A timer scheduling method and device
A scheduling method and timer technology, applied in digital transmission systems, data exchange networks, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low reliability and stability of network equipment, reduce sudden use of resources, improve stability and Reliability, guaranteed effect of processing delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
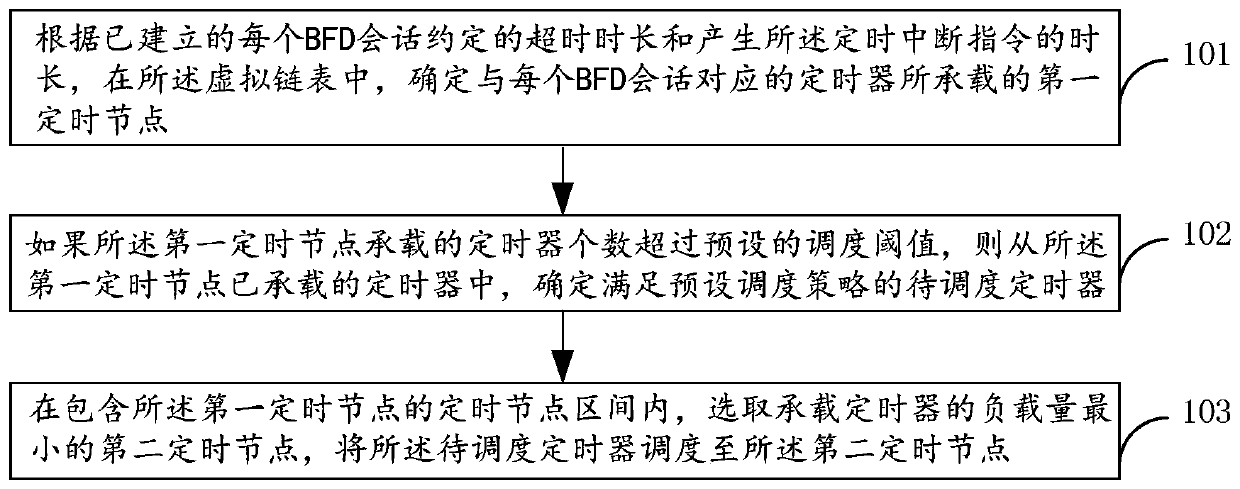
[0074] figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of the timer scheduling method provided by the embodiment of the present application. The method is applied to network equipment, and the network equipment may specifically be equipment such as routers and switches. The network device expresses the set timing interrupt instruction through a virtual linked list structure, and each timing node constituting the virtual linked list bears at least one timer, and each timer corresponds to the BFD session established by the network device one by one. The time step of is the duration of generating the timing interrupt instruction, such as figure 1 As shown, the process includes:
[0075] Step 101, according to the timeout duration agreed upon by each established BFD session and the duration of generating the timing interruption instruction, in the virtual linked list, determine the first timing node carried by the timer corresponding to each BFD session;
[0076] In the embodiment of the ...
Embodiment 2
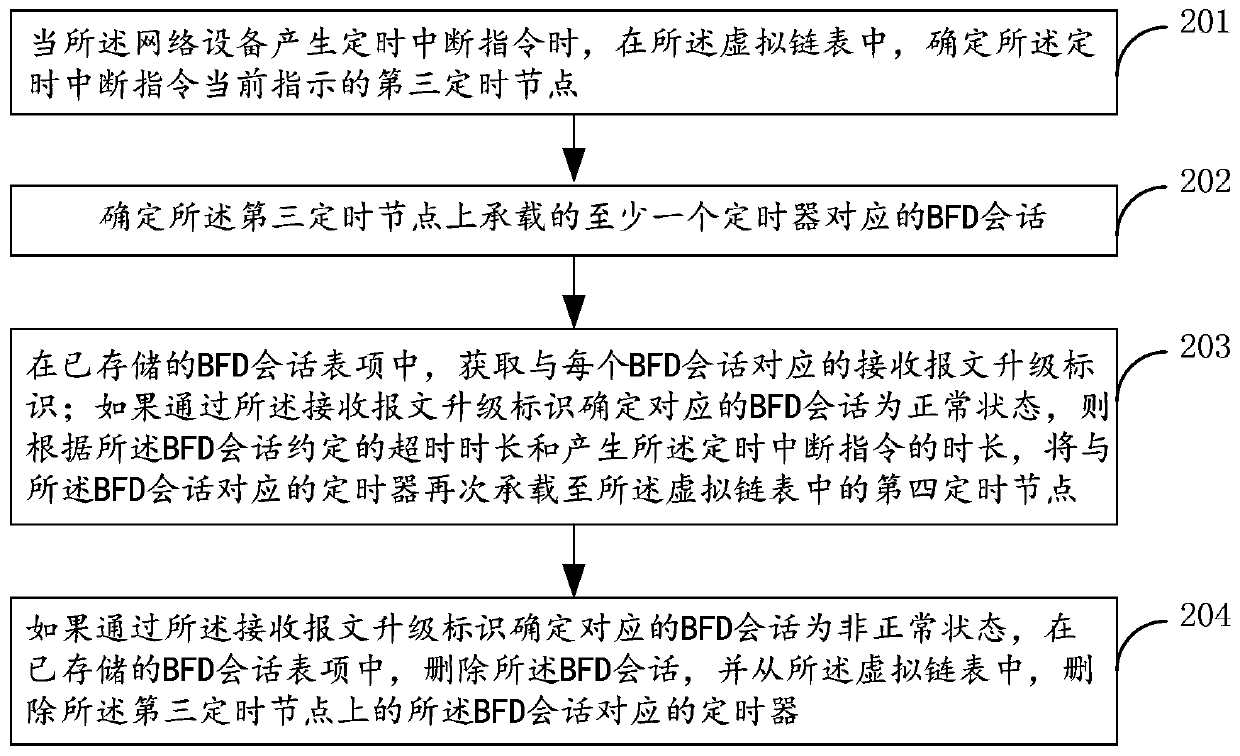
[0085] figure 2 for figure 1 One of the schematic flowcharts of the sub-steps before step 101 shown. Such as figure 2 As stated, the process includes:
[0086] Step 201, when the network device generates a timing interruption instruction, in the virtual linked list, determine the third timing node currently indicated by the timing interruption instruction;
[0087]In the embodiment of the present application, as an optional embodiment, the timing interrupt instruction is generated by using a shared timer set for each BFD session based on hardware, and the shared timer performs counting and timing based on CPU main frequency or bus frequency.
