Method for writing in graphic database, electronic device and computer-readable storage medium
A database and graph technology, applied in the field of graph database
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
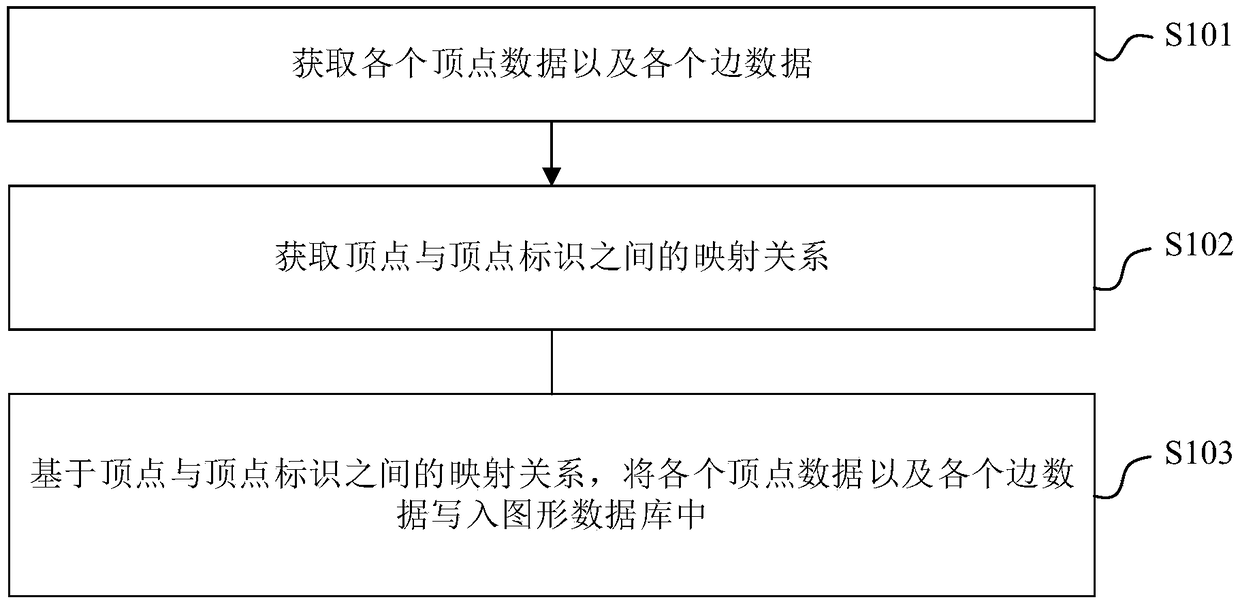
[0045] The embodiment of the present application provides a method for writing in a graph database, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0046] Step S101, obtaining each vertex data and each edge data.
[0047] Among them, the vertex data is the attribute information of the vertex; the edge data includes the relationship attribute information between vertices.
[0048]For the embodiment of the present application, the data to be written into the graph database is obtained from the source database, and the data includes each vertex data and each edge data to be written into the graph database. In the embodiment of the present application, the source database may be a relational database or a non-relational database, and the graph database may be non-relational data.
[0049] For this embodiment of the application, the vertices in the graph database may represent a person, a department, or a company. It is not limited in the embodiment of this application. In th...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Another possible implementation of the embodiment of the present application, on the basis of the first embodiment, also includes the operations shown in the second embodiment, wherein,
[0061] Step S102 includes: Step S1021 (not marked in the figure), wherein,
[0062] Step S1021. Obtain the mapping relationship between vertices and vertex identifiers from an external vertex identifier generator.
[0063] Wherein, the mapping relationship between vertices and vertex identifiers is pre-generated by an external vertex identifier generator.
[0064] For the embodiment of the present application, before writing each vertex data and each edge data into the graph database, an external vertex identifier generator is used to generate a mapping relationship between vertices and vertex identifiers. In the embodiment of the present application, when writing each vertex data and each edge data into the graph database, the pre-generated mapping relationship between vertices and v...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Another possible implementation of the embodiment of the present application further includes the operations shown in the third embodiment on the basis of the first or second embodiment, wherein,
[0072] Step S103 includes step S1031 (not marked in the figure), wherein,
[0073] Step S1031 , based on the mapping relationship between vertices and vertex identifiers, and through multi-node parallel mode, write each vertex data and each edge data into the graph database.
[0074] Wherein, the multi-node parallel mode is a mode in which data is written in parallel through multiple servers.
[0075] For the embodiment of the present application, each vertex data and each edge data are written into the graph database through a multi-node parallel mode, that is, the data to be written into the graph database is written into the graph database in parallel through multiple nodes. In this embodiment of the application, a node may be a server.
[0076] For example, a part of ve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com