Radar based tracking of slow moving objects
A technology for moving objects, objects, applied in the direction of reflection/re-radiation of radio waves, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as blur detection, information type or accuracy limitations, radar device detection blur, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
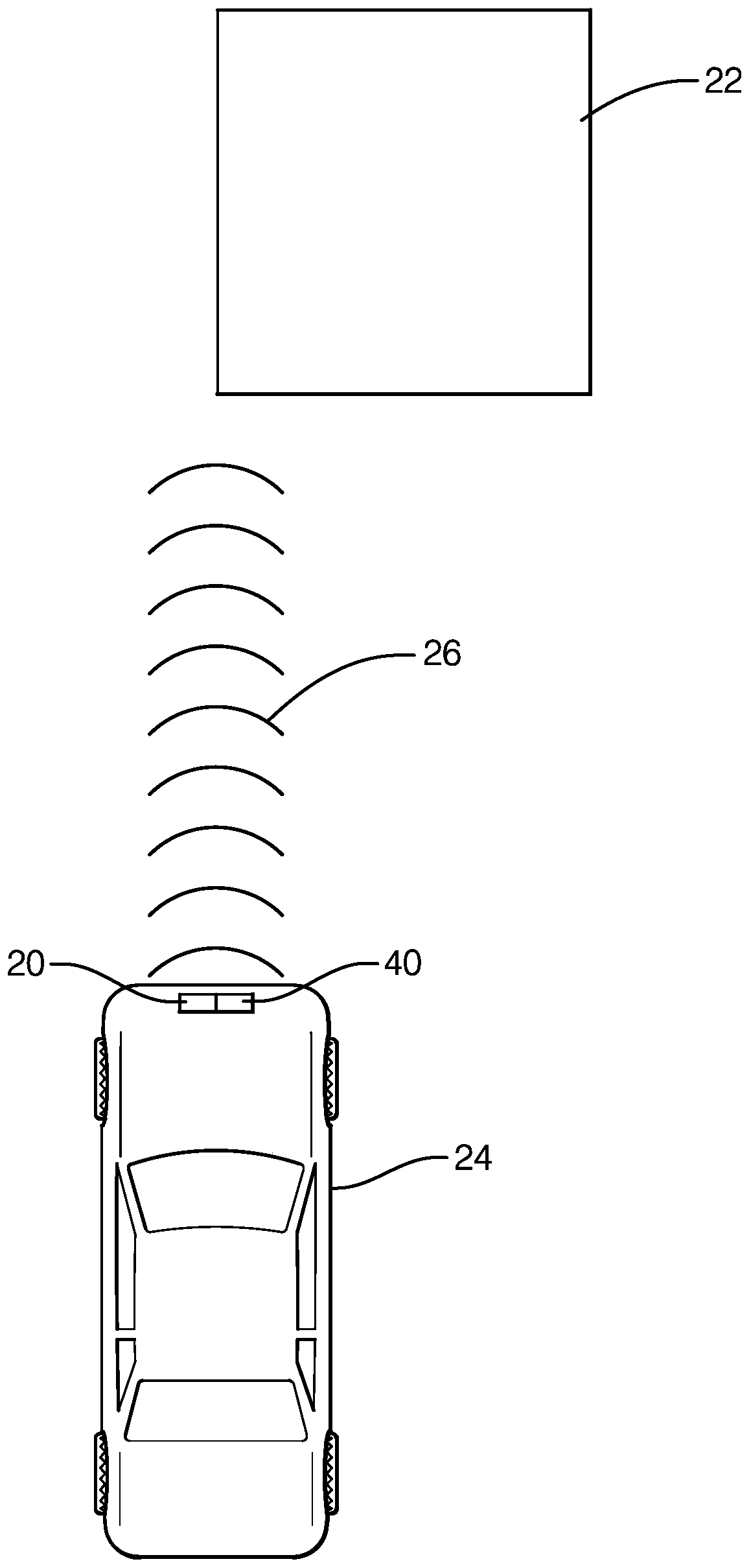
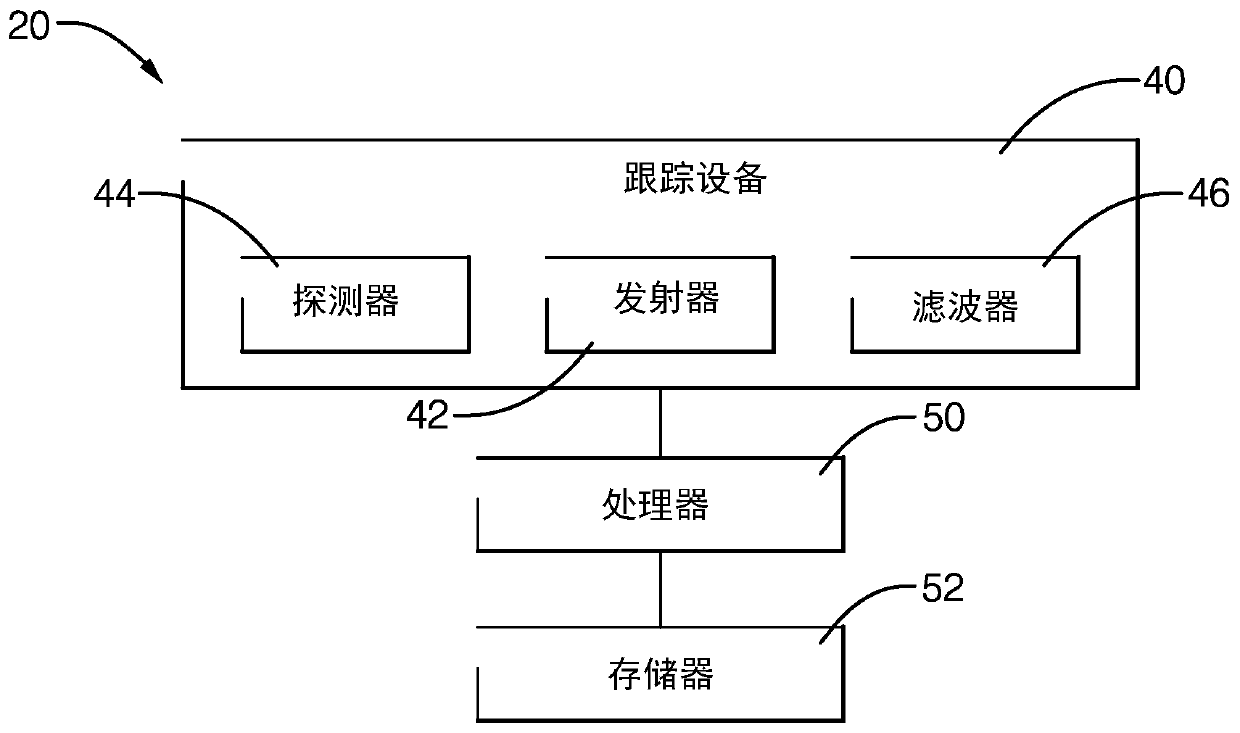
[0011] figure 1 A system 20 for detecting or tracking an object 22 is schematically shown. In this example, system 20 includes tracking device 40 located on host vehicle 24 . In some examples, host vehicle 24 may be an ego vehicle. System 20 determines information about object 22 to classify the object. For example, object 22 may be classified as a stationary object if object 22 is a building or a sign, or as a moving object if object 22 is another vehicle or a cyclist. One challenge presented by slow moving objects is that they may be misclassified as stationary. System 20 determines information about such objects 22 and compares it to several criteria to determine when to classify object 22 as a slow moving object. In some instances, object 22 is a pedestrian. In some embodiments, system 20 is configured to use additional criteria to classify pedestrians as slow moving objects.
[0012] System 20 uses known radar signaling, shown schematically at 26 , for detecting sev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com