A method and application of continuous casting slab crack risk prediction
A technology of risk prediction and continuous casting slabs, applied in geometric CAD, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve problems such as not being raised, and achieve the effects of convenient guidance, improvement of porosity, and improvement of center quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
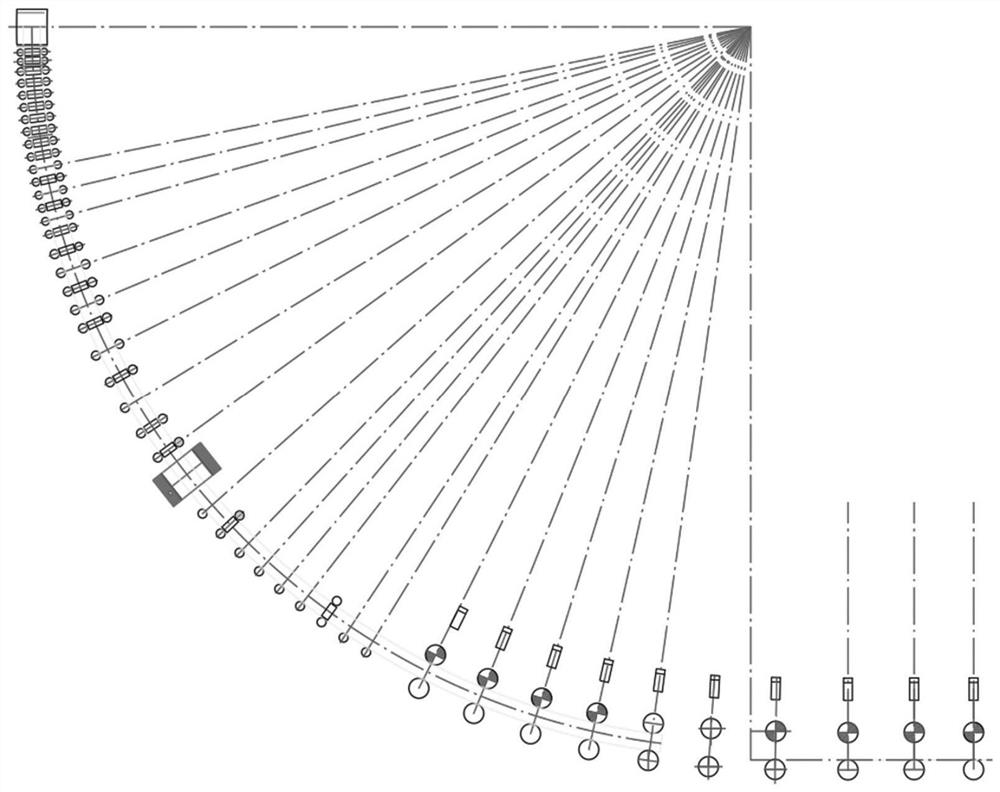
[0038] In this embodiment, the continuous casting production of GCr15 bearing steel with a cross-sectional size of 410mm×530mm is taken as an example. It adopts the solid-liquid two-phase region at the end of the solidification of the continuous casting slab, and implements the continuous casting light reduction technology. The casting speed of the casting machine is 0.58m / min, and keep the casting speed stable, select the nodes on the middle surface of the billet casting direction as the object, and study the variation of the tensile strain at each position on the middle surface with the position of the strand. The monitoring surface is shown in Figure 4 , When the reduction of 1~9# tension leveling machine is 0 / 1 / 1 / 1 / 2 / 3 / 4 / 4 / 2mm respectively, the schematic diagram of each position on the middle surface and the change of tensile strain with time, and analyze the crack Risk cloud map.