[0088] For example, if the shared timer is a clock timer with a CPU main frequency or a bus frequency of 1M, and the corresponding clock period of the clock timer is 1us, the count value of the shared timer increases by 1 every 1us. If the pre-configured counting threshold is 1000, the duration (the product of the clock cycle and t...
Embodiment 4
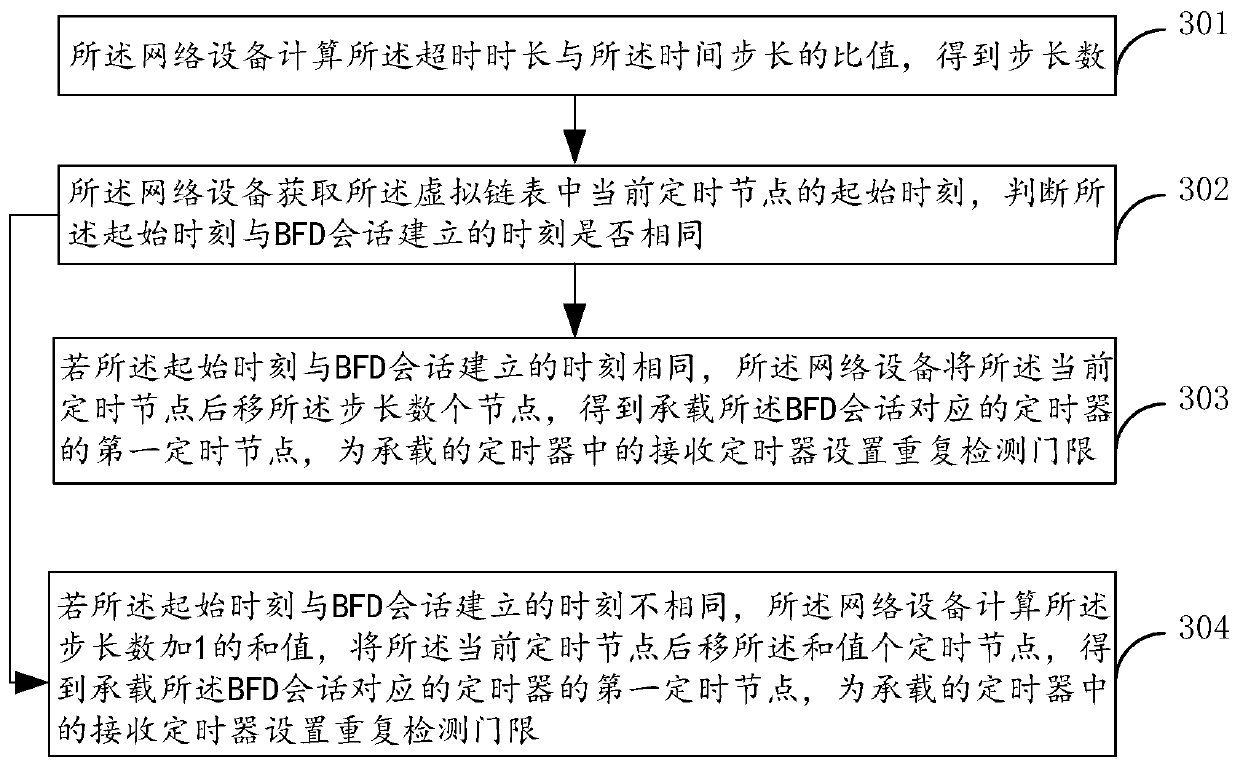
[0130] Figure 4 for figure 1 One of the sub-step flowcharts of step 102 shown. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the process includes:
[0131] Step 401, if the number of timers carried by the first timing node exceeds the scheduling threshold, then obtain the timeout duration of the BFD session corresponding to each timer carried by the first timing node and the scheduling of each BFD session Decay count of probabilities;
[0132] In this embodiment of the present application, an initial decay count is set for each BFD session, which is used to represent the probability that the BFD session can participate in scheduling within the timeout period of the initial decay count. As an optional embodiment, after the position of the BFD session in the virtual linked list is scheduled once, the position of the BFD session in the virtual linked list is no longer scheduled within the subsequent initial decay count timeout period to maintain a steady state. It's just that the decay count...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com