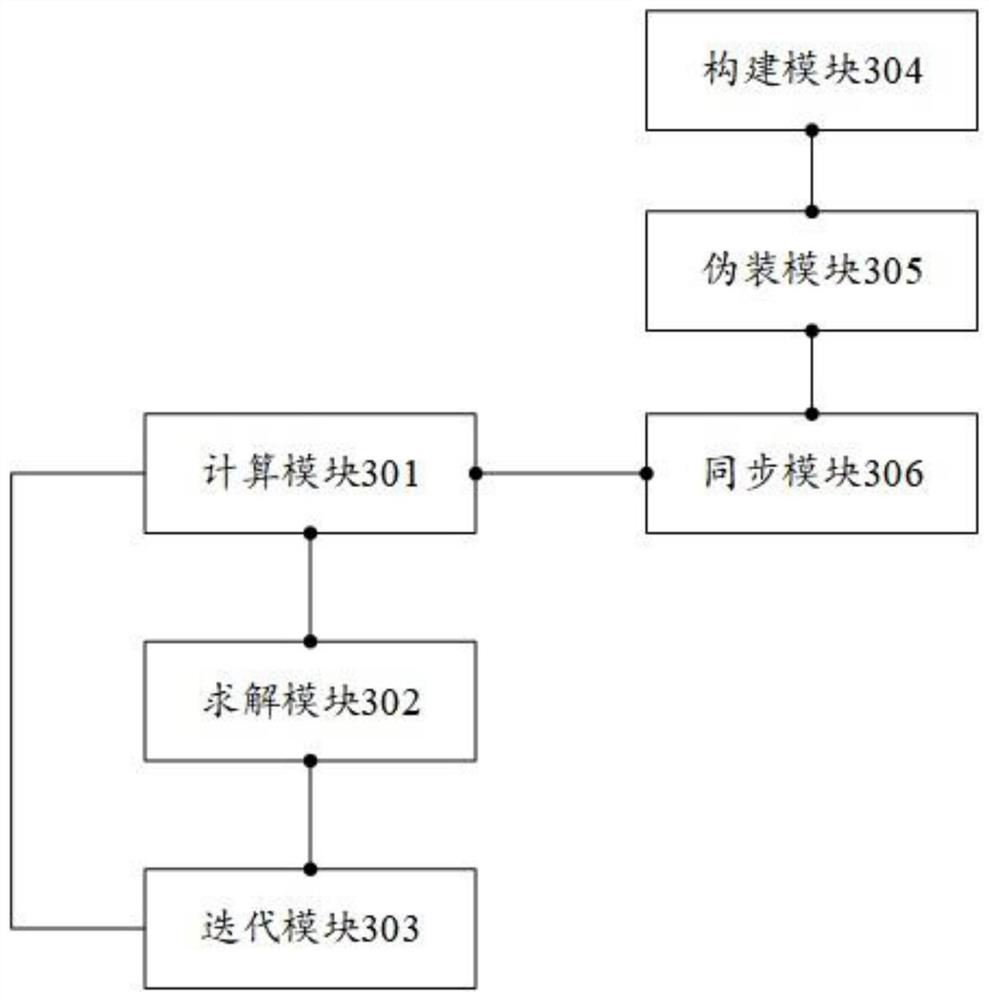
A method for synchronous iterative calculation of power flow in an interconnected power grid and related devices
A technology of synchronous iteration and interconnected power grids, which is applied in the direction of circuit devices, electrical components, AC network circuits, etc., can solve problems such as low applicability, large influence of power flow calculation, and poor efficiency of synchronous iterative calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
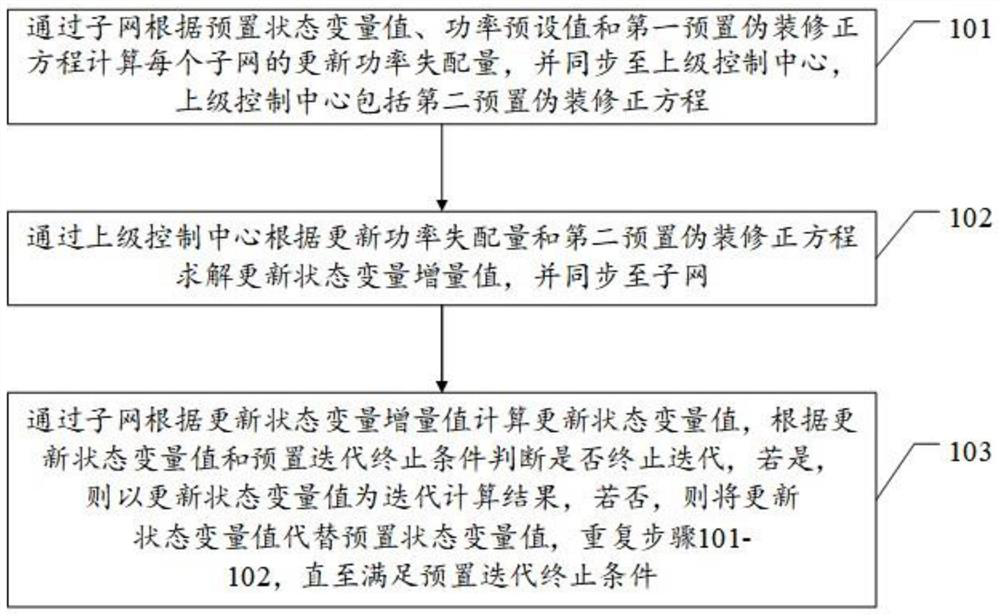
[0046] For ease of understanding, see figure 1 , Embodiment 1 of an iterative calculation method for power flow synchronization in an interconnected power grid provided by the present application, including:
[0047] Step 101. Calculate the updated power mismatch of each subnetwork through the subnetwork according to the preset state variable value, power preset value and the first preset pseudo-fitting equation, and synchronize to the upper control center. The upper control center includes the second preset Set the pseudo-fitting equation.
