Non-invasive method and system for measuring myocardial ischemia, stenosis identification, localization and fractional flow reserve estimation
A technology of blood flow reserve fraction and myocardial ischemia, which is applied in the directions of blood flow measurement, diagnostic recording/measurement, character and pattern recognition, etc., which can solve the problems of lack and enhance the identification of high-risk patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] The components in the figures are not necessarily to scale relative to each other, like reference numerals refer to corresponding parts throughout the several views.
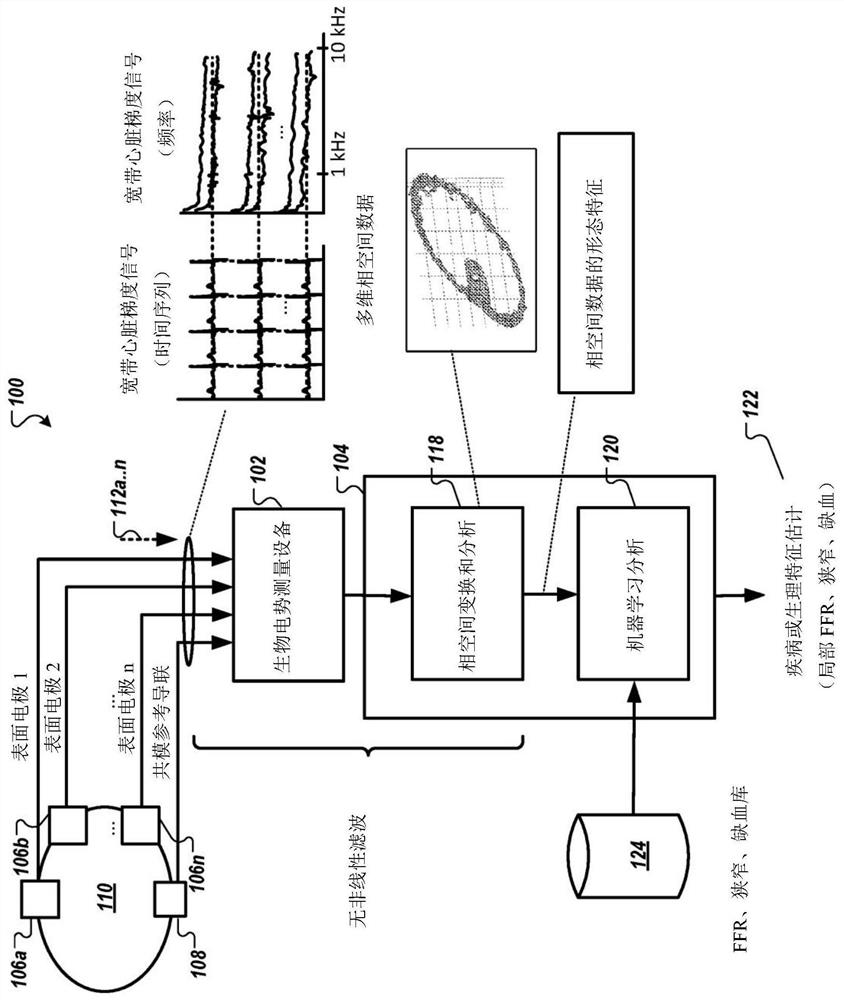
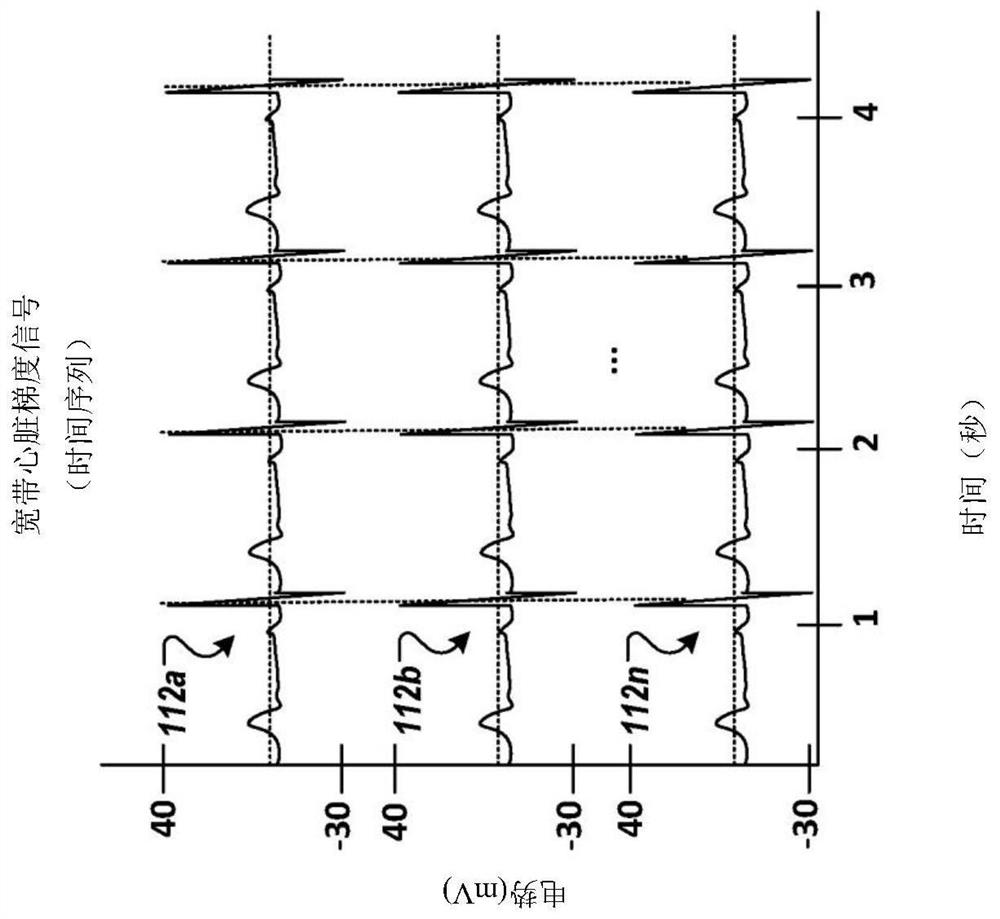
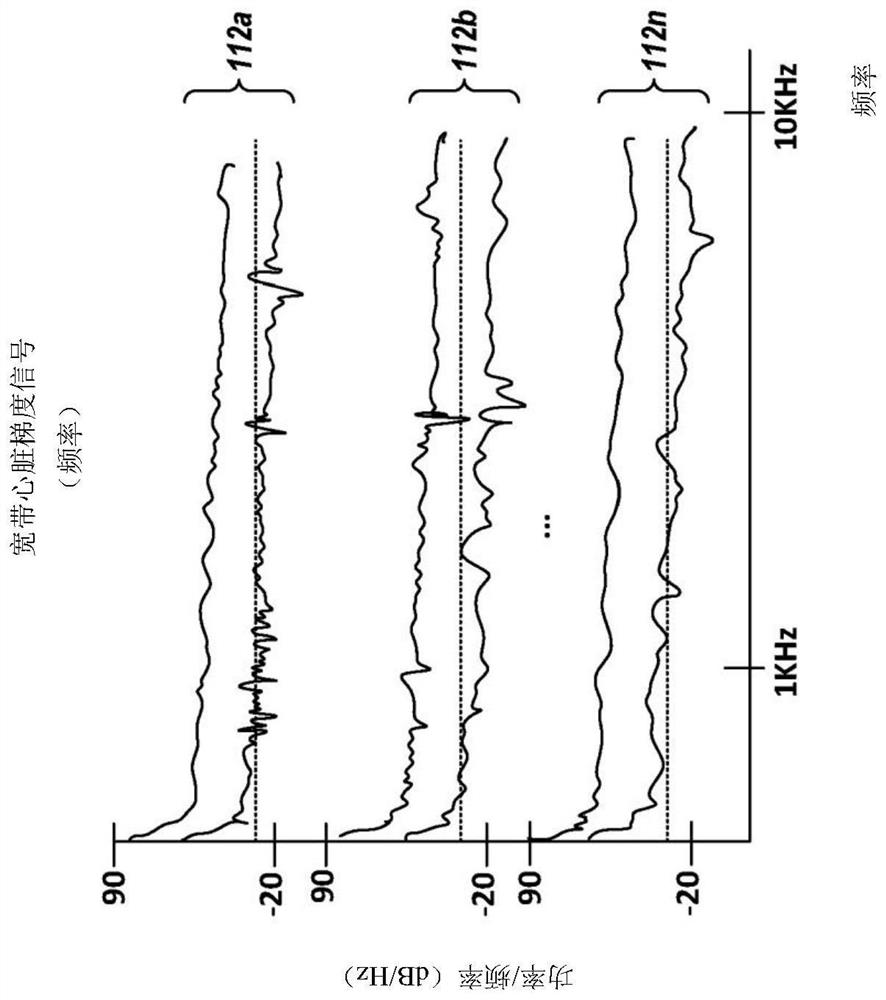
[0061] figure 1 is a diagram of a system for non-invasively determining arterial flow characteristics in the heart using wide-band cardiac gradient data, according to an exemplary embodiment. like figure 1 As shown, the system 100 includes a broadband biopotential measurement device 102 and an analysis subsystem 104 . Broadband biopotential measurement device 102 acquires broadband biopotentials from subject or patient 110 via at least one electrode 106 (shown as surface electrodes 106a, 106b, . . . , 106n ) and corresponding common mode reference leads 108 Signals 112 (shown as 112a, . . . , n) (also referred to herein as broadband cardiac gradient signal data 112), the at least one electrode 106 and the corresponding common mode reference lead 108 are both in figure 1 and are attached to the surface ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com