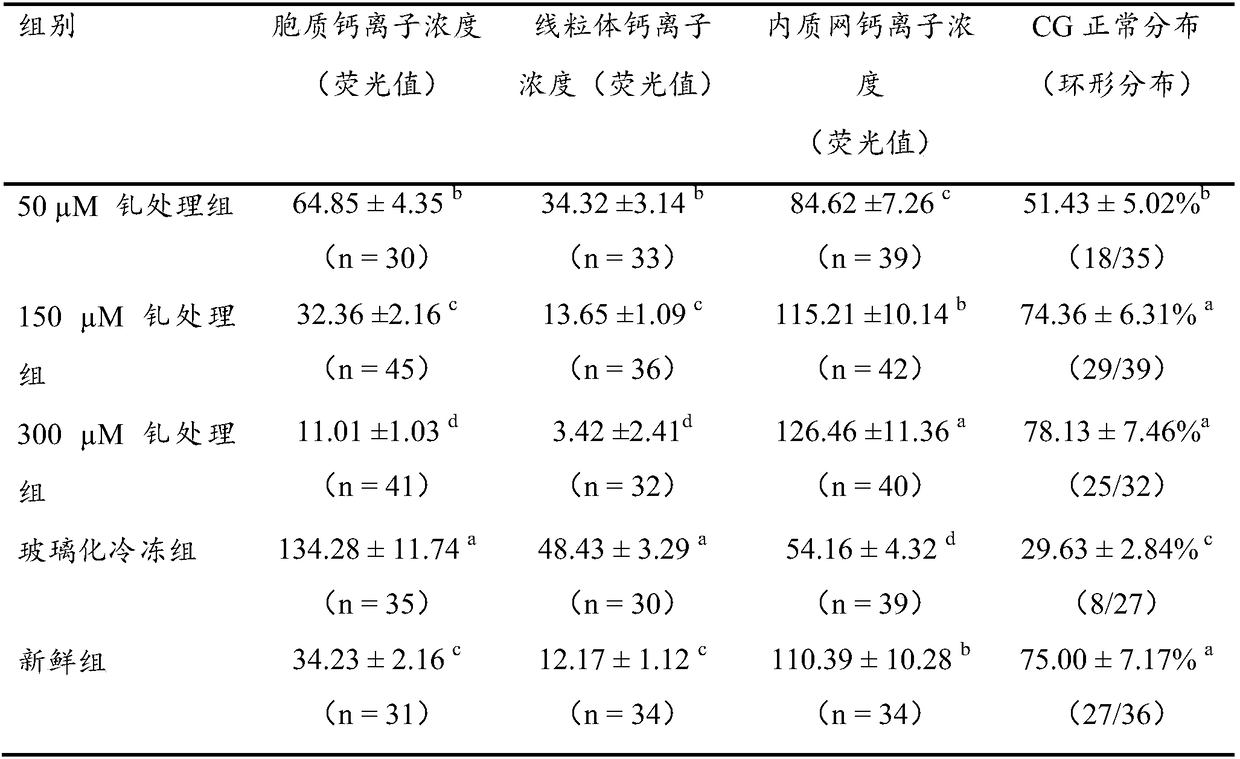
[0060] Example 1 Effect of Gadolinium Treatment on Vitrified Bovine Oocyte Cytoplasmic Calcium, Mitochondrial Calcium, Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium, and CG Distribution
[0061] Bovine oocytes were treated with 50 μM, 150 μM, and 300 μM gadolinium for 40 minutes, and then vitrified. The effects of different gadolinium treatments on the distribution of oocyte cytoplasmic calcium, mitochondrial calcium, endoplasmic reticulum calcium, and CG were compared.
[0062] As shown in Table 1, the cytoplasmic calcium ion concentration and mitochondrial calcium ion concentration in the gadolinium treatment group were significantly lower than those in the vitrification group, the endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion concentration in the gadolinium treatment group was significantly higher than that in the vitrification group, and the cytoplasmic calcium ion concentration in the 150 μM gadolinium treatment group There was no significant difference in internal calcium ion concentration, mitochon...
