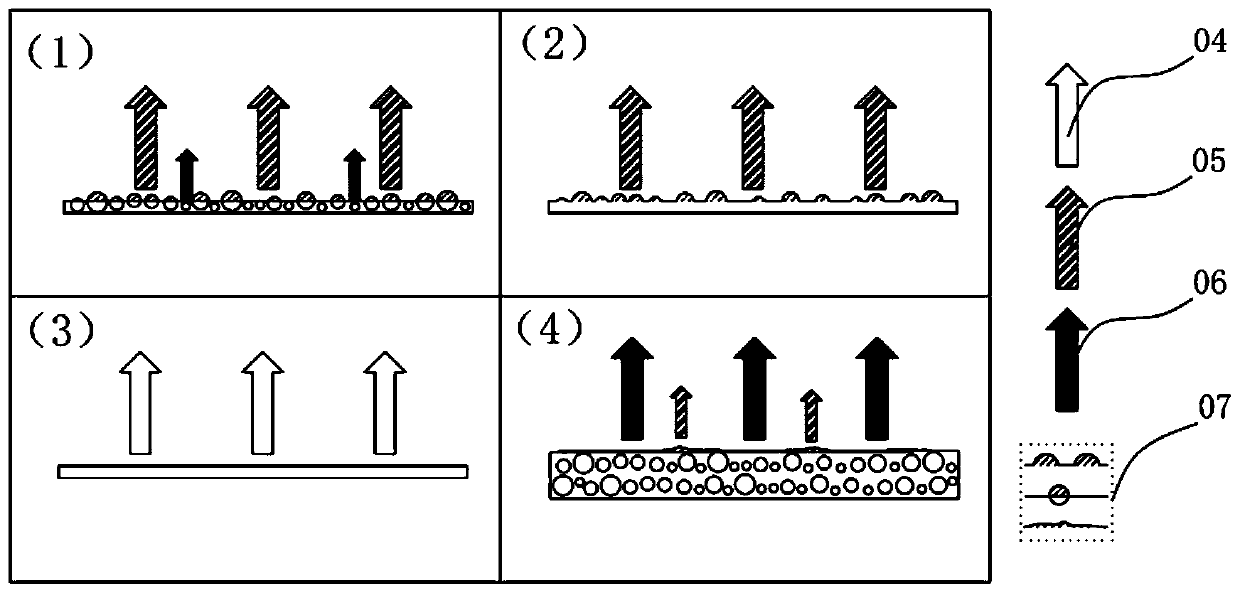
Sensor dimming layer and preparation method thereof
A sensor and dimming technology, applied in optics, instruments, optical components, etc., can solve the problem of controlling high-purity bulk scattered light without realizing the advantages of high-purity bulk scattering control methods, without emphasizing surface scattering interference, and without scattering control. issues of sex
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
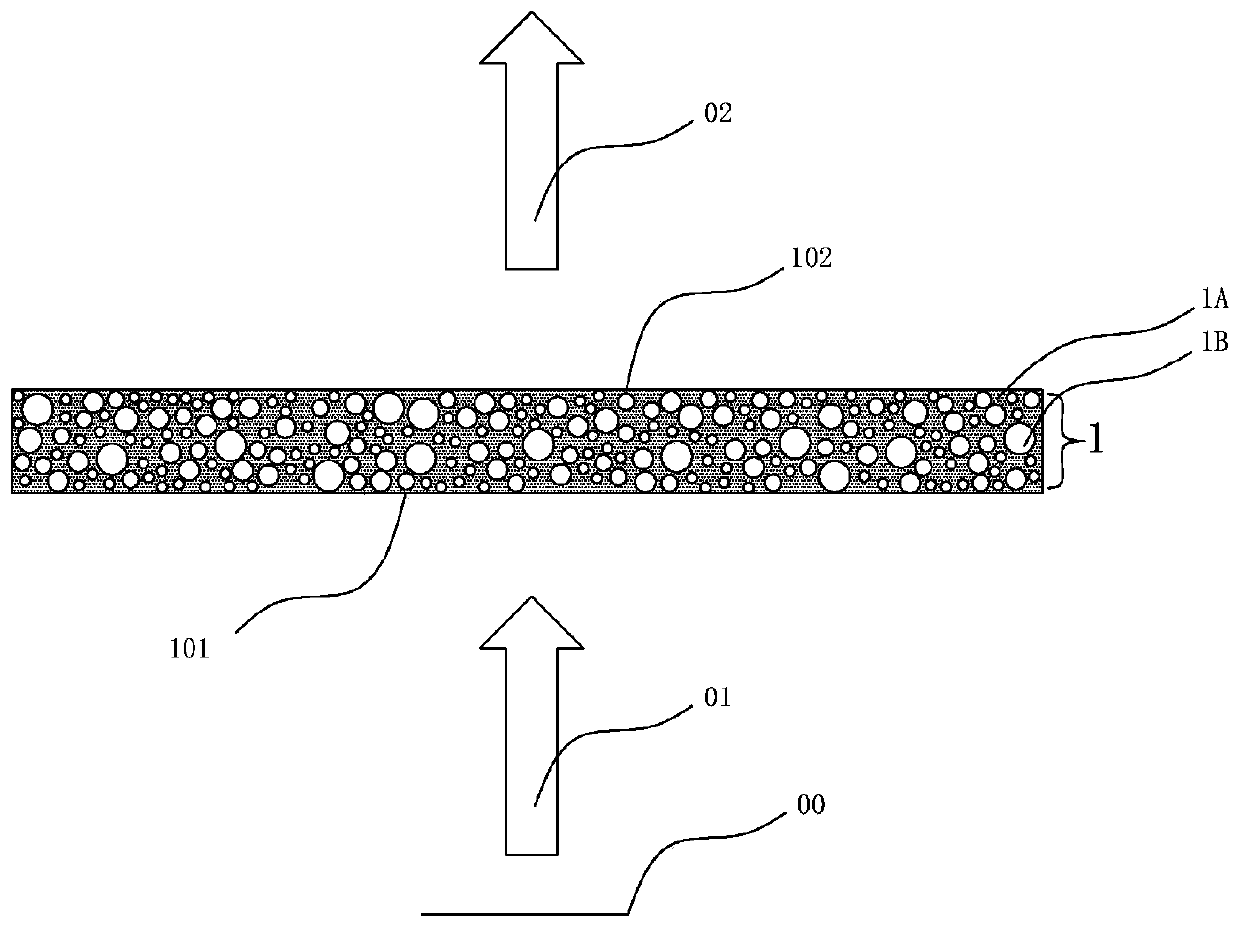
[0157] Such as image 3 As shown, the dimming layer 1 provided by the present invention has a thickness T of 50 μm, contains a propagation medium 1A and a light scattering agent 1B, a light incident surface 101, a light output surface 102, and 1B are uniformly dispersed in 1A, forming a volume scattering system, and input light 01 It emits from the light-emitting surface 00 of the input light source, enters from the light-incident surface 101, and is controlled by the volume scattering of the dimming layer, and then emits from the light-emitting surface 102 to produce the final output light 02. Among them, 1A is the acrylic resin system in the light-curing polymer resin, and the light scattering agent 1B is the Al in the inorganic particle system 2 O 3 The particles are polydisperse, with a particle size of 0.5 to 1.5 µm, and the filling rate D'of the volume scattering system is 0.4. The light incident surface 101 and the light exit surface 102 are very flat and smooth, and the ...
Embodiment 2-15
[0173] Like the dimming layer 1 provided in Example 1, the parameters are listed in Table 3.
[0174] Table 3 Performance comparison of Examples 2-15 under collimated input light
[0175]
[0176]
[0177] Notes 1~3 are the same as Table 2
