Symmetrical type variable-pivot rigidity regulating module capable of realizing full-range rigidity regulation
An adjustment module and symmetrical technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems that the stiffness adjustment mechanism cannot be modularized, and the VSJ stiffness adjustment range is limited, so as to achieve the effect of improving reliability and stability, fewer parts, and simple and compact structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
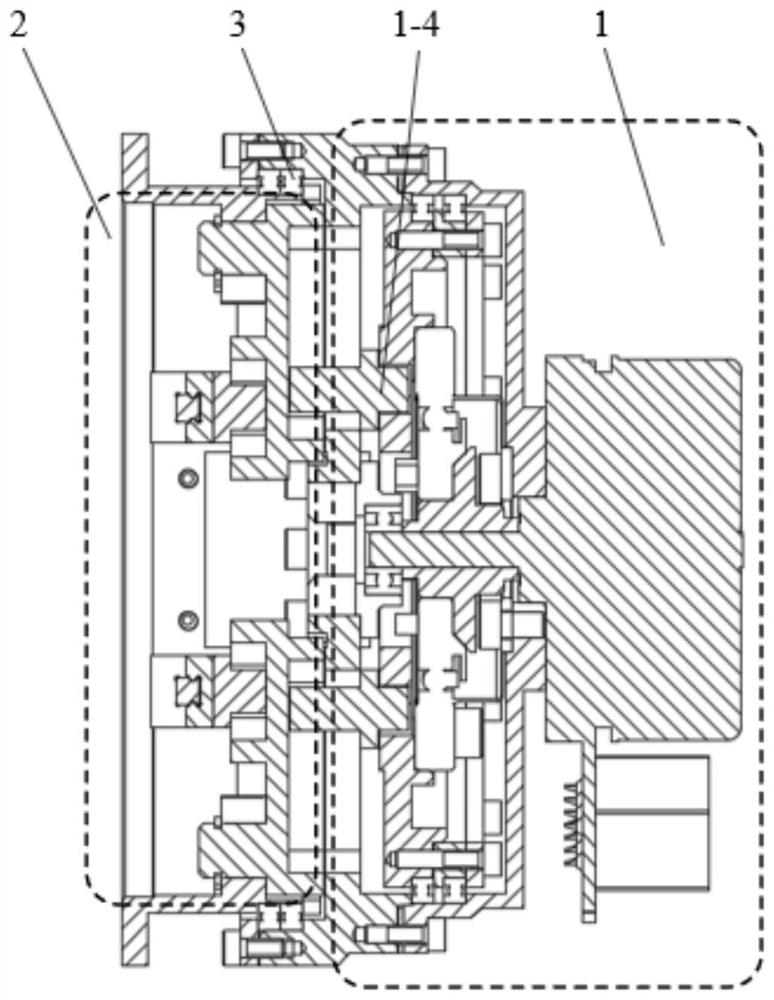
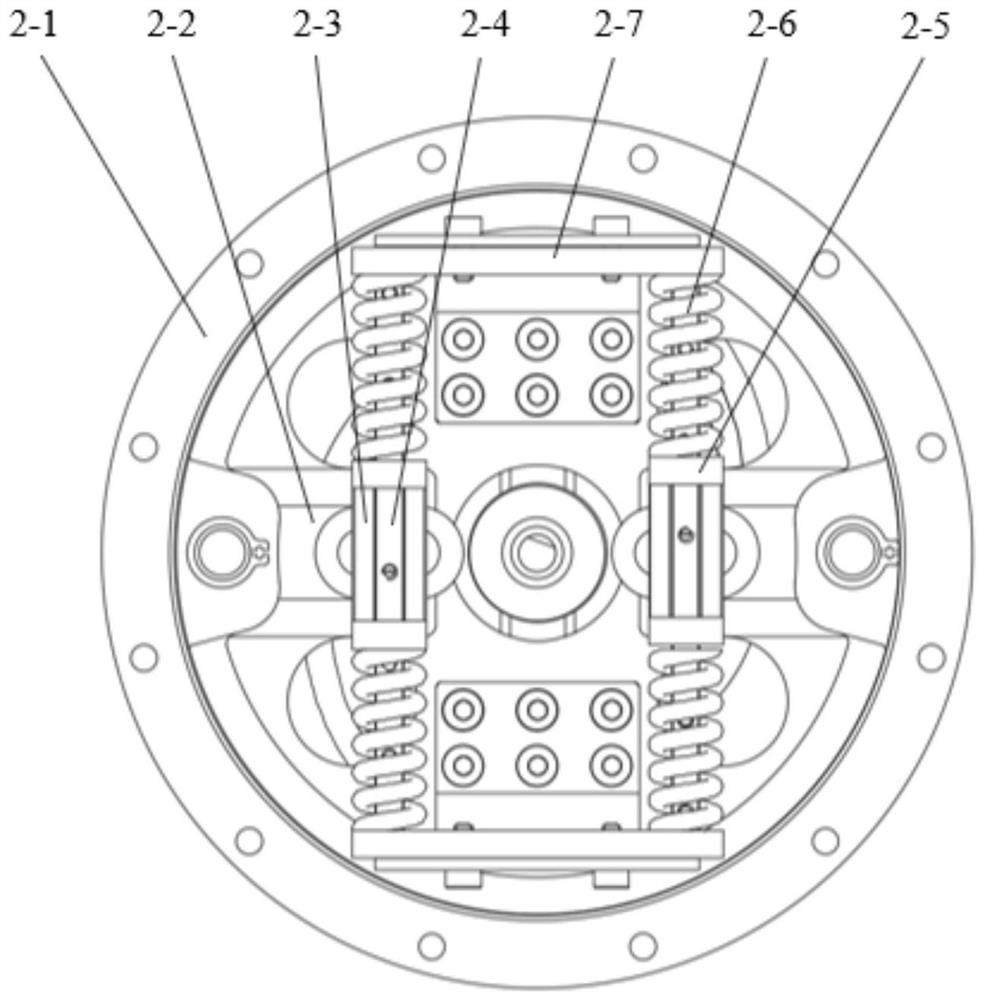
[0022] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1 to Figure 8 Describe this embodiment. A symmetrical variable fulcrum stiffness adjustment module described in this embodiment that can realize full-range stiffness adjustment includes a fulcrum adjustment mechanism 1, an elastic transmission mechanism 2, and a pair of first bearings 3. The fulcrum adjustment mechanism 1 and the elastic The transmission mechanisms 2 are rotationally connected by a pair of first bearings 3 .