[0048] It should be noted that the preset state variable value here is the initial state variable value in the sense of actual iterative calculation. During the subsequent iterative calculation process, the state variable value will be updated continuously until the iteration stops; node power preset The set value includes active power and reactive power; the first preset pseudo-fitting positive equation is obtained by camouflaging the b...
Embodiment 2
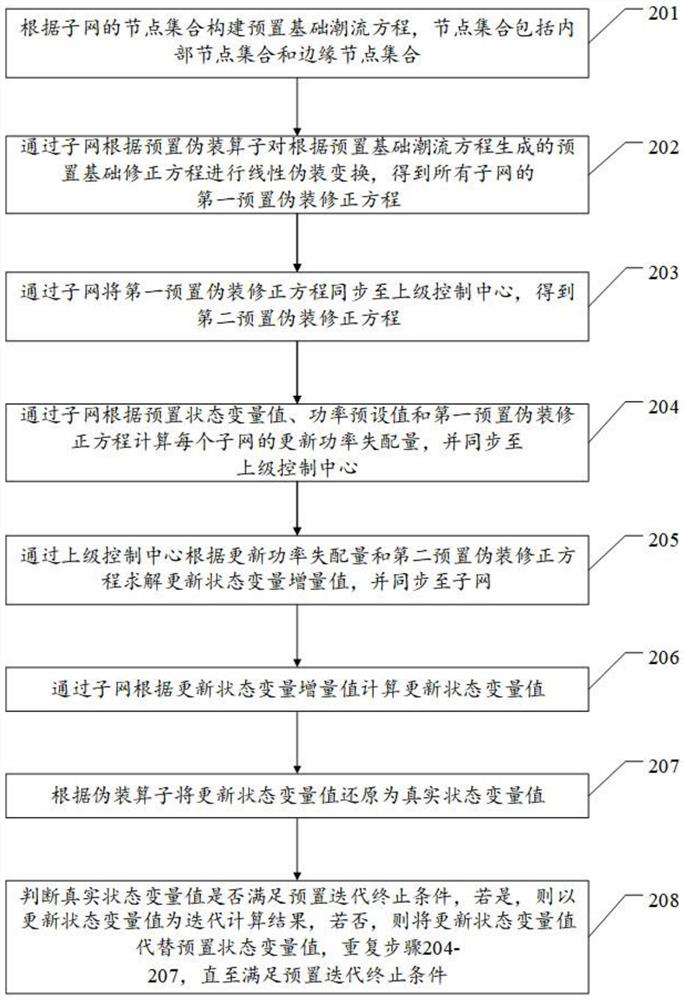
[0054] For ease of understanding, see figure 2 , the present application provides a second embodiment of an iterative calculation method for power flow synchronization in an interconnected power grid, including:
[0055] Step 201, constructing a preset basic power flow equation according to the node set of the subnetwork, the node set includes an internal node set and an edge node set.
[0056] It should be noted that the set of subnets is defined as Q=1,2,...,A, where A is the number of subnets, and the total node set of each subnet is iD. The total node set can be divided into Internal node set iα and edge node set iβ, where iD=iα∪iβ, iα∩iβ=φ, the specific node set is defined as follows:
[0057]
[0058] Among them, J(m) is the set of all adjacent nodes of internal node m, and J(n) is the set of all adjacent nodes of edge node n; adjacent nodes refer to nodes that have direct topological connections with this node . Taking subnetwork i as an example, the basic power ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com