Embodiment 2
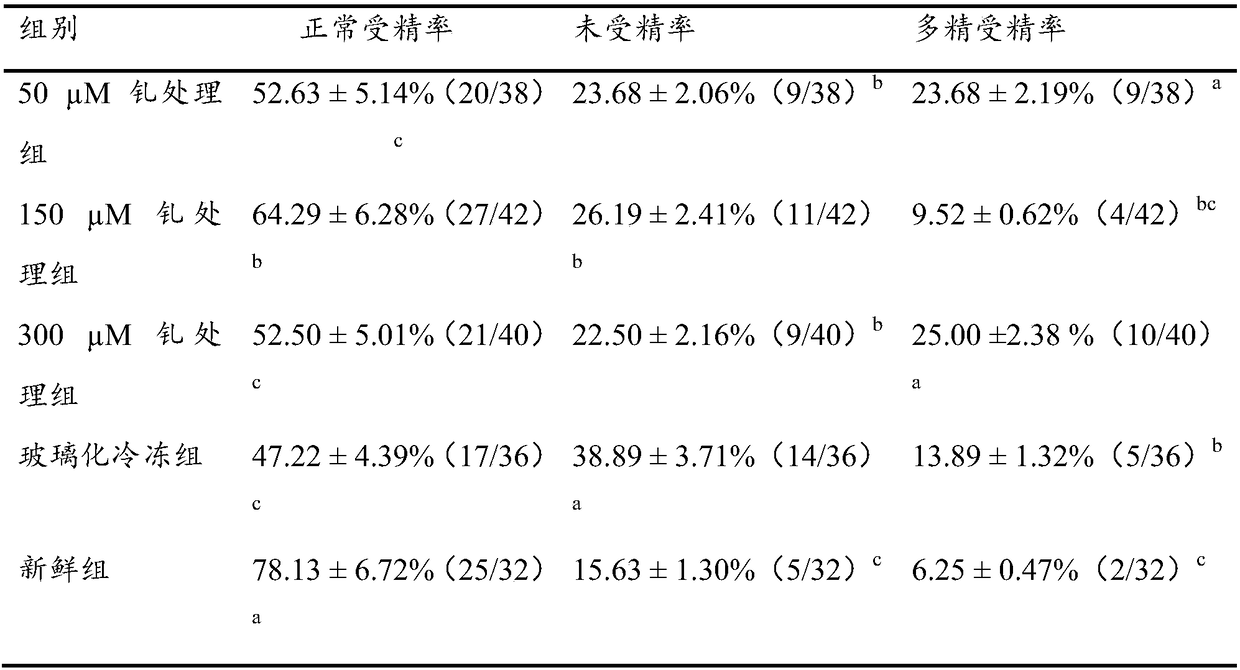
[0067] Example 2 Effect of Gadolinium Treatment on Fertilization Ability of Vitrified Bovine Oocytes
[0068] Bovine oocytes were treated with 50 μM, 150 μM, and 300 μM gadolinium for 40 min, and then vitrified. After thawing, the surviving oocytes were selected for IVF, and the oocytes were tested for fertilization ability after 8 hours of IVF. Then compare the effects of different gadolinium treatments on the fertilization ability of bovine oocytes.
[0069] As shown in Table 2, the normal fertilization rate in the 150 μM gadolinium treatment group (64.29±6.28%) was significantly higher than that in the vitrification group (47.22±4.39%), but still lower than that in the fresh group (78.13±6.72%). Meanwhile, the infertilization rate (26.19±2.41%) in the 150 μM gadolinium treatment group was significantly lower than that in the vitrification group (38.89±3.71%), but still significantly higher than that in the fresh group (15.63±1.30%). The fertilization rate of polyspermia i...
Embodiment 3
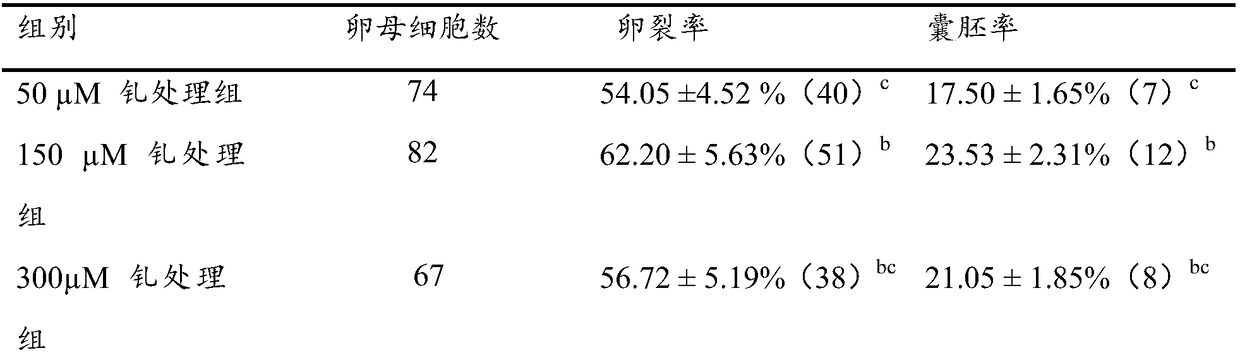
[0072] Example 3 Effect of Gadolinium Treatment on Fertilization Efficiency of Vitrified Bovine Oocytes
[0073] Bovine oocytes were treated with 50 μM, 150 μM, and 300 μM gadolinium for 40 min, and then vitrified. After thawing, the surviving oocytes were selected for IVF, and the cleavage rate and blastocyst rate were counted, and then the effects of different gadolinium treatments on the fertilization efficiency of bovine oocytes were compared.
[0074] As shown in Table 3, the cleavage rate and blastocyst rate (62.20±5.63%, 23.53±2.31%) of the 150 μM gadolinium treatment group were significantly higher than those of the vitrification group (40.85±3.82%, 13.79±1.05%), but both were significantly Lower than fresh group (79.03±7.62%, 36.73±3.28%).
[0075] Table 3 Effect of gadolinium on in vitro fertilization efficiency of vitrified bovine oocytes
[0076]
[0077]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com