[0023] In this embodiment, the outer ring of the first bearing 3 is fixed by screws through the spigot and retaining ring processed by the module input 1-1, and the inner ring of the first bearing 3 is fixed by the notch and retaining ring processed by the module output 2-1. Fixed, the fulcrum adjustment mechanism 1 and the elastic transmission mechanism 2 can relatively rotate through the first bearing 3 .
specific Embodiment approach 2
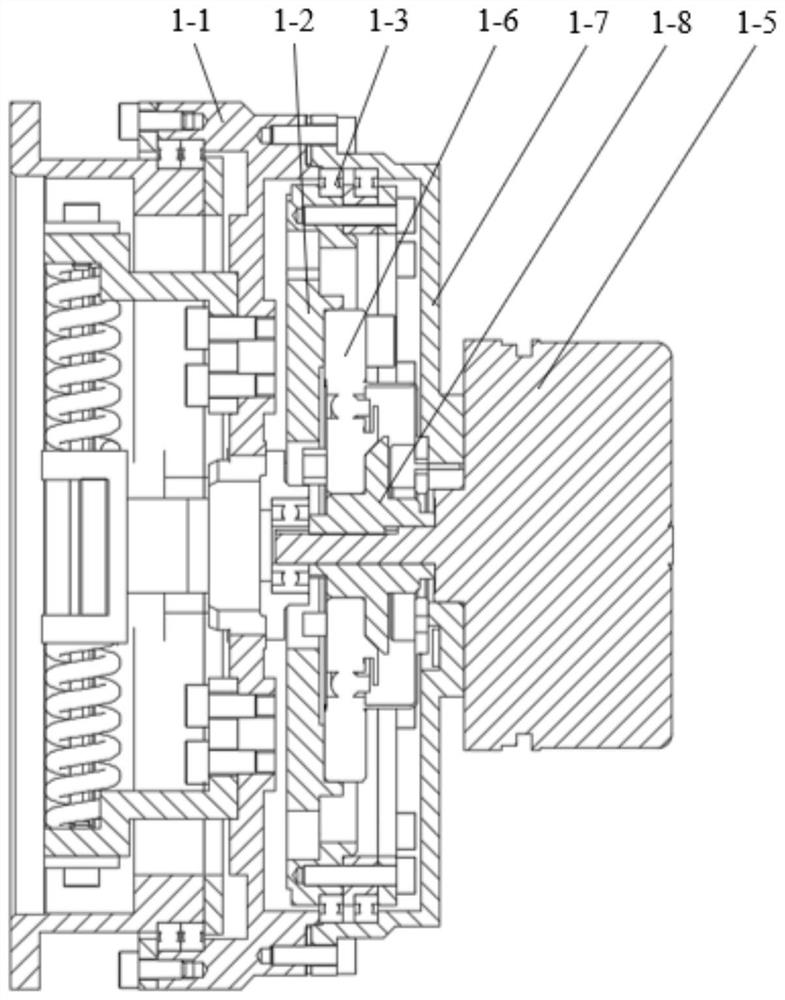
[0024] Specific implementation mode two: combination Figure 1 to Figure 8 Describe this embodiment, the fulcrum adjustment mechanism 1 described in this embodiment includes a module input terminal 1-1, an Archimedes spiral coil 1-2, a stiffness adjustment motor 1-5, a harmonic reducer 1-6, a motor base Seats 1-7 and two fulcrums 1-4,
[0025] The module input terminal 1-1 is fixedly connected to the end of the motor base 1-7, and the Archimedes spiral coil 1-2 is arranged on the inner side of the motor base 1-7 and rotates between the motor base 1-7 connection, the inner end surface of the module input end 1-1 is symmetrically provided with two linear through grooves 1-1-1 along the axial direction, and the outer end surface of the Archimedes spiral coil 1-2 is symmetrically arranged along the axial direction. a curved groove 1-2-1, two fulcrums 1-4 are set between the module input end 1-1 and the Archimedes spiral coil 1-2, and one end of each fulcrum 1-4 is respectively in...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0028] Specific implementation mode three: combination Figure 1 to Figure 8 To illustrate this embodiment, the motor shaft of the stiffness adjustment motor 1-5 in this embodiment is connected to the wave generator of the harmonic reducer 1-6 through the motor shaft connector 1-8. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in the second embodiment.
[0029] In this embodiment, the D-type motor shaft of the stiffness adjustment motor 1-5 is inserted into the D-type hole processed by the motor shaft connector 1-8; the axial position of the motor shaft connector 1-8 is determined by the support stiffness adjustment motor 1-5 The deep groove ball bearing of the motor shaft is fixed through the retaining ring and the rigidity adjustment motor 1-5; the motor shaft connector 1-8 is connected with the wave generator of the harmonic reducer 1-6 by screws.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com