A method and apparatus for beam failure recovery
A beam, user equipment technology, applied in the field of communications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0126] Example 1: Two cell wireless network temporary identities are monitored, and one can be discarded later.
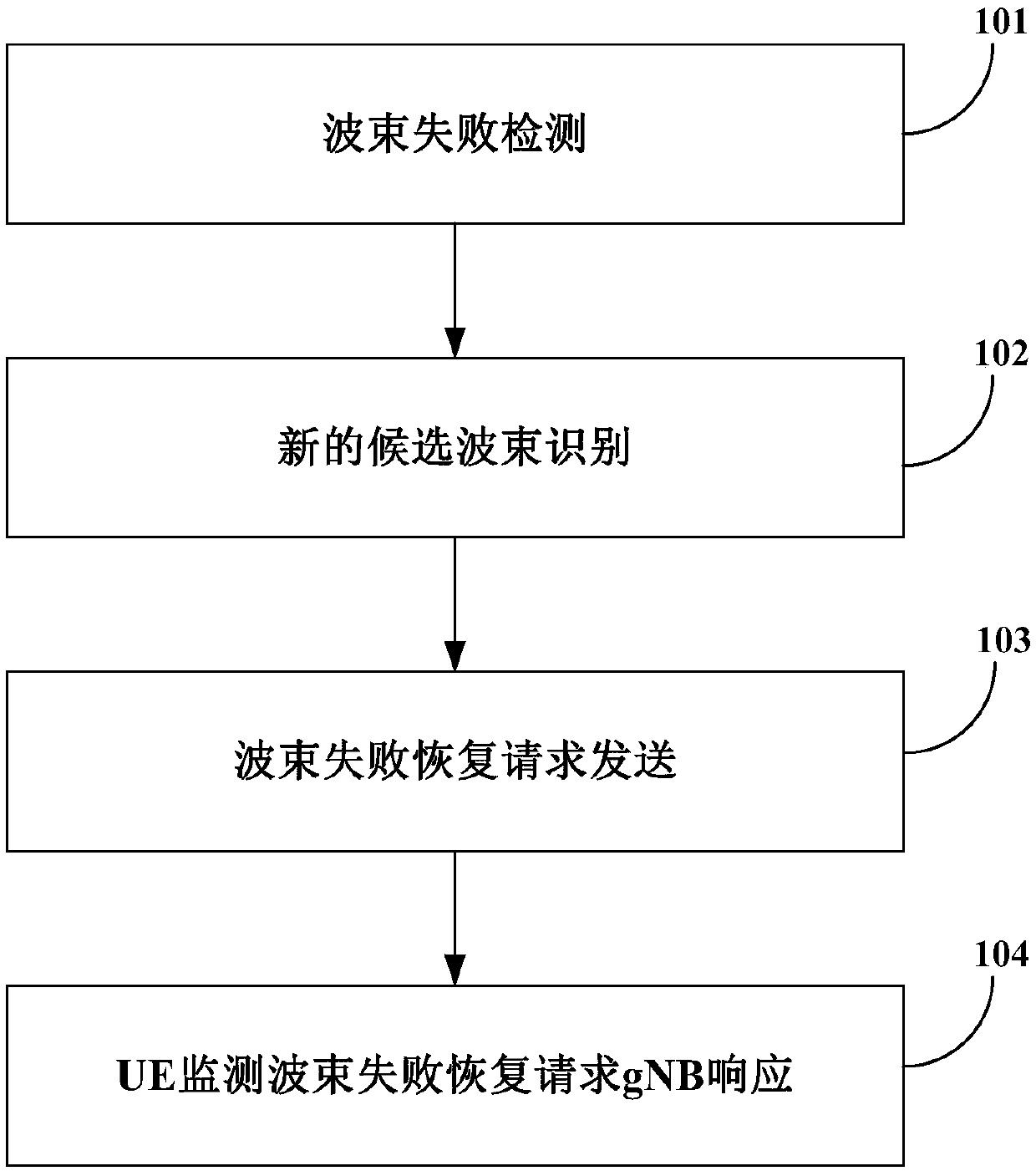
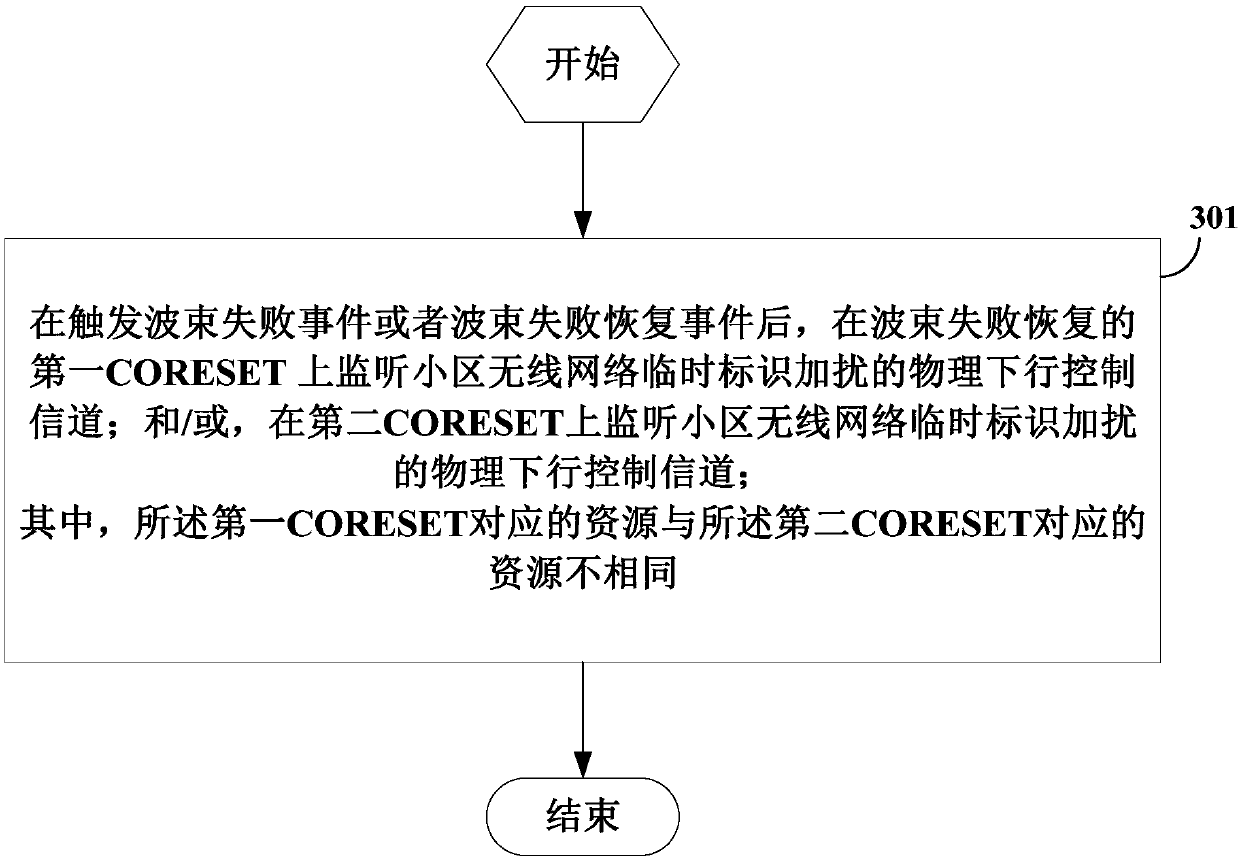
[0127] After a beam failure event is triggered or a beam failure is recovered, the UE behavior includes at least one of:
[0128] (1) Monitor the physical downlink control channel scrambled by the wireless network temporary identifier of the cell on the first control channel resource set CORESET of beam failure recovery.
[0129] (2) Monitor the physical downlink control channel scrambled by the wireless network temporary identity of the cell on the second CORESET.
[0130] Further, before the above actions (1) and (2) occur in the UE, the media access control (Media Access Control, MAC) layer instructs the physical (Physical, PHY) layer to indicate that a beam fails. After receiving the instruction, the PHY layer executes the above actions (1) and (2).
[0131] Furthermore, before the above behaviors (1) and (2) occur on the UE, the UE sends a beam failure recov...
example 2
[0135] Example 2: monitor two C-RNTIs, further, do not send a preamble code to the network side device, or monitor two C-RNTIs after preamble.
[0136] After a beam failure event is triggered or a beam failure is recovered, the UE behavior includes at least one of:
[0137] (1) Monitor the physical downlink control channel scrambled by the wireless network temporary identifier of the cell on the first control channel resource set CORESET of beam failure recovery.
[0138] (2) Monitor the physical downlink control channel scrambled by the wireless network temporary identity of the cell on the second CORESET.
[0139] Scenario 1: When the cell wireless network temporary identity is monitored on the second CORESET, the UE behavior includes at least one of:
[0140] The UE continues (does not stop) the beam failure recovery procedure;
[0141] The UE continues (does not stop) the random access process in the beam failure recovery process;
[0142] The PHY layer indicates to the...
example 3
[0166] During the RACH procedure in the beam failure recovery procedure, the UE behavior includes at least one of:
[0167] (1) When the non-competitive random access fails, directly declare that beam failure recovery fails, or use CBRA to continue the random access process of beam failure recovery.
[0168] The failure of the non-contention random access includes: the timer of the non-contention-free random access (CFRA) expires and / or the counter of the CFRA reaches the maximum value. That is, when using contention-based random access (Contention-based random access, CBRA) to continue the random access process of beam failure recovery, if the CBRA timer expires and / or after the CBRA counter counts to the maximum value, directly declare Beam failure recovery failed.
[0169] (2) When non-competitive random access fails and no indication of candidate beams and / or candidate resources of the physical layer is received, declare beam failure recovery failure, or use CBRA to conti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com