An airspace complexity unsupervised assessment method
A complex and unsupervised technology, applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to obtain calibration samples, high cost of acquisition, performance dependence on calibration samples, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be described in further detail below through specific embodiments and in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
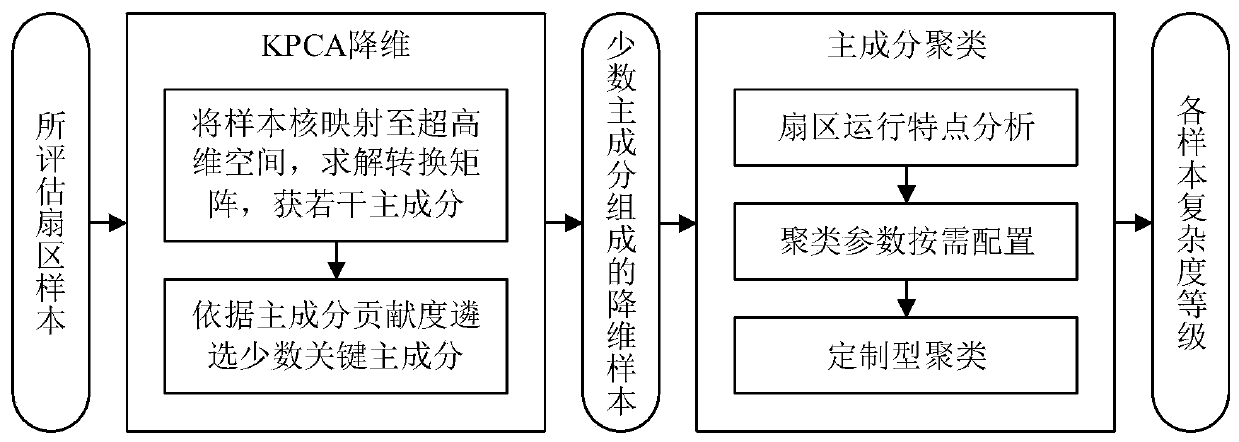
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, an unsupervised evaluation method for airspace operation complexity of the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0036] Step 1: KPCA dimensionality reduction.
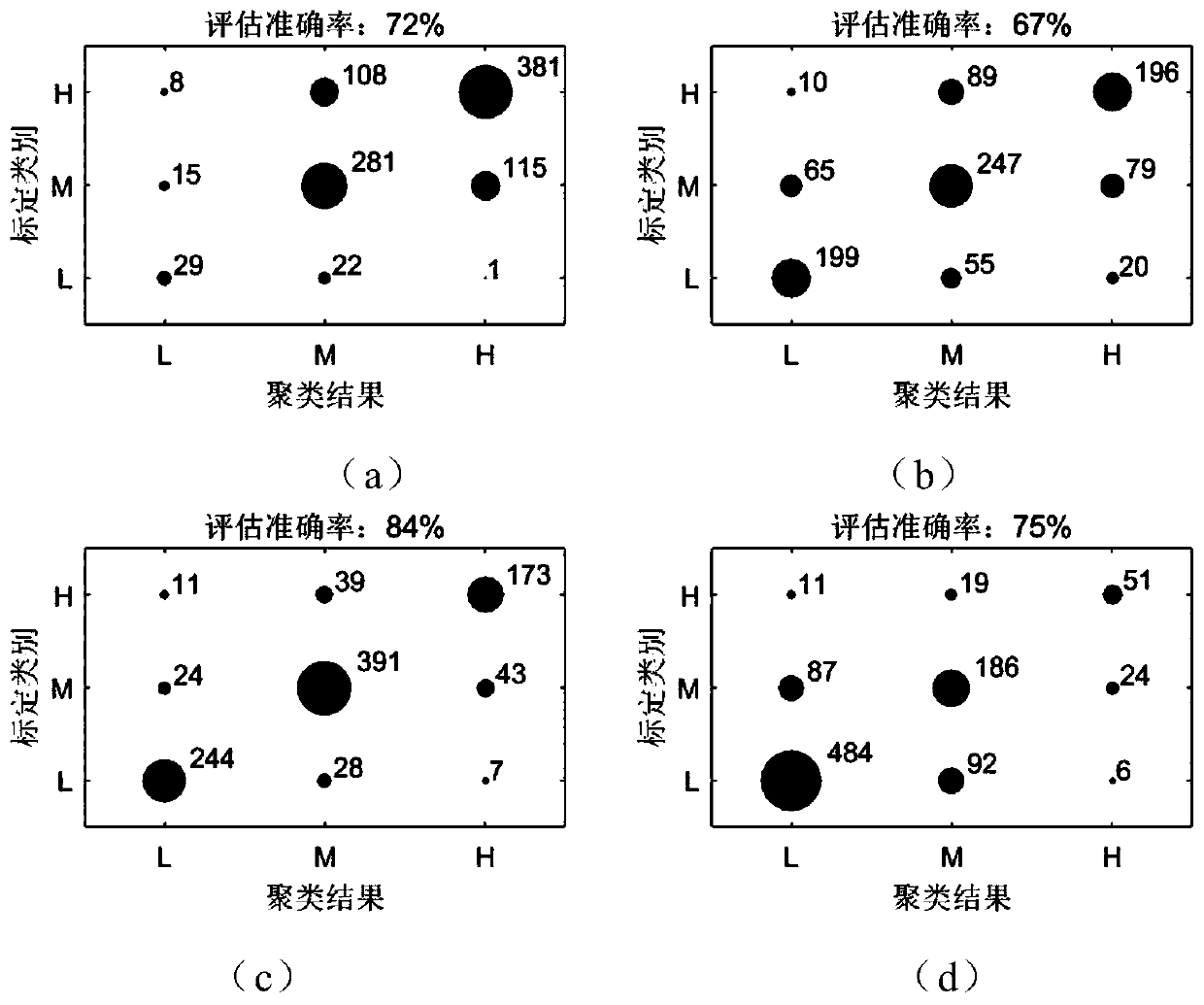
