A kind of genetic engineering horseshoe crab blood g factor and its preparation method and application
A technology of genetic engineering and G factor, which is applied in the field of genetically engineered Limulus blood G factor and its preparation, can solve the problem that the limulus reagent cannot be directly used to detect fungal infection, cannot completely block endotoxin interference, and the demand for detection reagents is increasing, etc. problems, to avoid excessive consumption and dependence, to avoid interference, and to reduce false positives
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1 Codon optimization of Limulus blood factor G α subunit gene and β subunit gene
[0051] In this example, through a lot of research, according to the codon preference of Escherichia coli, the codons of the synonymous genes preferred by Escherichia coli are used to replace the original codons of the Limulus gene while keeping the expressed protein sequence unchanged.
[0052] The nucleotide sequence of the α subunit gene after codon optimization is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the original sequence of the α subunit gene before optimization is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0053] The nucleotide sequence of the β subunit gene after codon optimization is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, and the original sequence of the β subunit gene before optimization is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 Preparation method of genetically engineered horseshoe crab blood G factor
[0055] 1. Obtaining recombinant plasmids
[0056] The codon-optimized α subunit gene and β subunit gene obtained in Example 1 were respectively constructed into pET32a-sumo Vector to obtain recombinant plasmids pETsuom-α and pETsuom-β.
[0057] 2. Induced expression of recombinant plasmids
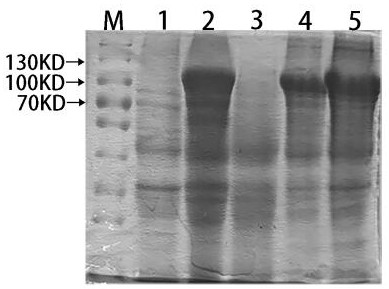
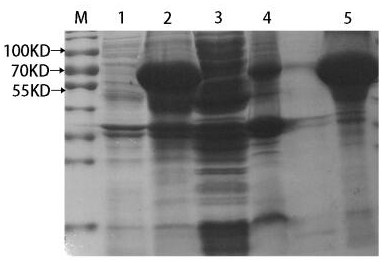
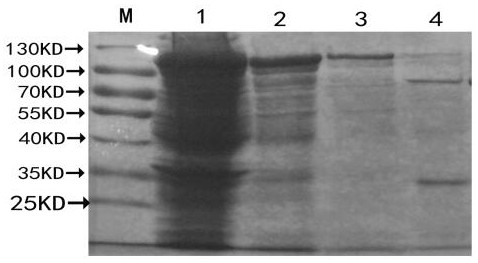
[0058] Transform the successfully constructed recombinant expression plasmid into E.coli BL21(DE3) competent medium, culture it on LB solid culture plate containing ampicillin for 12 h, pick a single colony containing the recombinant plasmid and add 5 mL of LB containing Amp to culture Shake culture overnight, take 5 μL overnight culture bacteria, add 2ml LB medium (containing Amp), and place in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C for vigorous shaking culture. When the A595nm value reached 0.5 (about 3 hours), one tube was added with IPTG to a final concentration of 1 mmol / L to induce expressi...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3 Verification of biological activity of genetically engineered horseshoe crab blood factor G
[0064] (1) method
[0065] Detection of enzyme activity by enzymatic fluorescent substrate method: Dissolve 5.4 mg of Boc-Glu-(OBzl)-Gly-Arg-MCA fluorescent substrate in 760 μL DMSO solution, store at -20°C in the dark, and store the solution at a concentration of 10 mM. Add 5 μL of 1mM fluorescent substrate and 5 μL of 2000pg / mL (1-3)-β- Mix the D-glucan evenly, put it in a water bath at 37°C for 30 minutes, extinguish the fire at 80°C for 5 minutes, and cool it down to room temperature quickly. The production amount of the product MCA was measured with a microplate reader, the excitation wavelength λex=380 nm, and the emission wavelength λem=440 nm.
[0066] (2) Results
[0067] The α and β subunits alone are inactive and cannot be activated by (1-3)-β-D-glucan. After α and β subunits are assembled into factor G holoenzyme structure, (1-3)-β-D-glucan can activa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com