Gain calculation method for caustic convergence region under deep sea complete sound channel based on ray normal mode theory
A caustics and theoretical technology, which is applied in the field of caustics convergence area gain calculation under the deep-sea complete channel, and can solve problems such as the reduction of the convergence area gain.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
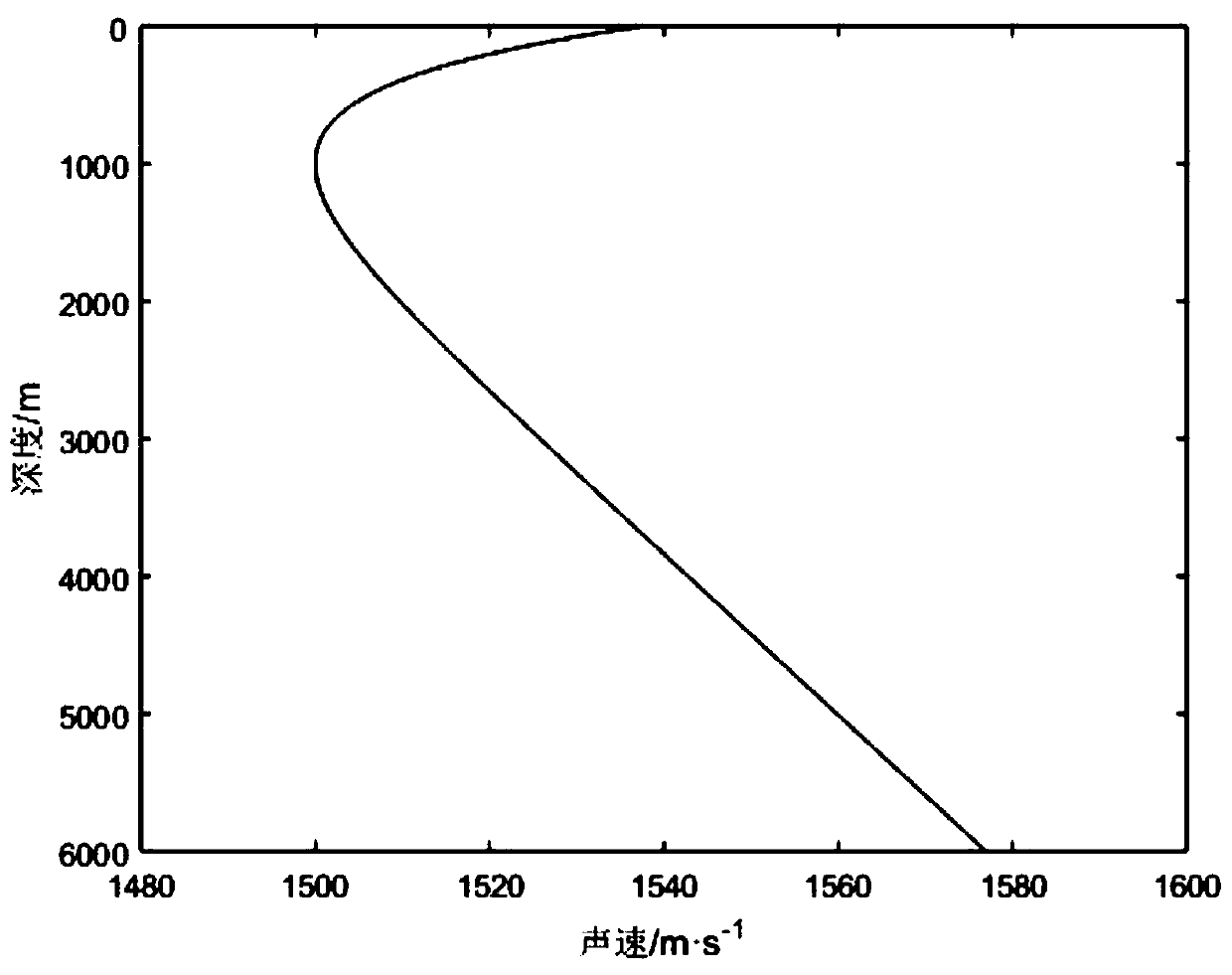
[0059] Analyzing the Munk profile, a typical deep-sea sound velocity profile, the sound velocity expression of the Munk profile is:
[0060] c(z)=c 0 {1+ε[e -η -(1-η))) (1)
[0061] Among them, η=2(z-z 0 ) / B, z 0 Is the depth of the channel axis, B is the waveguide width, c 0 Is the minimum value of sound speed, and ε is the magnitude of deviation from the minimum value. For a typical Munk model, the parameters are: B=1000m, z 0 =1000m, c 0 =1500m / s, ε=0.57×10 -2 . Sound velocity profile like figure 1 Shown.
