Efficient clustering of noisy polynucleotide sequence reads
A reading and clustering technology, applied in sequence analysis, instrumentation, code conversion, etc., can solve problems such as inability to read and the sequence of nucleotide bases cannot be directly observed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
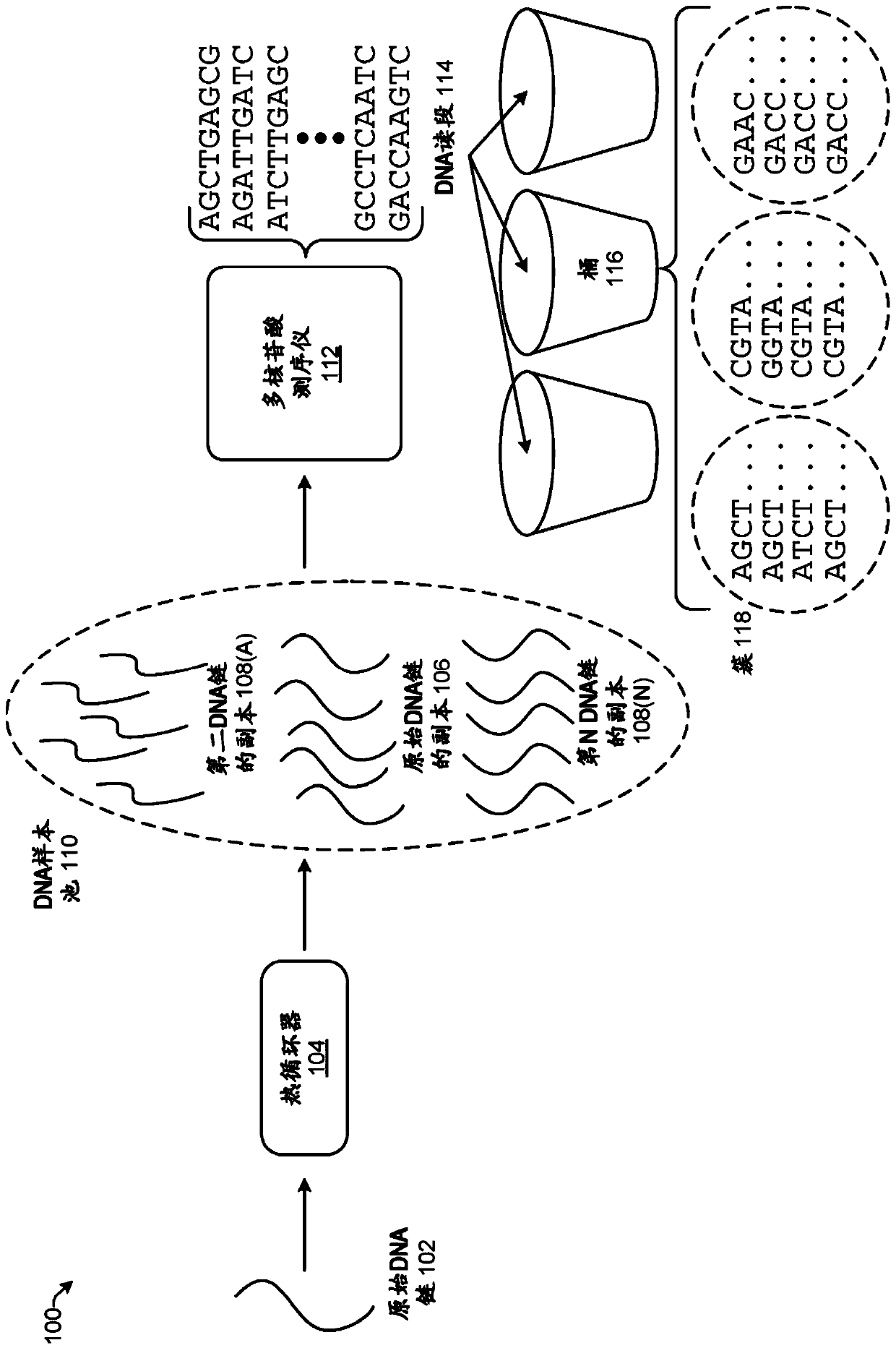
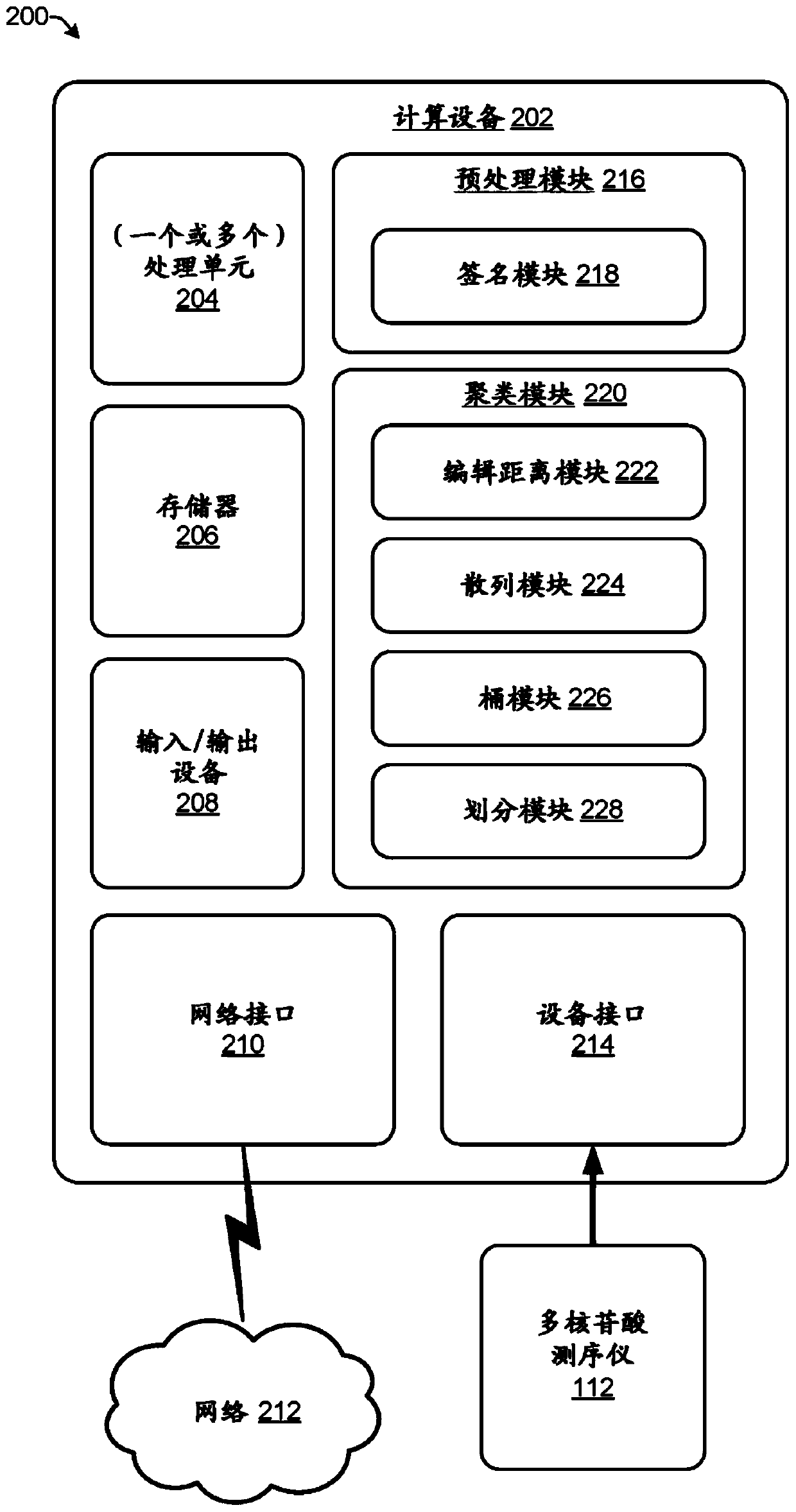
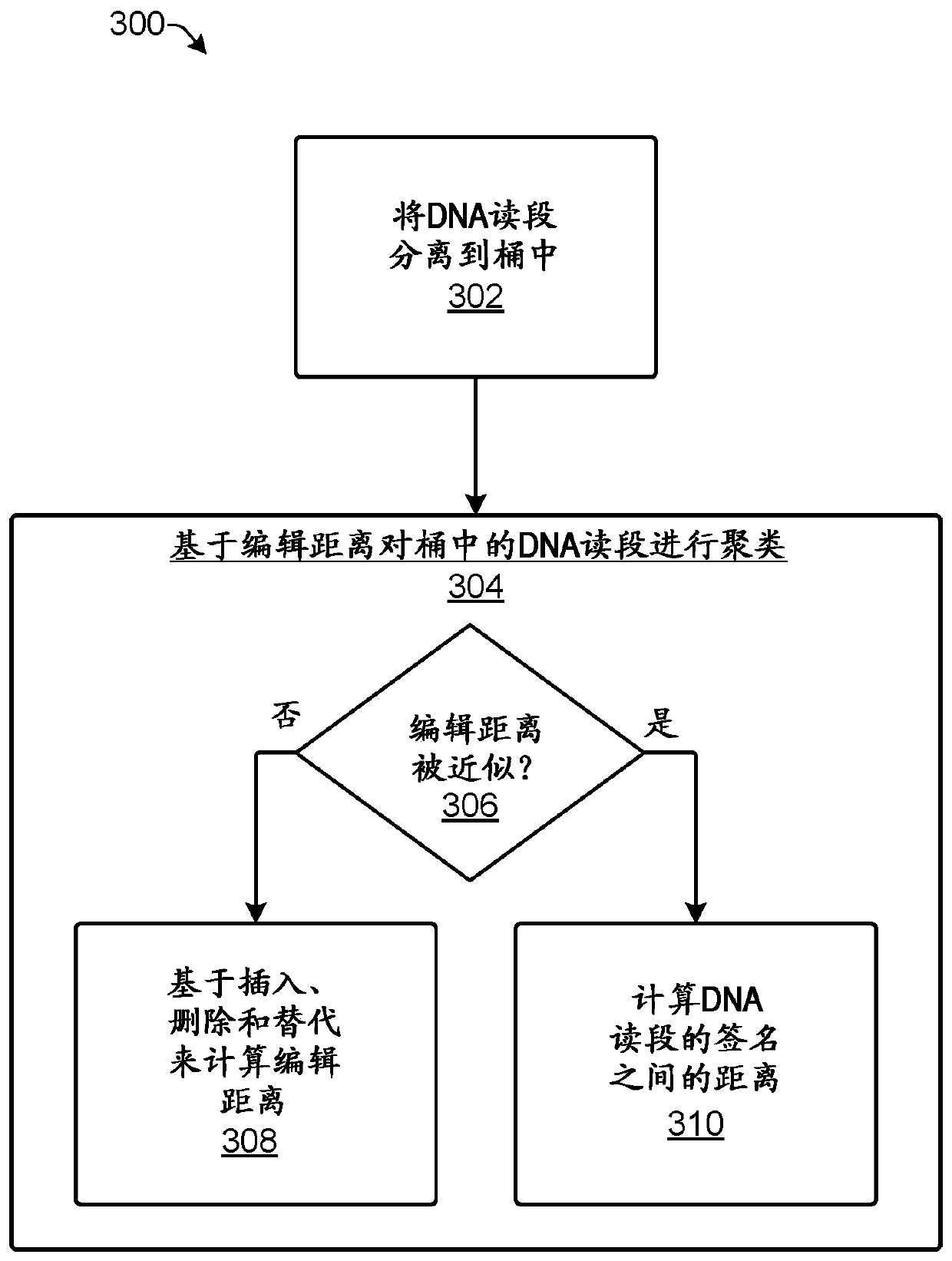
[0011] The present disclosure provides computationally efficient techniques for clustering reads in sequence data such that reads directed to the same original DNA strand are placed in the same cluster. Clustering reads by itself cannot correct errors in the sequence data but it can organize DNA reads in a manner that makes error correction more efficient and / or accurate. One example of error correction for sequence data using clustering is described in US Provisional Patent Application No. 62 / 329,945. Due to the large amount of data generated by polynucleotide sequencers, computational efficiency is desired for applications involving DNA sequences. For example, data output by a single run of a polynucleotide sequencer can contain over a billion different DNA reads representing millions of different DNA strands.
[0012] The term "DNA strand" or simply "strand" refers to a DNA molecule. As used herein, "read" may be a noun referring to a string of data generated by a polynuc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com