A method for segmenting human organs in medical images based on a neural network
A medical imaging and neural network technology, applied in image analysis, instruments, image enhancement, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve accurate positioning of the initial layer and the end layer of blood vessels, damage to the Z axis, and small differences, etc., to solve multiple problems. Effects on the organ segmentation problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for segmenting human organs in medical images based on a neural network, suitable for execution in a computing device, comprising the following steps:
[0036] (1) Coarsely locate the medical imaging layer where the target organ to be delineated is located; the target organ to be delineated includes several organs; preferably further comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1a) Divide the organs in the medical image into several categories according to their high and low positions;
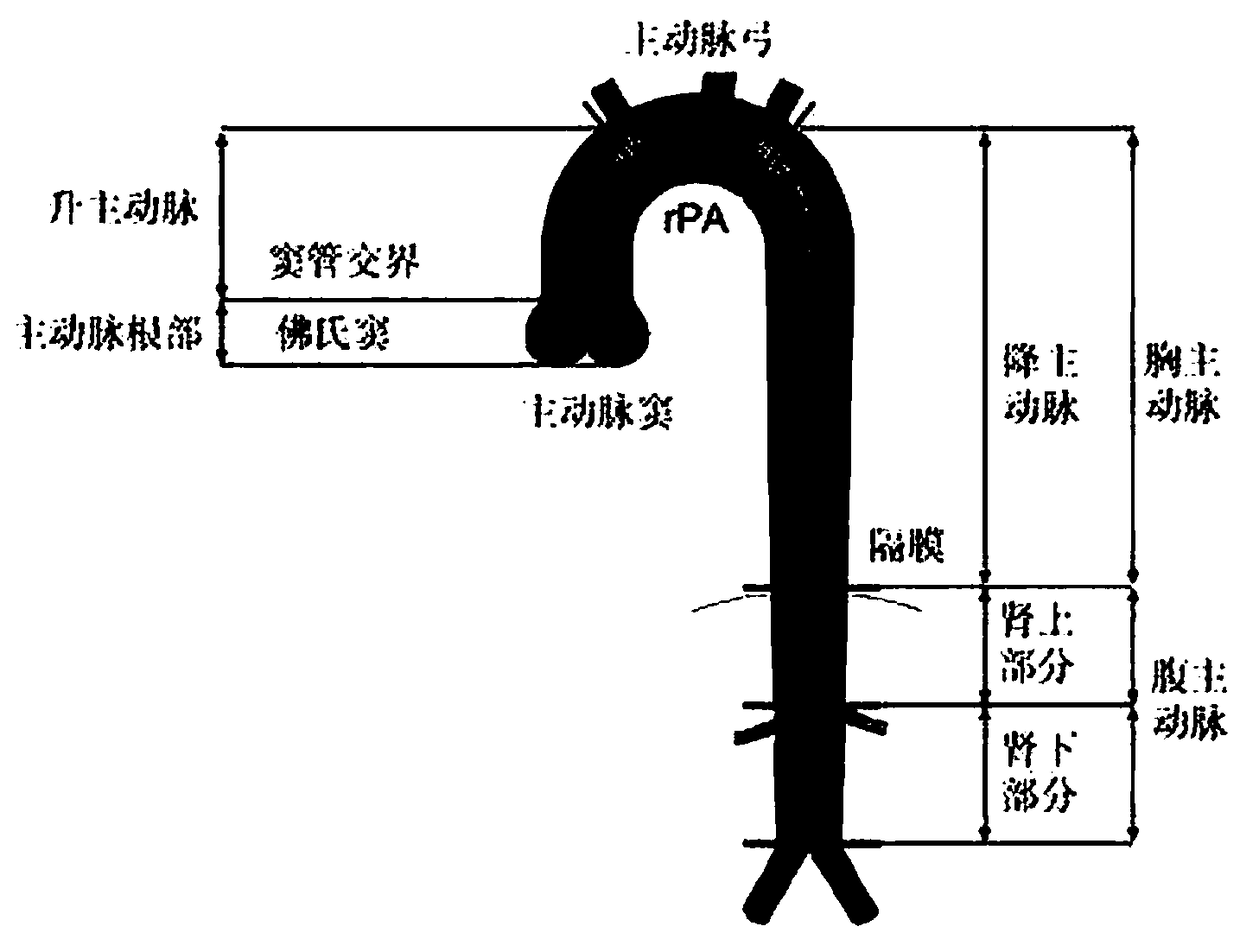
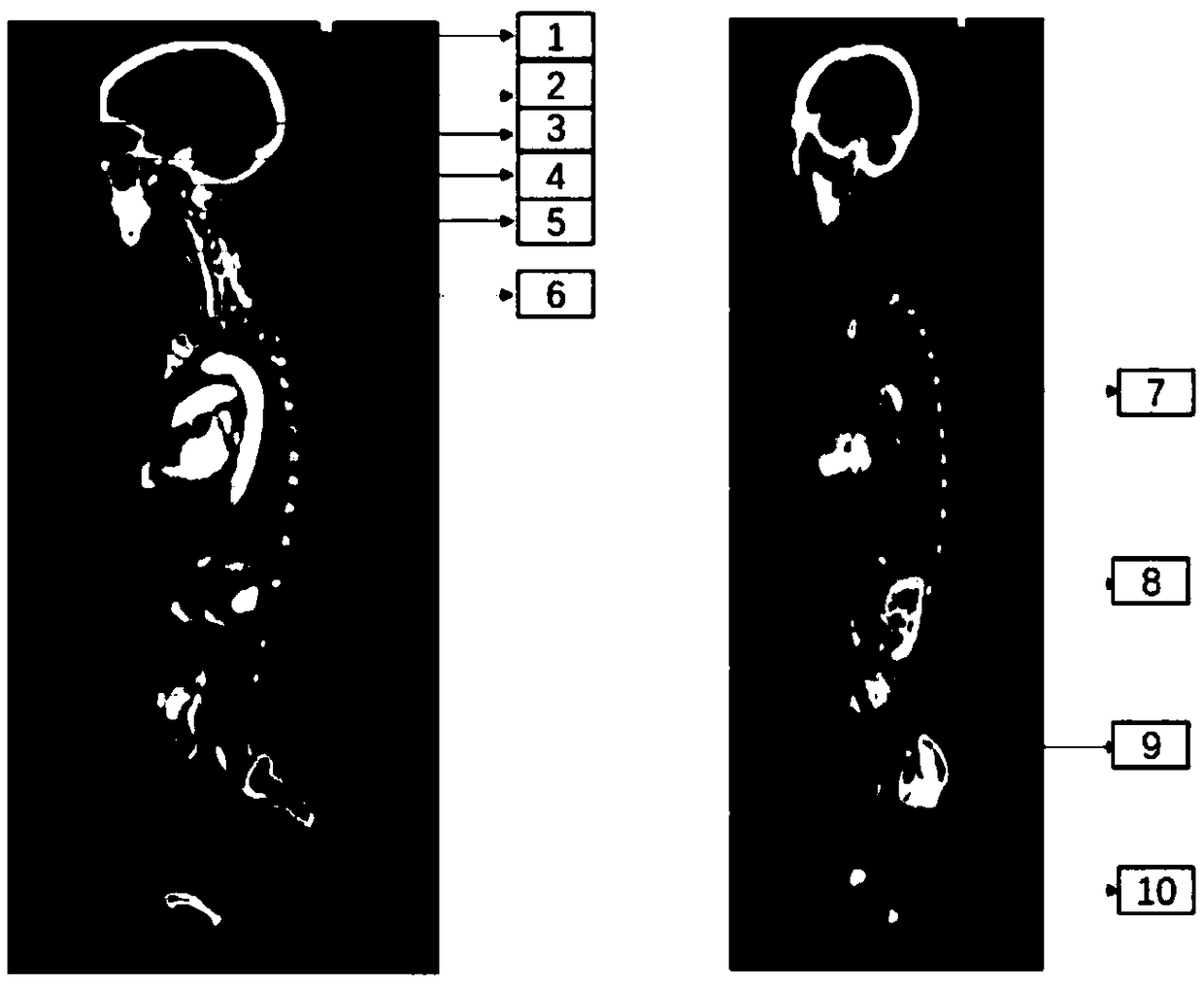
[0038] in such as figure 1 In the exemplary embodiment shown in Table 1, the organs in the human body medical image are classified into ten categories from top to bottom or from bottom to top, which are from the first picture to the top of the head, from the top of the head to the top layer of the eye, From the upper roof of the eye to the lower roof of the eye, from the lower roof of the eye to the lower roof of the cerebellum, from the lower roof of the cerebellum to the last l...
