Methods for treating HcV
A recipient, patient technology applied in the field of treatment of HcV
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0188] Example 1. Clinical modeling of DAA combination therapy without interferon
[0189] Treatment regimens involving the administration of Compound 1 and Compound 2 were evaluated using the clinical model described in U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2013 / 0102526, filed October 19, 2012, and entitled "Methods of Treating HCV," The aforementioned US patent application publications are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety. These treatment regimens included the administration of Compound 1 and Compound 2, but not the administration of interferon or ribavirin. Interferon nonresponders are expected to have comparable SVR rates.
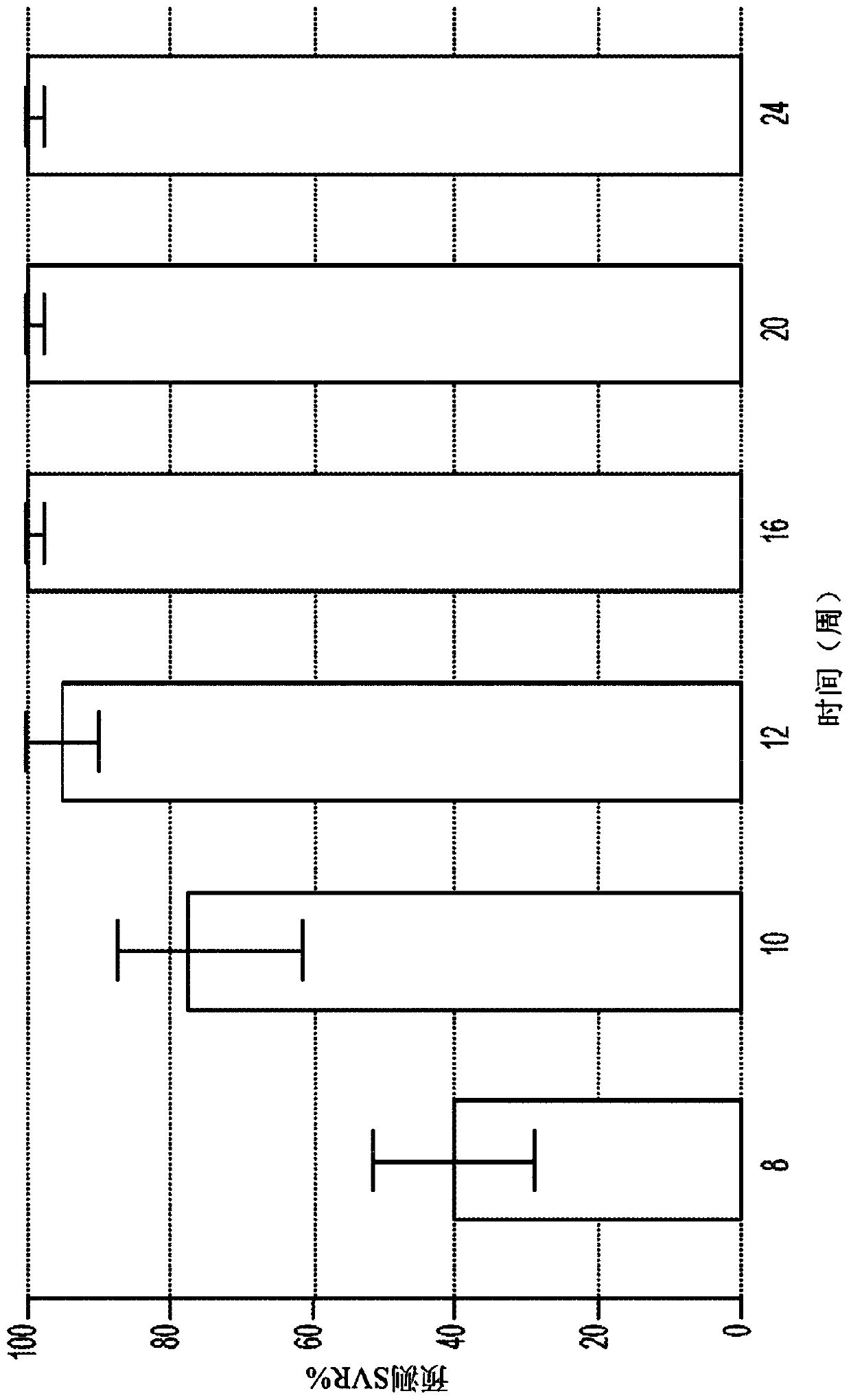
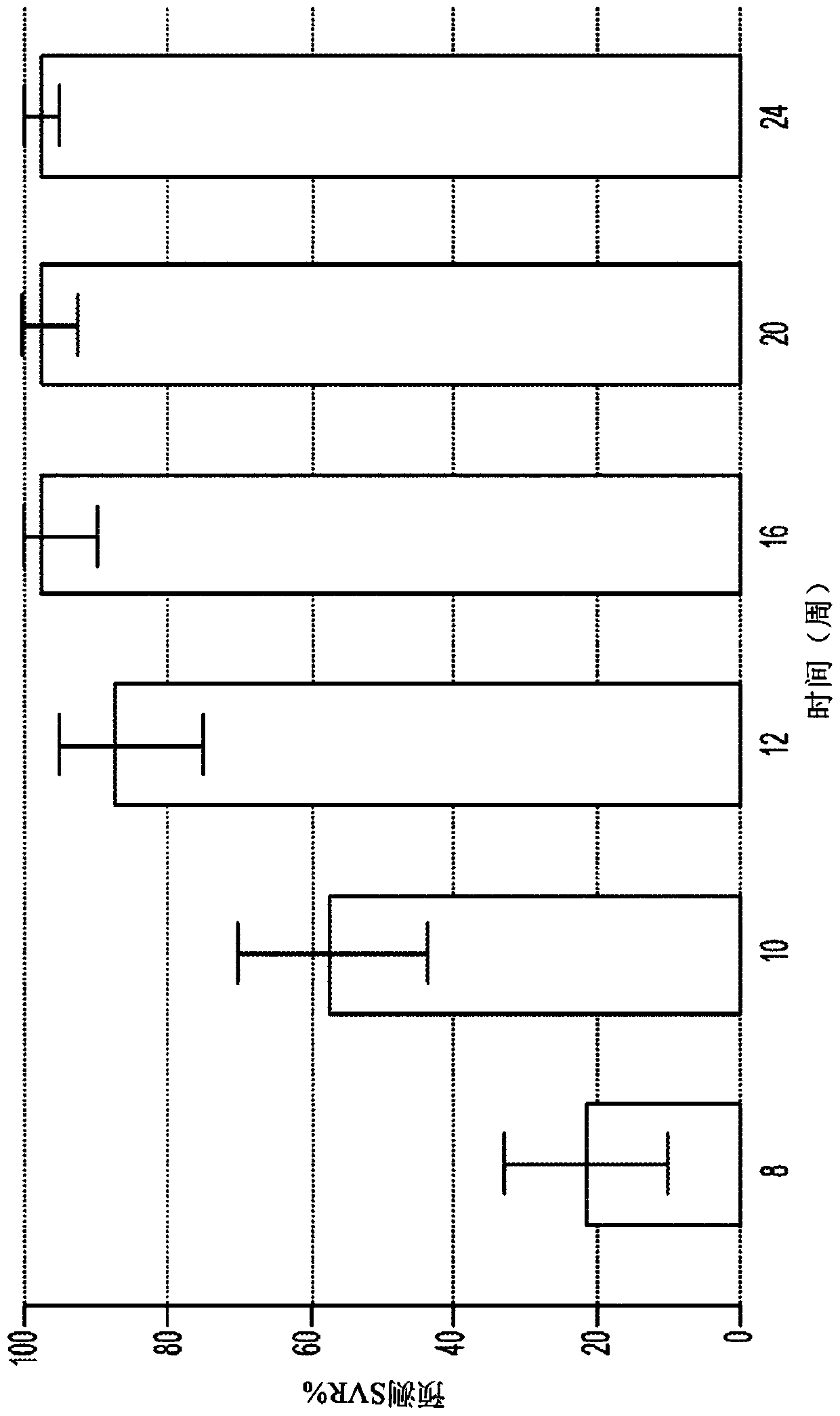
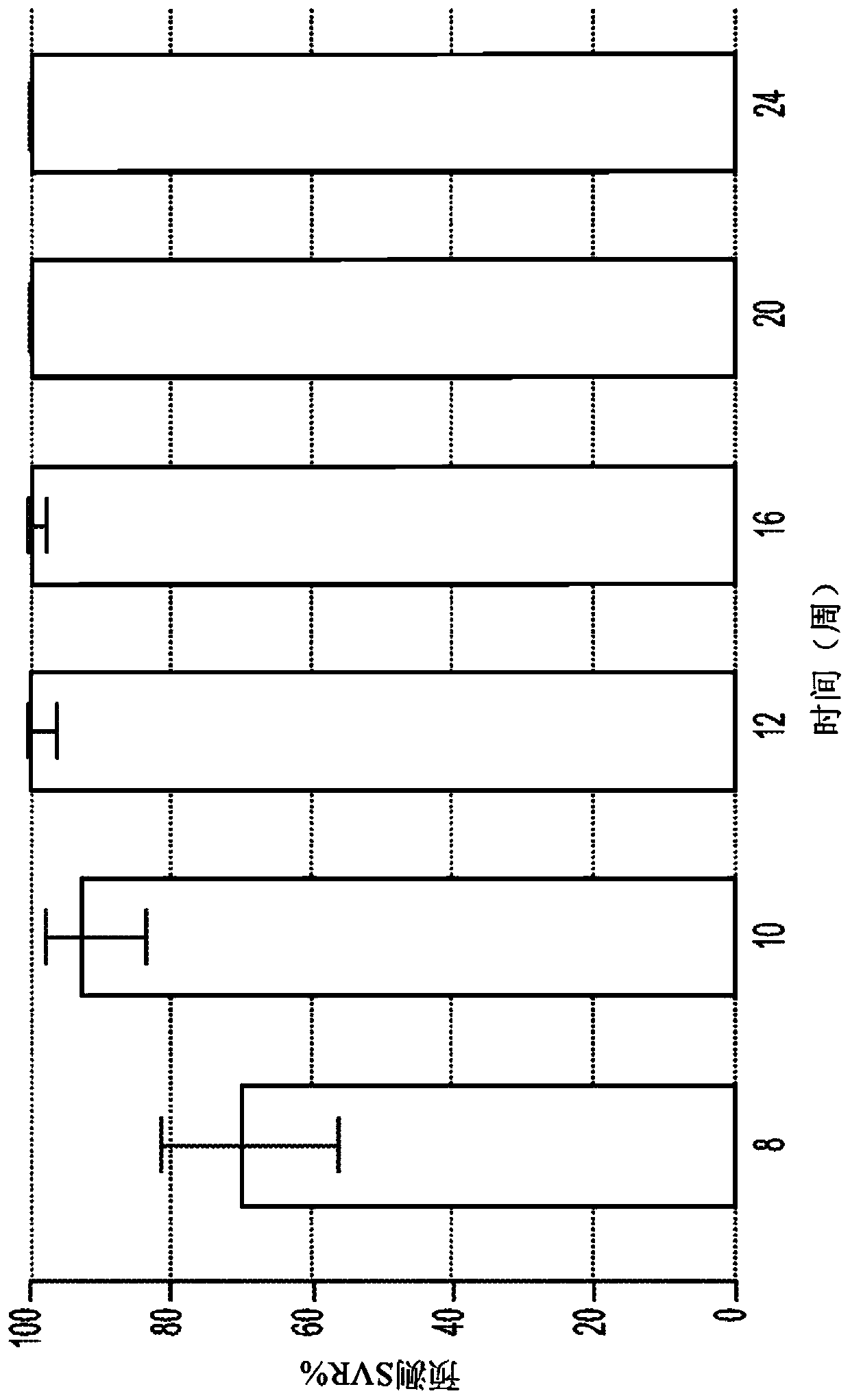
[0190] figure 1 Predicted median SVR percentages and 90% SVR confidence intervals for genotype 1 untreated individuals treated with a 2-DAA regimen consisting of Compound 1 (400 mg once daily) and Compound 2 (120 mg once daily) are shown. Different treatment durations were evaluated. The predicted SVR rate for 12 weeks of treatm...
