A Design Method for Separable Two-Dimensional FIR Filters with Sparse Coefficients
A technique of sparse coefficients, design methods, applied in design optimization/simulation, computer-aided design, digital technology network, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0119] Example 1. Design a quarter-symmetric circular two-dimensional FIR filter, the ideal frequency response is as follows:
[0120]
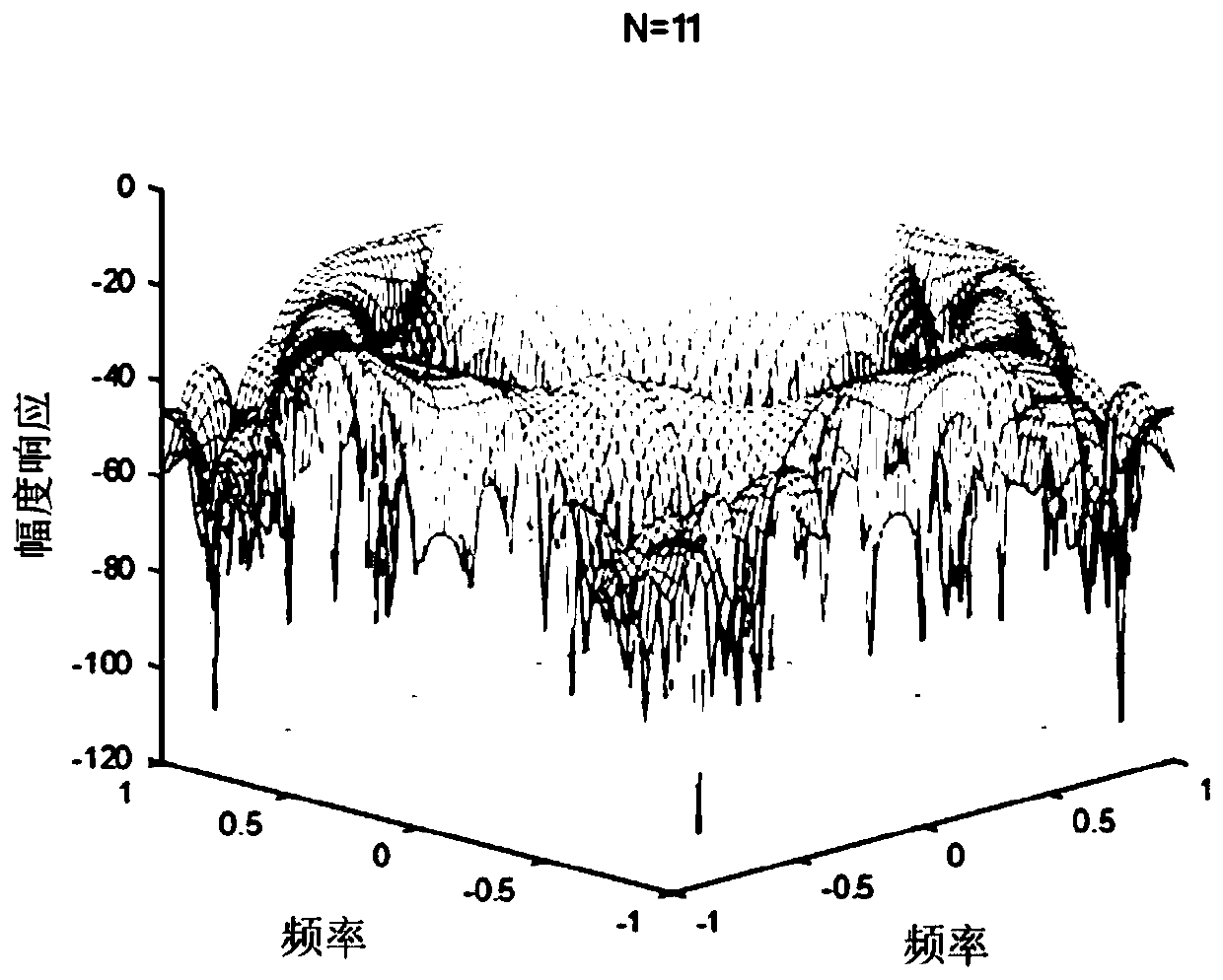
[0121] Where ω p =0.5·π,ω s =0.7·π, the order of the filter is N=11×11, 17×17, 23×23 and 29×29 orders, N 1 And N 2 Satisfy For different orders, the number of frequency sampling points Γ is sequentially set to 1521, 1521, 1521, and 1225; the values of K are 4, 5, 5, and 6 sequentially. The parameter ε=0.15 in step two, and the number of iterations is 10. Parameter ε of step 3 cof_bound = 0.0001, parameter σ = 0.0001, number of iterations is 15. For filters of different orders, the number of iterations in step 5 is 3, 1, 4, and 2 in order. Table 1 shows the results of the separable FIR circular filter with sparse coefficients and the corresponding design parameters. The frequency response is shown in Figure 3(a)-(d);
[0122] Table 1 Design results of a separable two-dimensional FIR circular sparse filter
[0123]
[0124] Note: The prototype...
example 2
[0125] Example 2. Design a quarter-symmetrical diamond two-dimensional FIR filter, the ideal frequency response is as follows:
[0126]
[0127] Where ω p =0.6·π,ω s =π, the order of the filter is N=11×11, 17×17, 23×23 and 29×29 orders, N 1 And N 2 Satisfy For different orders, the number of frequency sampling points Γ is taken as 1521, 1521, 1521, and 1521 in order; the value of K is 5, 5, 5, and 6 in order. The parameter ε=0.15 in step two, and the number of iterations is 10. Parameter ε of step 3 cof_bound = 0.0001, parameter σ = 0.0001, number of iterations is 15. For filters of different orders, the number of iterations in step 5 is 2, 4, 1, and 1 in order. Table 2 shows the results of the designed separable FIR diamond filter with sparse coefficients and the corresponding design parameters. The frequency response is shown in Figure 4(a)-(d);
[0128] Table 2 Design results of a separable two-dimensional FIR diamond sparse filter
[0129]
[0130] It can be seen from Table...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com