Embodiment 2
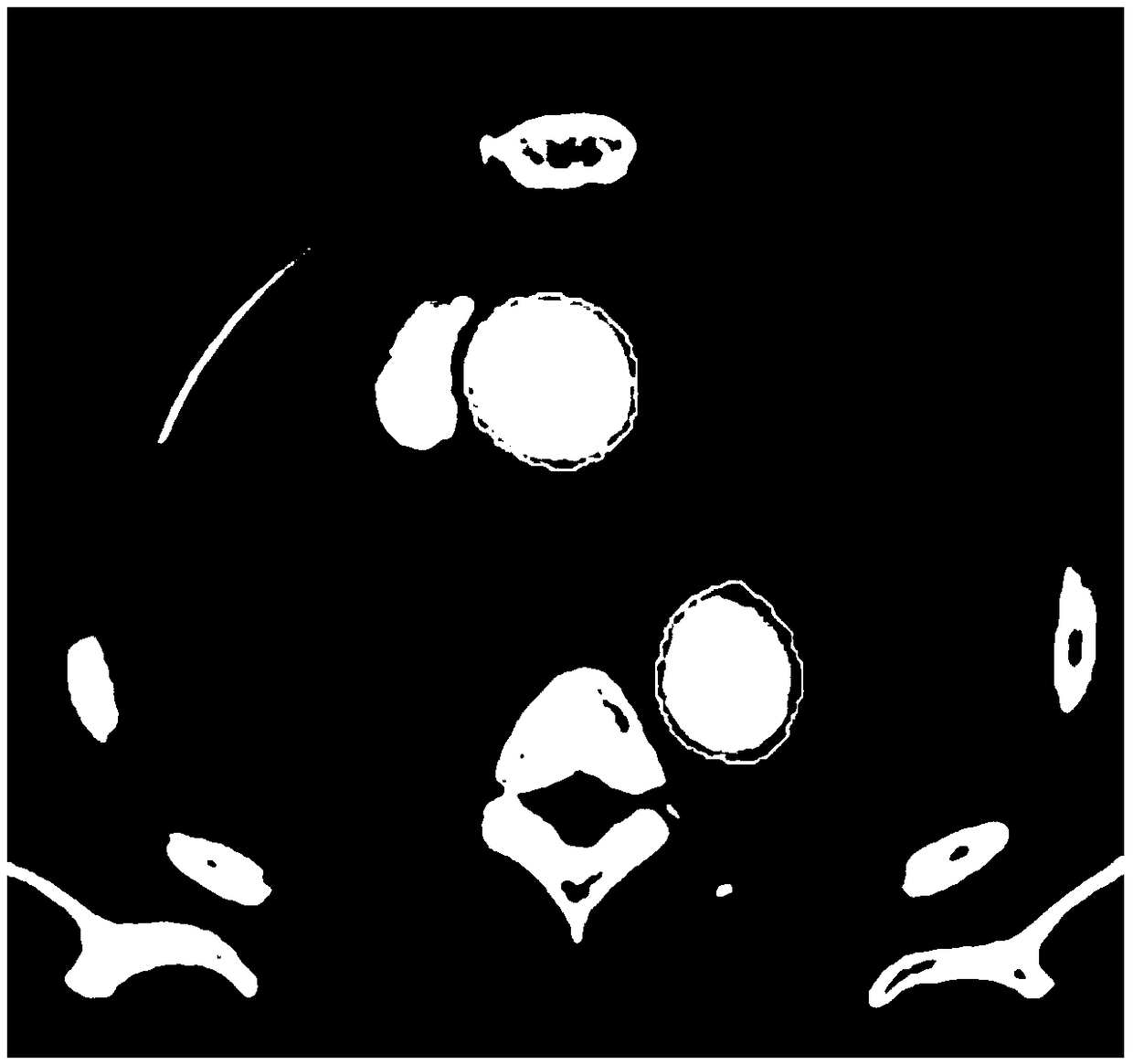
[0049] In an exemplary embodiment, for example, in organ segmentation of medical images, especially in the segmentation of slender organs like blood vessels, the regions corresponding to different names often have different lengths, and it is easy to cause differences in data between categories during training. Balance, such as the ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta, these three vessels (organs) are on the same vessel (see figure 1 ), have different names because of the location of the area. These three blood vessels are respectively located in the [7,8,9] layer of the multi-classification localization network of the human body (as shown in Table 1). The descending aorta is the longest, and the ascending aorta is the longest. The arteries are next, and the aortic arch is the shortest. Specifically, taking a CT of a patient as an example, when the Z-axis spacing (spacing) is 3 mm, that is, when the CT slice thickness is 3 mm, there are 23 slices of the ascending...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The invention also provides a computing device, comprising:
[0059] one or more processors;
[0060] storage; and
[0061] One or more programs, wherein the above one or more programs are stored in the above memory and configured to be executed by one or more processors, the above one or more programs include a method for performing neural network-based analysis of the human body in medical images Instructions for a method for segmenting an organ, the method comprising the steps of:
[0062] (1) roughly locating the medical image layer where the target organ to be delineated is located; the target organ to be delineated includes several organs;
[0063] (2) Determine the start layer and end layer of all target organs to be delineated as a whole;
[0064] (3) Input the middle layer of the start layer and the end layer into the 2D multi-classification U-shaped network, perform fine delineation and segmentation, and determine the corresponding start layer and end layer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com