example 2
[0198] Example 2. Combination of Compound 1 and Compound 2 in vitro
[0199] Figure 9 It was shown that the combination of Compound 1 and Compound 2 exhibited a significant synergistic effect on HCV inhibition as tested in HCV GT1b Con-1 replicating cells. Results were generated using the Prichard and Shipman model (Prichard et al. ANTIVIRAL RESEARCH 14:181-205 (1990)).
[0200] Compound 1 inhibits the replication of HCV stable subgenomic replicons containing the NS3 gene from GT 1a, 1b, 2a, 3a, 4a or 6a, where EC 50 Values ranged from 0.85 to 2.8 nM. Notably, compound 1 was potent against replicon containing GT3a protease, in which EC 50 The value is 1.6nM. Compound 1 retained its activity against common GT1a and Ib variants at NS3 amino acid positions 155 and 168, which confer resistance against other HCV protease inhibitors (Pis). Resistant colony selection studies in GT1a and 1b subgenomic replicon cells identified A156T in GT1a and A156V in GT1b as the most common...
example 3
[0210]Example 3. High SVR in HCV Genotype 1 (GT1 ) Non-Cirrhosis-Naive Patients or Pegylated Interferon / Ribavirin Nonresponders Treated with Combination of Compound 1 and Compound 2
[0211] Compounds 1 and 2 were characterized by potent pan-genotype in vitro antiviral activity against major HCV genotypes (GTs), including activity against key known resistance-associated variants and a high resistance selection barrier. Monotherapy with Compound 1 or Compound 2 resulted in a mean 4-log reduction in HCV plasma viral load from baseline in GT1-infected individuals with or without compensated cirrhosis 10 IU / mL.
[0212] In this Phase 2 study, 12 weeks of treatment with Compound 1 and Compound 2 were evaluated in HCV GT1 -infected individuals without cirrhosis. Non-cirrhotic GT1-infected treatment-naïve (TN) individuals or pegIFN / RBV-neutral responders received 200 mg Compound 1 + 120 or 40 mg Compound 2 once daily for 12 days weeks, and followed up for 24 weeks. Efficacy was m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| retention rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com