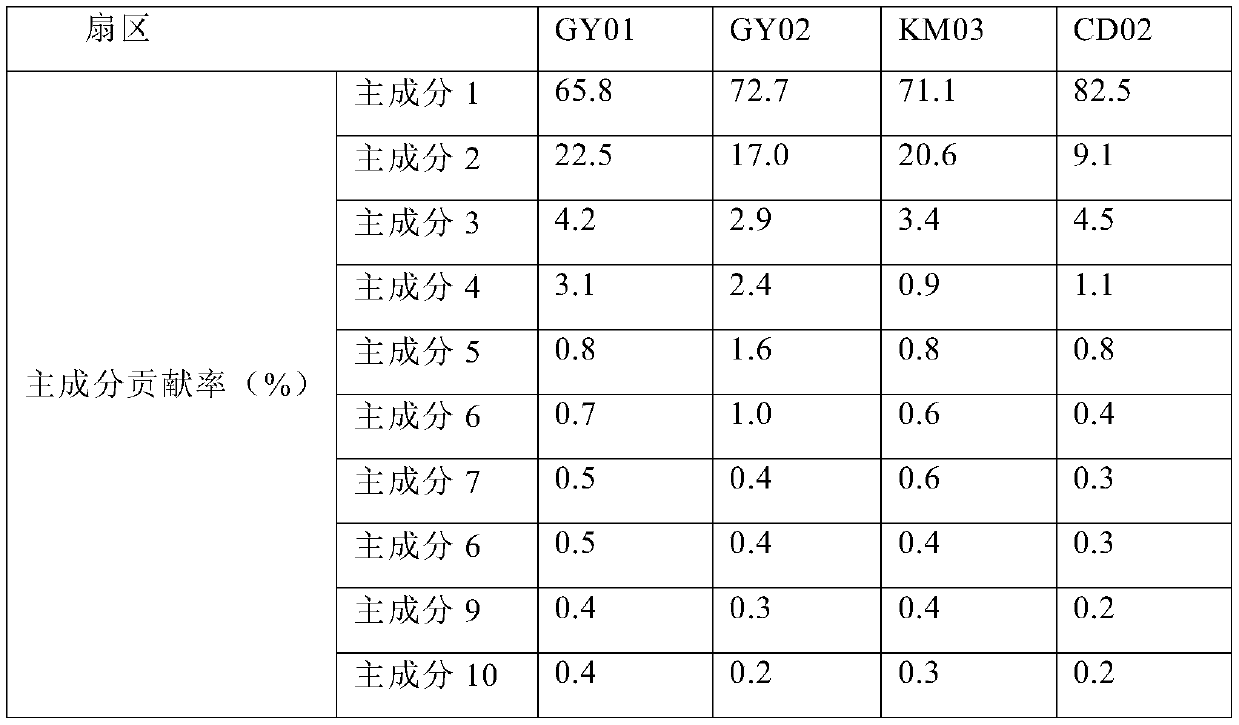
[0037] There are dozens of key factors affecting the sector complexity, and each factor contributes differently to the information contribution of the sector complexity assessment task, and the coupling and correlation are complex, and the complexity assessment knowledge contained overlaps. The above characteristics make it very difficult to extract the knowledge of sector complexity evaluation under unsupervised conditions. In order to mine sector complexity assessment knowledge from high-dimensional original samples, it is necessary to reduce the dimensionality of the samples, extract principal components tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com