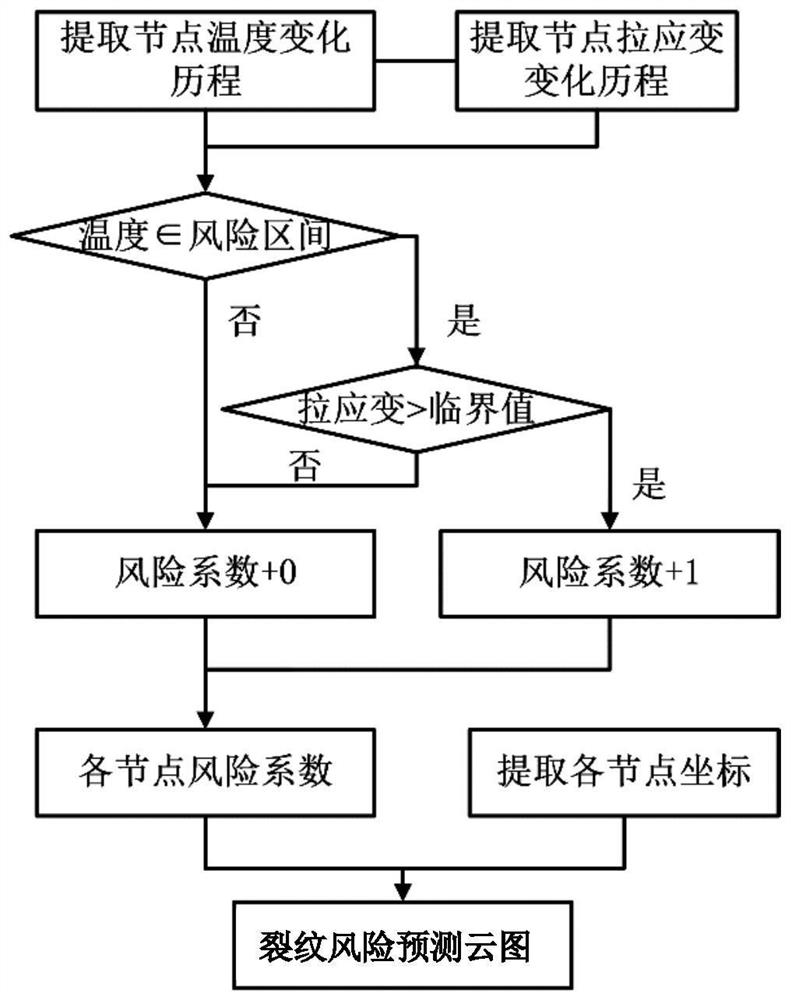
[0039] A method for predicting the risk of continuous casting slab cracks in this embodime...
Embodiment 2
[0046] In this embodiment, the continuous casting production cross-sectional size is 300mm * 2200mm Q345E microalloy steel wide and thick slab, the caster casting speed is 0.80m / min, and the casting speed is kept stable;
[0047] A method for predicting the risk of continuous casting slab cracks in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0048] Step 1: Select the critical strain for initiation of intermediate cracks in Q345E steel as the criterion for crack initiation. Specifically, the critical strain for initiation of intermediate cracks in Q345E steel in this embodiment is 0.04.
[0049] Step 2: According to the continuous casting process parameters for microalloy wide and thick slabs, import the geometric dimensions of each equipment in the continuous casting process into MSC.Marc finite element software, and establish in the finite element software from the mold meniscus to air cooling The thermal / mechanical coupling model of the whole process of continuous casti...
Embodiment 3
[0052] In this example, TiMo microalloy steel with a cross-sectional size of 200mm×1200mm is produced by continuous casting, the casting speed of the casting machine is 1.1m / min, and the casting speed is kept stable, and the occurrence rate of cracks at the corners of the surface of the wide and thick slab is relatively high , has a greater impact on the production of slabs, and the addition of microalloying elements also increases crack sensitivity. A TiMo microalloyed steel with high microalloy content was selected as the research object, and the critical criterion for crack propagation at the corner of the TiMo microalloyed steel wide and thick slab, the simulation results of temperature and deformation, and the crack risk prediction model were used to determine the risk of crack growth at the corner. for analysis.
[0053] Its continuous casting slab crack risk prediction method includes the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: Select the critical strain for crack propagatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com