A New Electromagnetic Vibration Isolator with Adjustable Negative Stiffness
A negative stiffness, electromagnetic technology, applied in the functional characteristics of springs/shock absorbers, magnetic springs, springs/shock absorbers, etc., can solve the problem of system reliability reduction, increased design workload, and the difficulty of designing passive support mechanisms in isolation Problems inside the vibrator, etc., to achieve the effect of shortening the design cycle and good applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
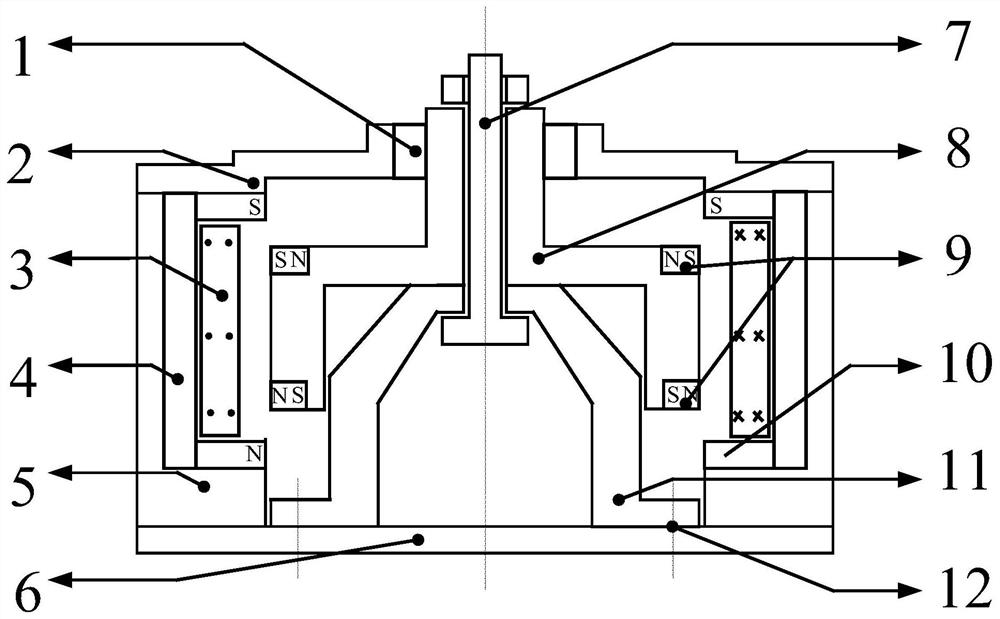
[0040] like figure 1 As shown, a new type of electromagnetic vibration isolator with adjustable negative stiffness includes a stator housing 5, a mover 8 arranged in the inner cavity of the stator housing 5 and movable along the longitudinal axis of the stator housing 5, assembled A positive stiffness component that acts as a positive stiffness on the mover 8 below the mover 8,
[0041] It also includes a permanent magnet 9 mounted on the outer wall of the mover 8, arranged on the first layer along the longitudinal axis of the mover 8, and a permanent magnet 9 arranged on the second layer, the permanent magnet 9 of the first layer and the permanent magnet of the second layer The polarity end face of the permanent magnetic field of 9 faces the radial direction, and the polarity of the permanent magnet 9 of the first layer is opposite to that of the permanent magnet 9 of the second layer;
[0042] It also includes a coil assembly assembled on the inner wall of the stator housin...
