A Content Caching Method Based on Social Relationship
A social relationship and content caching technology, applied in the field of content caching based on social relationships, can solve the problem of heavy burden on important nodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
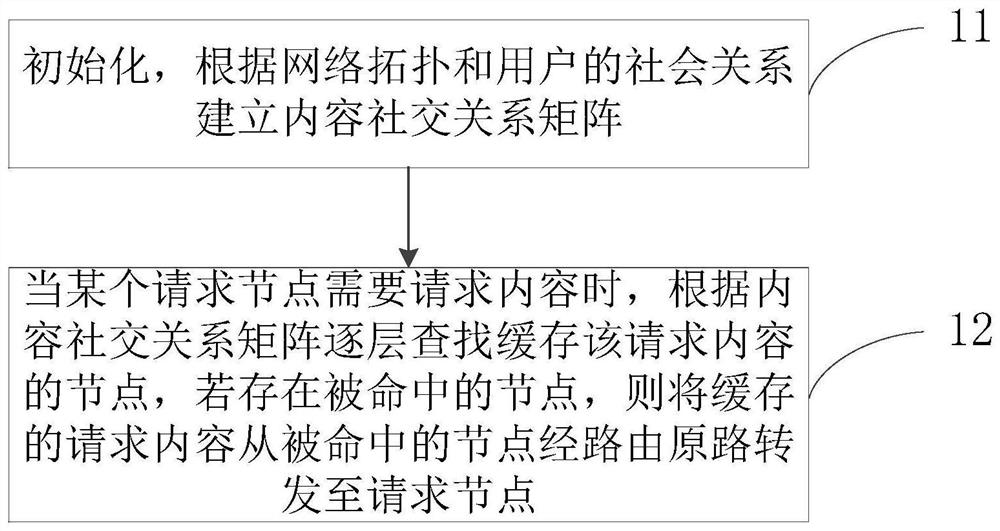
[0036] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a content caching method based on social relations, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0037] Step 11: Initialize, establish a content social relationship matrix according to the network topology and the user's social relationship;
[0038] Exemplarily, assuming that there are m nodes in the entire network, the initially established content social relationship matrix is:
[0039]
[0040] Among them, the matrix changes dynamically with the change of social relations, U c is the content social relationship matrix, and the cache for content c (that is, the Interest package) is determined by this matrix; u ij Indicates the relative importance of nodes, i.e. the importance of i to j, I i Indicates the importance of the node itself of node i, and the importance of node i itself is determined by the social relationship of the node.
[0041] Step 12: When a request node needs to request content, search for the node that c...
Embodiment 2
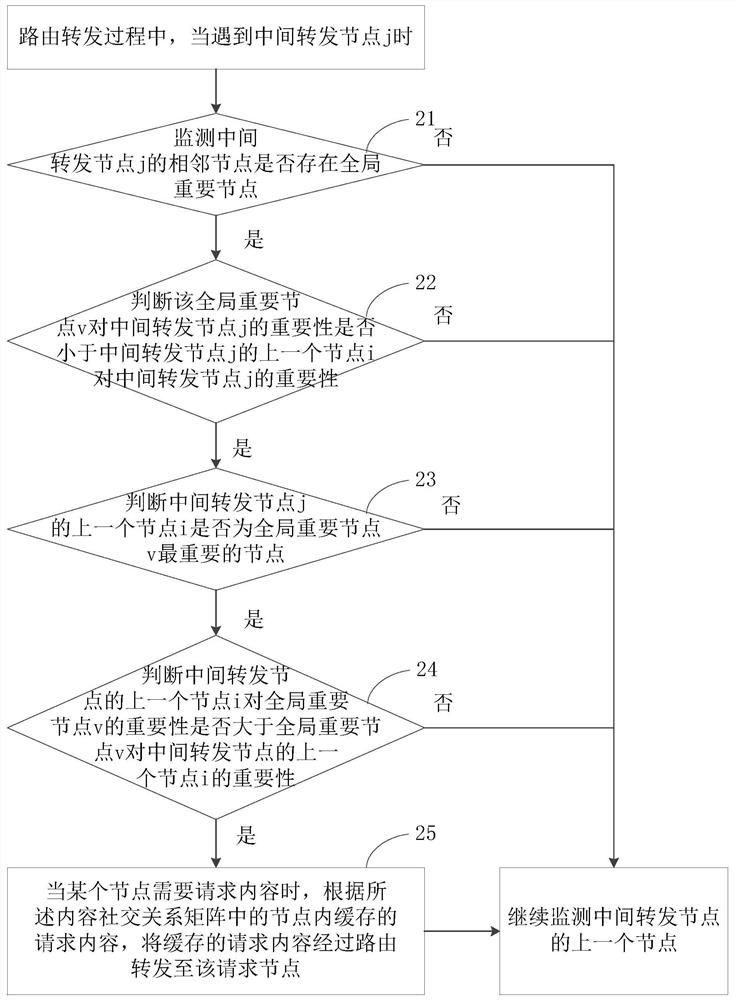
[0047] Embodiment 2 of the present invention is a preferred embodiment of the present invention, specifically including:
[0048] In this embodiment, the network controller maintains the content social relationship matrix, sorts the nodes according to their own importance from high to low in advance, and selects a preset number of nodes (for convenience of description, the preset number is defined as L here) as nodes. global important nodes;
[0049] The value of L is determined according to the importance of the content β and the total number of nodes in the entire network m, that is, L=β*m, and the value of L is adjusted according to the needs of network users for content.
