Artificial potential field method for automatic driving vehicle decision-making layer path planning
A technology of artificial potential field and path planning, which is applied to vehicle components, input parameters of external conditions, control devices, etc., can solve the problem that the vehicle cannot reach the end point, and achieve the effect of low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
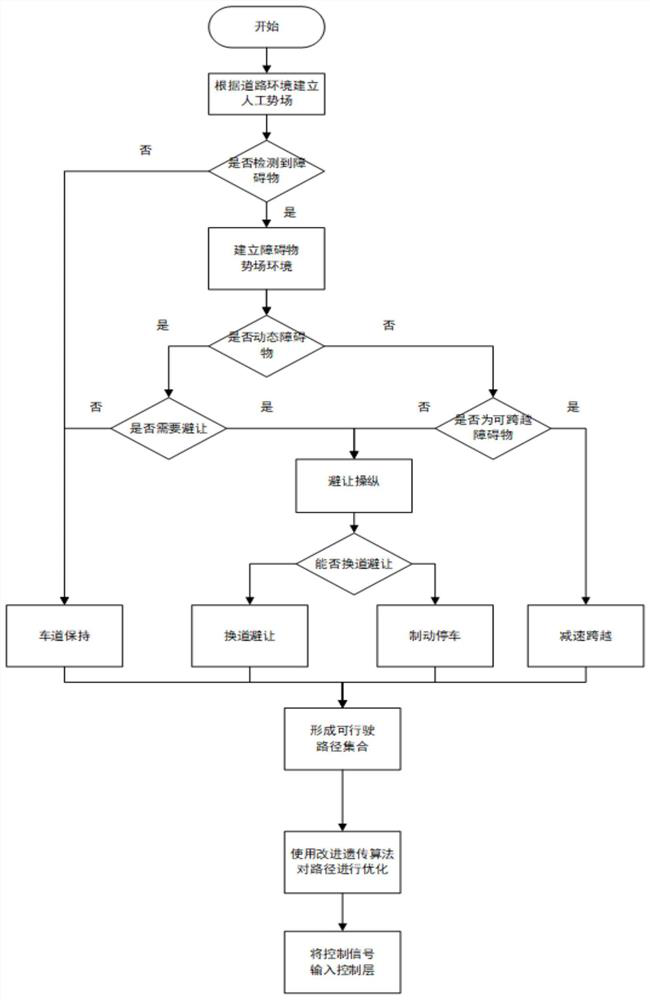
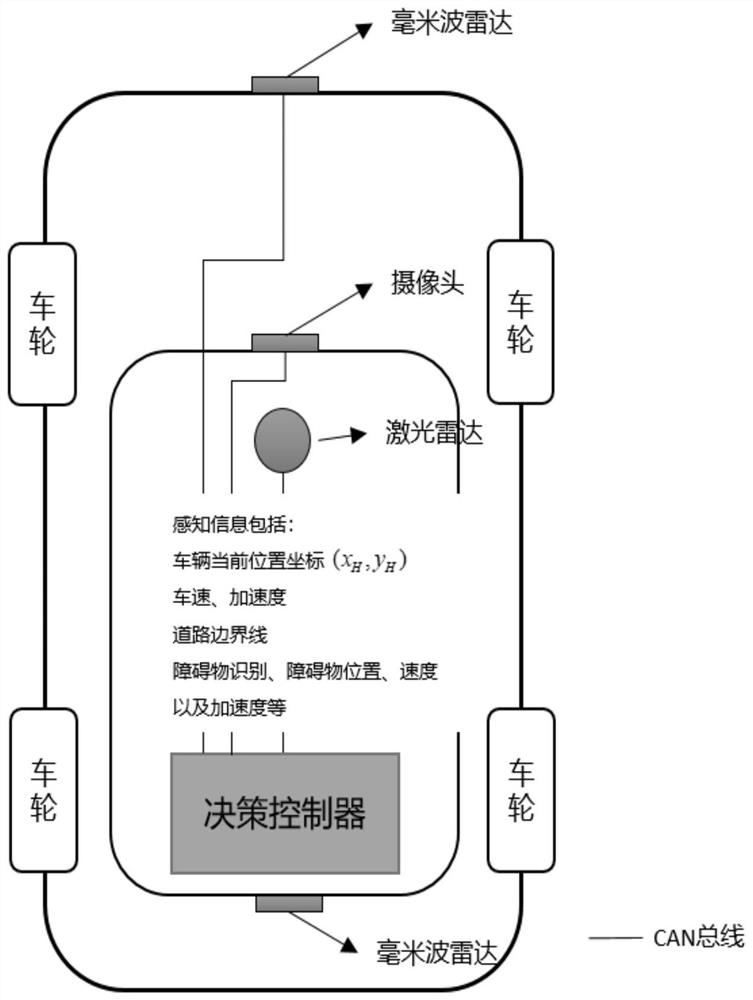
[0022] The vehicle travels straight along the lane, and the road environment is established so that the vehicle cannot drive beyond the lane boundary. And there is a speed bump ahead to remind the driver to slow down. At this time, the perception layer transmits the information to the decision-making layer to judge that there is no need to change lanes at this time, and the decision-making layer establishes a potential field so that the value of the potential field on both sides of the road is high enough that vehicles cannot cross. And as the vehicle gradually approaches the deceleration belt ahead, the potential field value gradually increases to decelerate the vehicle, and when the deceleration reaches a certain level, the potential field gradient decreases to allow the vehicle to pass smoothly.
Embodiment 2
[0024] A pedestrian suddenly appeared in front of the vehicle. The perception layer transmits the position of the obstacle to the decision-making layer, judges that the lane change distance is exceeded, and quickly establishes a potential field. As the longitudinal distance between the vehicle and the pedestrian in front decreases, the value of the potential field increases rapidly. And when it is close enough to pedestrians, the potential field value increases to infinity, so that the vehicle brakes to ensure the safety of pedestrians.
Embodiment 3
[0026] The vehicle is traveling at a speed of 30km / h, and the vehicle 100m ahead is traveling at a speed of 25km / h. The perception layer transmits the position and speed of the vehicle in front of the obstacle to the decision-making layer. By judging the longitudinal distance between the obstacle and the vehicle, the lane change operation can be performed. The value of the potential field near the obstacle is increased through the artificial potential field, so that the vehicle cannot be too close Obstacles, so that the vehicle double-lane shifting condition can be safely carried out.
[0027] Comparison with traditional potential field methods:
[0028] The traditional artificial potential field path planning algorithm only performs path planning based on state information such as obstacle position and velocity, and is mostly used in the field of robotics. One of the existing methods, Zheng Jifa. A path planning method based on the artificial potential field method: China, 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com