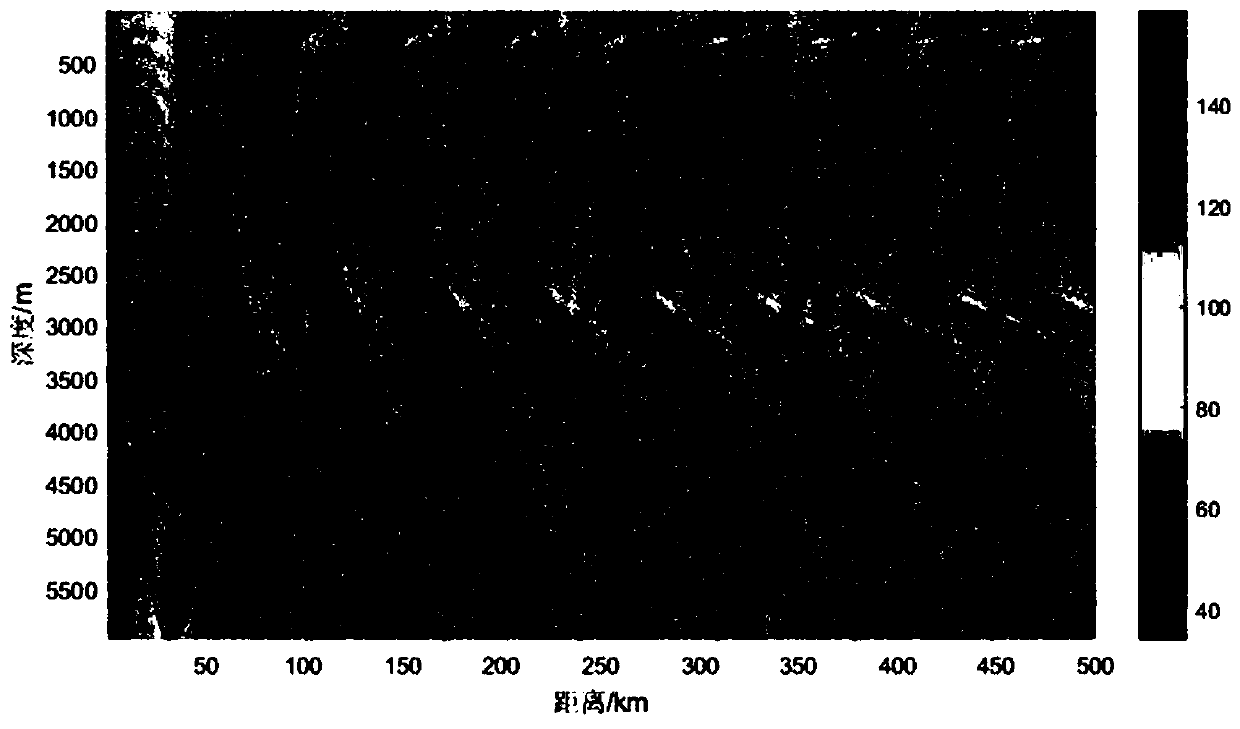
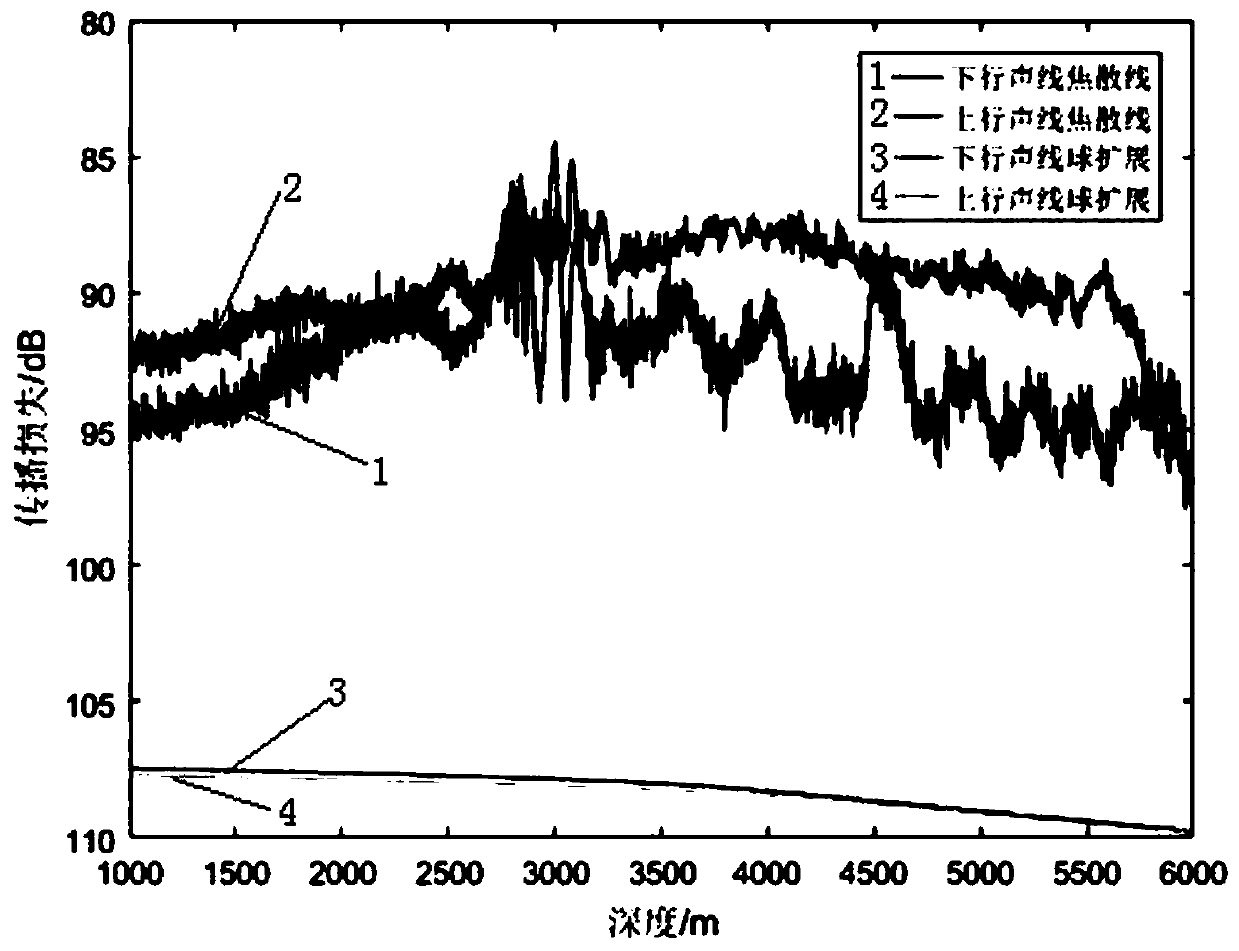
[0062] The sound source depth is 300m, and the environment at a sea depth of 6000m is selected for simulation. The signal is filtered at one-third octave of the center frequency of 200Hz. Using the sound field calculation software, the frequency range is 178-224Hz, with 1Hz as the step size. Calculate the sound field separately for each frequency point, then use equation (4) to calculate the frequency average sound intensity, and then calculate the frequency average propagat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com