[0050] During routing and forwarding, when a globally important node is encountered, a copy of the request content is kept in the cache space of the globally important node;
[0051] Preferably, a counter is maintained in the network to record the number of copies reserved, and after each copy is reserv...
Embodiment 3
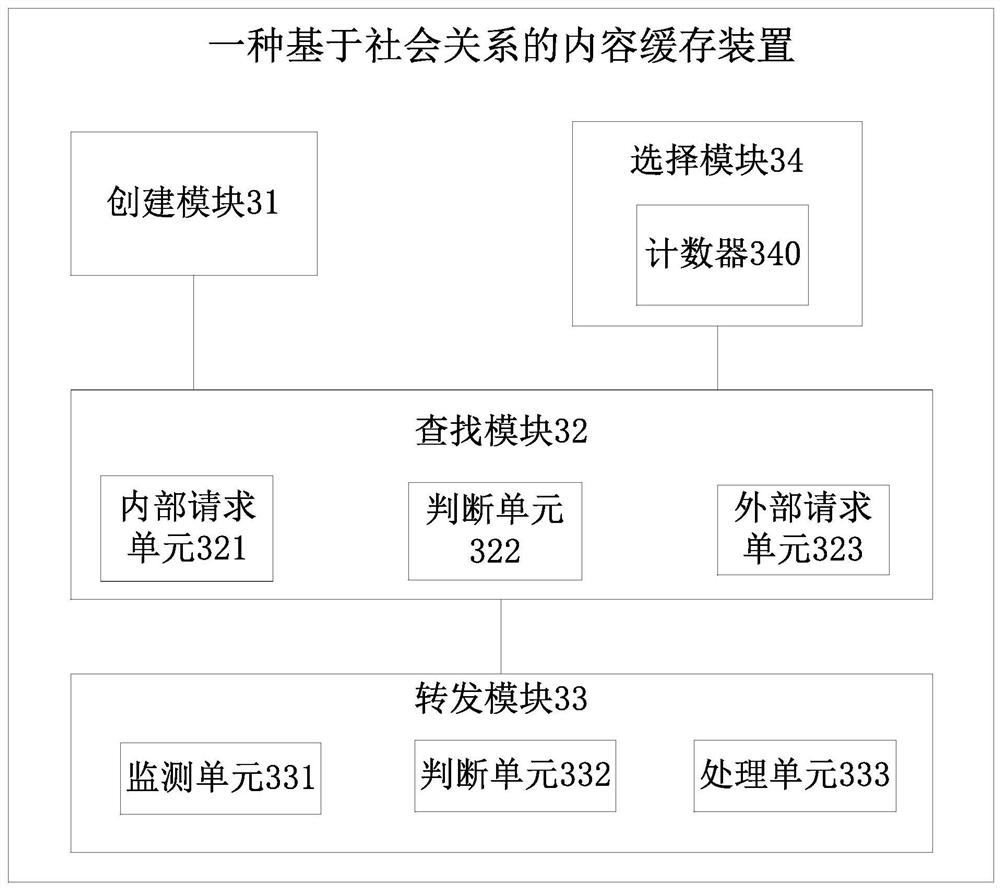
[0064] Embodiment 3 of the present invention describes the characteristics of nodes in detail, including:
[0065] Node characteristics include node betweenness, node self-importance and node relative importance;
[0066] Node betweenness: if the shortest path (distance) between a pair of nodes has g jk bar with g jk (i) item passes through node i, then the contribution of node i to this pair of nodes is g jk (i) / g jk , add up the contribution of node i to all node pairs and divide by the total number of node pairs, you can get the betweenness B of node i i ,Right now
[0067]
[0068] Node self-importance: Indicates the comprehensive importance of node i in the entire network for content c; according to the node betweenness and the user's own interest preference, the user's own importance I of content c is calculated i ,Specifically:
[0069] I i =B i ψ(i,c)
[0070] I i The larger the value of , the more preferred the node i is to the content c, and the stronger...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com