Embodiment 2
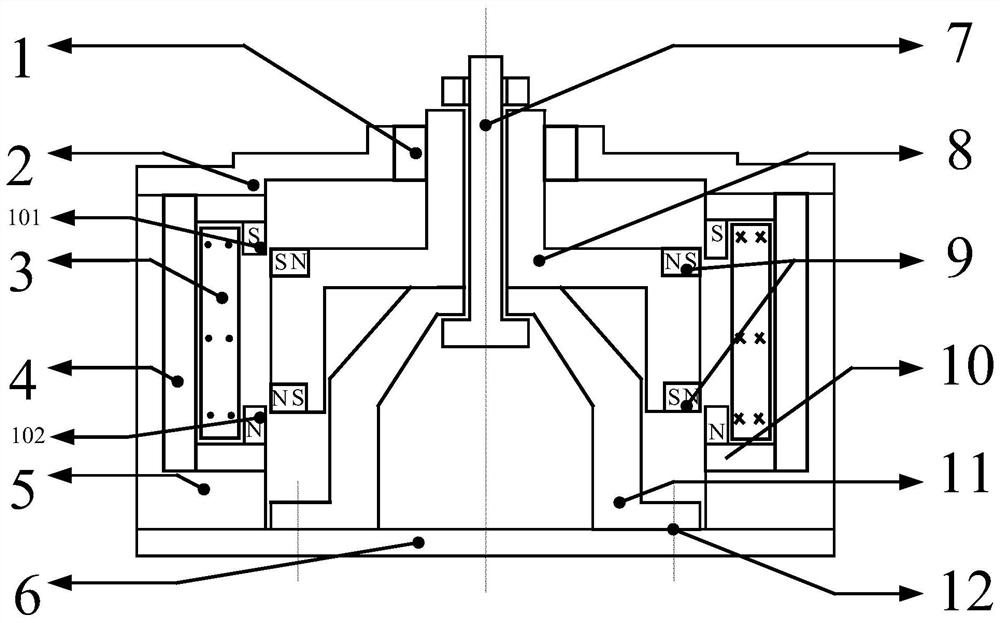
[0051] Although in embodiment 1, in order to construct the repulsive force relationship, the outer end faces of the coil yoke at the upper and lower ring openings will form a polarity, and when the negative stiffness and positive stiffness are balanced, the coil yoke will be positive to its corresponding permanent Magnets, therefore, the effective travel range of its negative stiffness is related to the size of the polar end face of the coil yoke or permanent magnet, and in order to miniaturize the size, and to seek a better repulsive force relationship and a good negative stiffness effective travel range. This embodiment is constructed on the basis of Embodiment 1, such as figure 2 As shown, the further technical solution is: the end of the coil yoke 10 facing the mover at the upper ring mouth is bent downward and extended to form an upper yoke tongue 101, and the coil yoke 10 at the lower ring mouth is bent upward at the end facing the mover. The lower yoke tongue 102 is fo...
Embodiment 3
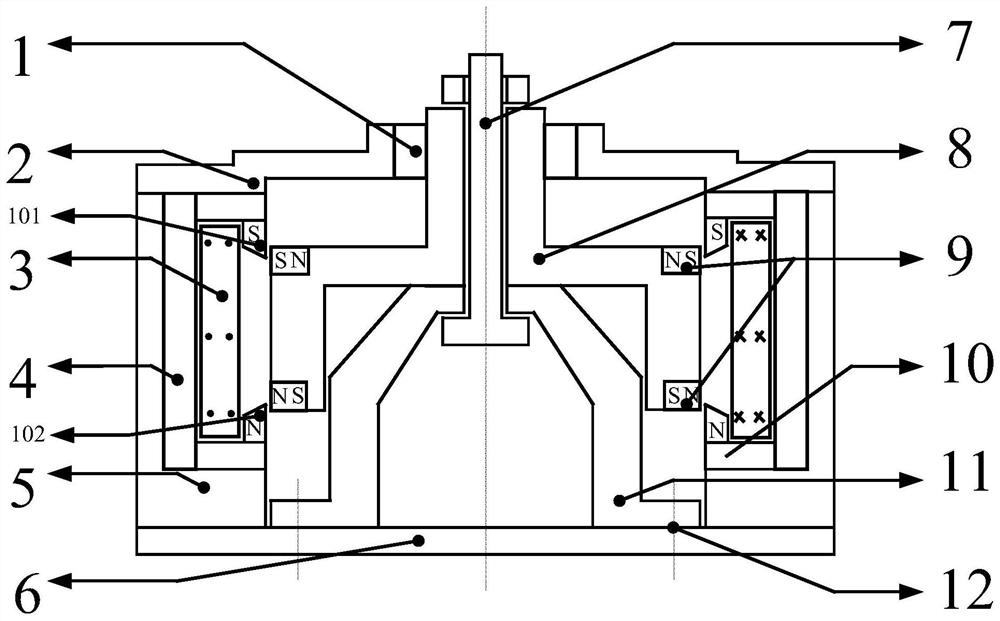
[0054] like image 3 As shown, further, in order to overcome the problem of weakening of the above-mentioned repulsive force, the end faces of the upper yoke iron tongue 101 and the lower yoke iron tongue 102 are treated with the splitting tip used in the present invention, specifically: the lower end surface of the upper yoke iron tongue is an upwardly inclined slope 1. The upper end face of the lower yoke tongue is a downwardly inclined slope. At this time, the projected size of the magnetic field air gap between the upper yoke tongue and the lower yoke tongue adjacent to the outer surface of the mover on the longitudinal axis is smaller than that far away from Based on the projection size of the inner surface of the mover on the longitudinal axis, the projected size of the outer surface of the lower yoke tongue and upper yoke tongue adjacent to the mover side on the longitudinal axis is larger than the inner surface far away from the mover side in the longitudinal direction....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com