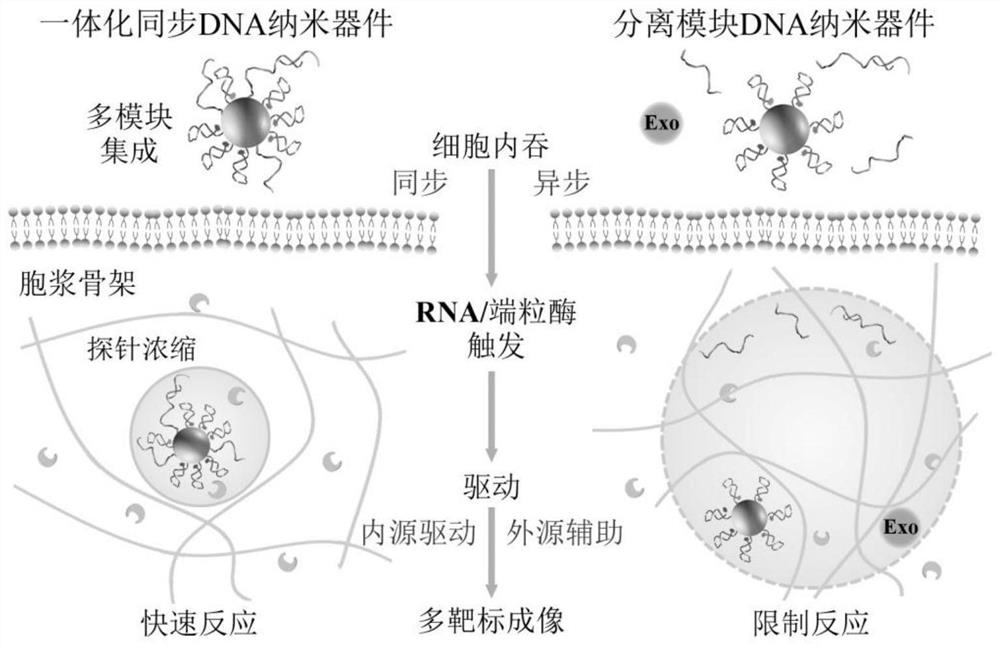
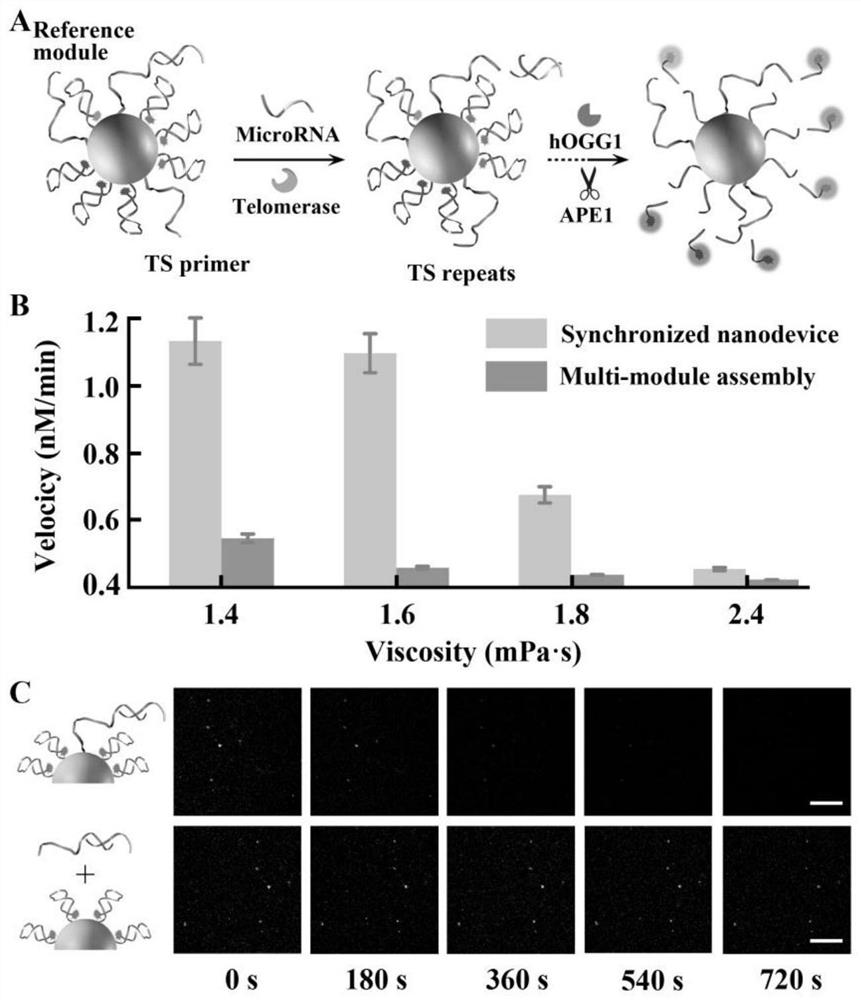
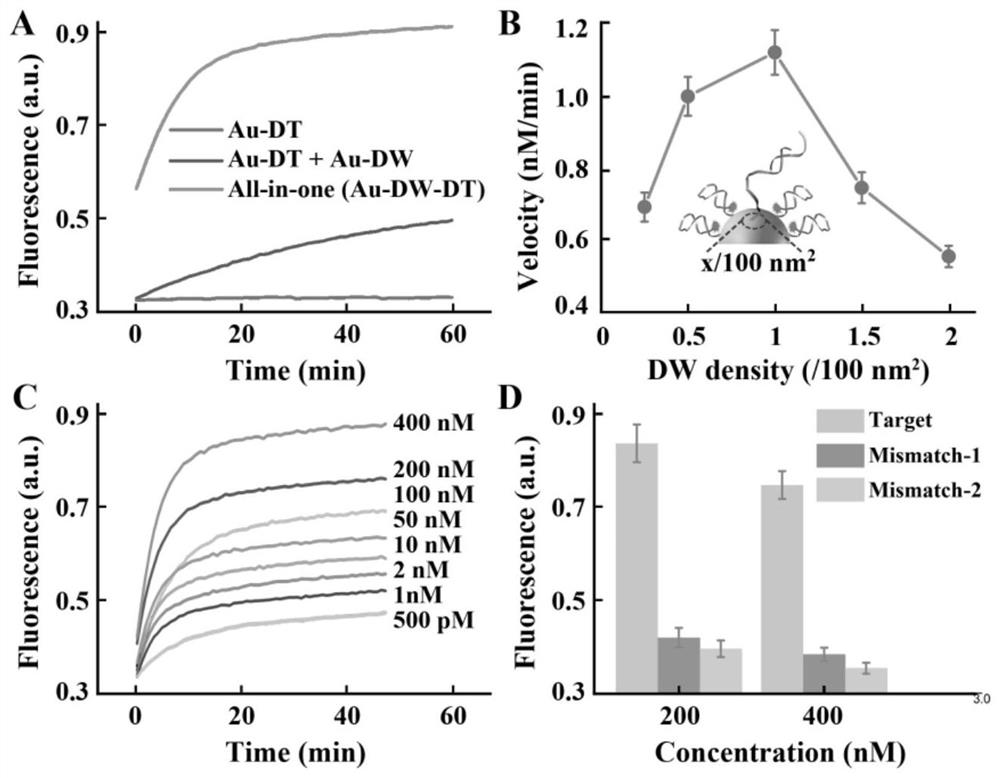
Integrated synchronized dna nanodevice and its live-cell multi-target imaging application and imaging method
A nano-device and living cell technology, applied in the field of live cell imaging, can solve the problems of limited reaction rate, loss of intracellular stoichiometric information, poor interference ability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Imaging of single target miR-21 in living cells by using integrated synchronous DNA nanodevices of different designs.
[0037] Using the HeLa cell line of cervical cancer cells as the basic model, 20 μL of integrated synchronous DNA nanodevice probes were added to HeLa cells pre-cultured in eight-well confocal culture dishes (0.2 mL, 1×10 6 mL -1), incubated at 37°C for 4 hours. After washing with PBS, imaging was performed using a confocal laser fluorescence microscope. In the target miR-21-positive cells, miR-21 replaces the Block chain that seals the R-SD and releases the single-stranded R-SD, whose 5' end 14 bases are connected to the loop corresponding to the R-HD chain The 14 bases in the shape part are complementary to form a double strand, and the damaged base oG site on the R-HD chain can be acted on by the enzyme hOGG1 to form an apurinic / apyrimidinic AP site, which is then digested by APE 1 to release FAM fluorescence.
[0038] In addition, the...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Using an integrated synchronous DNA nano-device to simultaneously image multiple targets in different living cells.
[0041] Using the HeLa cell line of cervical cancer cells as the basic model, 20 μL of integrated synchronous DNA nanodevice probes were added to HeLa cells pre-cultured in eight-well confocal culture dishes (0.2 mL, 1×10 6 mL -1 ), incubated at 37°C for 4 hours. After washing with PBS, imaging was performed using a confocal laser fluorescence microscope. In the presence of the target miR-21, the strand displacement reaction and the Block DNA strand complement each other to form a double strand, releasing the R-SD strand; the T-SD-S strand, the primer at the 5' end is extended in the presence of the target telomerase T-SD chain. The 14 bases at the 5' end of the R-SD chain, T-SD chain and C-SD chain are complementary to the 14 bases of the ring part of the corresponding R-HD chain, T-HD chain and C-HD chain to form a double chain; After the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com