[0178] Comparing Examples 2-5, 6-8, 9-10, it can be seen that when other conditions remain unchanged and T increases, the volume scattering effect is strengthened, and Φ 2 As it becomes larger, the output light is getting closer and closer to the ideal Lambertian level. Comparing Examples 11-13, it can be seen that when other conditions remain unchanged and D'increases, the volume scattering effect is strengthened, and Φ 2 As it becomes larger, the output light is getting closer and closer to the ideal Lambertian level. Comparing Example 11 with Examples 14 and 15, it can be seen that when other conditions remain unchanged and D decreases, the particle concentration M increases, and the volume scattering effect is strengthened. 2 As it becomes l...
Embodiment 16-31
[0180] Like the dimming layer 1 provided in Example 1, the parameters are listed in Table 4.
[0181] Table 4 Performance comparison of Examples 16-31 under different forms of normal input light
[0182]
[0183]
[0184] Notes 1~3 are the same as Table 2
[0185] As shown in Table 4, comparing Examples 16-19, for a specific sensor dimming layer, when the normal direction collimated incident (Example 16), the output light Φ 2 When it is less than 120°, the ideal Lambertian level is not reached. At this time, as the input light Φ 1 Becomes larger, the volume scattering effect is still further strengthened, Φ 2 It becomes bigger and closer to the ideal Lambertian level. Comparing Examples 20-28, it can be seen that for a specific sensor dimming layer, when its D'is large enough and the optical properties of the light scattering agent and the propagation medium are properly matched, the light output after the normal collimated incidence (Example 20) Φ 2 It can be equal to 120°, that is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com