Active power distribution network fault determination method and system
A distribution network fault and determination method technology, which is applied to the fault location, fault detection according to the conductor type, and electrical measurement, can solve the problems of increasing calculation workload and reducing fault detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
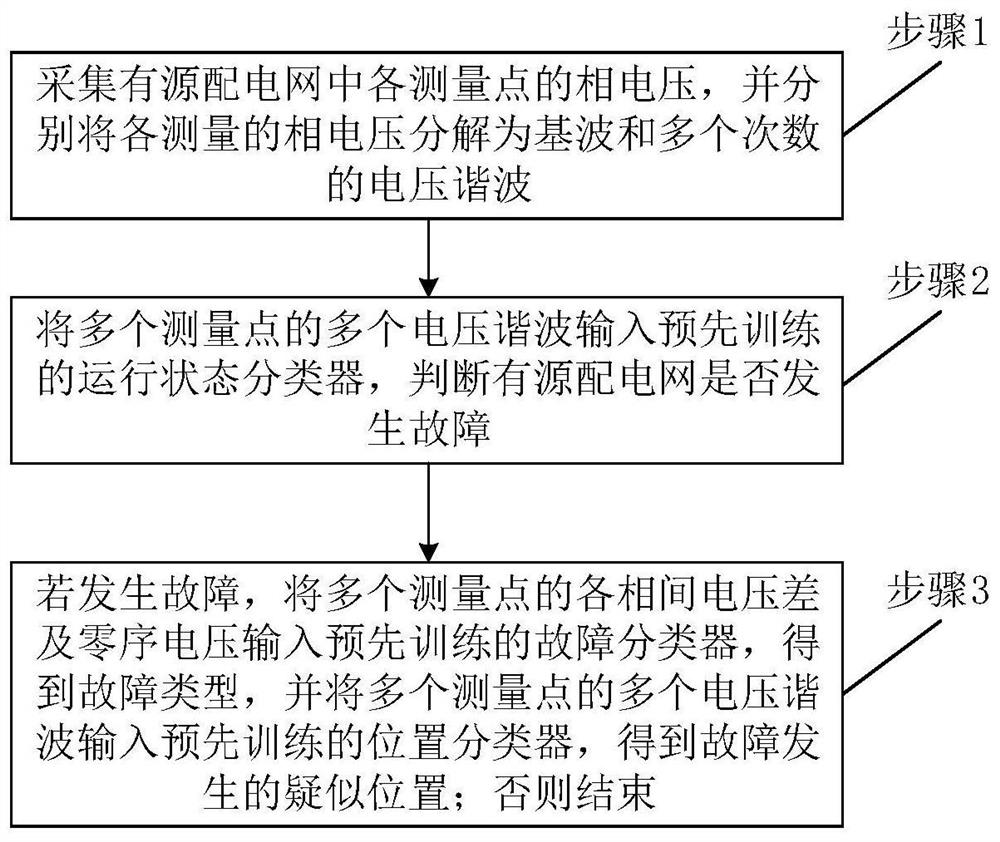
[0101] A schematic flowchart of a method for determining faults in an active distribution network provided by the present invention is as follows: figure 1 shown, including:
[0102]Step 1: Collect the phase voltages of each measurement point in the active distribution network, and decompose the measured phase voltages into fundamental waves and voltage harmonics of multiple orders respectively;
[0103] Step 2: Input multiple voltage harmonics of multiple measurement points into the pre-trained operating state classifier to determine whether the active distribution network is faulty;
[0104] Step 3 If a fault occurs, input the phase-to-phase voltage difference and zero-sequence voltage of multiple measurement points into the pre-trained fault classifier to obtain the fault type, and input multiple voltage harmonics of multiple measurement points into the pre-trained location classification. to get the suspected location of the fault; otherwise, end.
[0105] The object of ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Specific examples of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. The present invention includes the following key steps:
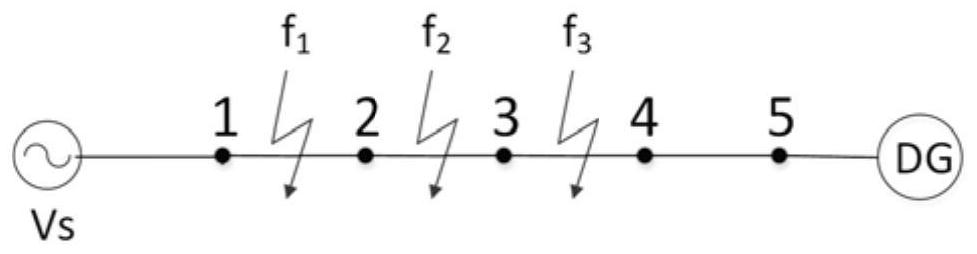
[0113] Step 11: Carry out PSCAD modeling for the active distribution network to be studied, and collect the original data. The collected data includes the phase voltages at each measurement point. The established PSCAD model such as Figure 9 As shown, the IEEE 33-node active distribution network PSCAD model has 32 nodes and two distributed power sources, with a total of 34 measurement points.
[0114] Step 12: Data processing for judging the running state.
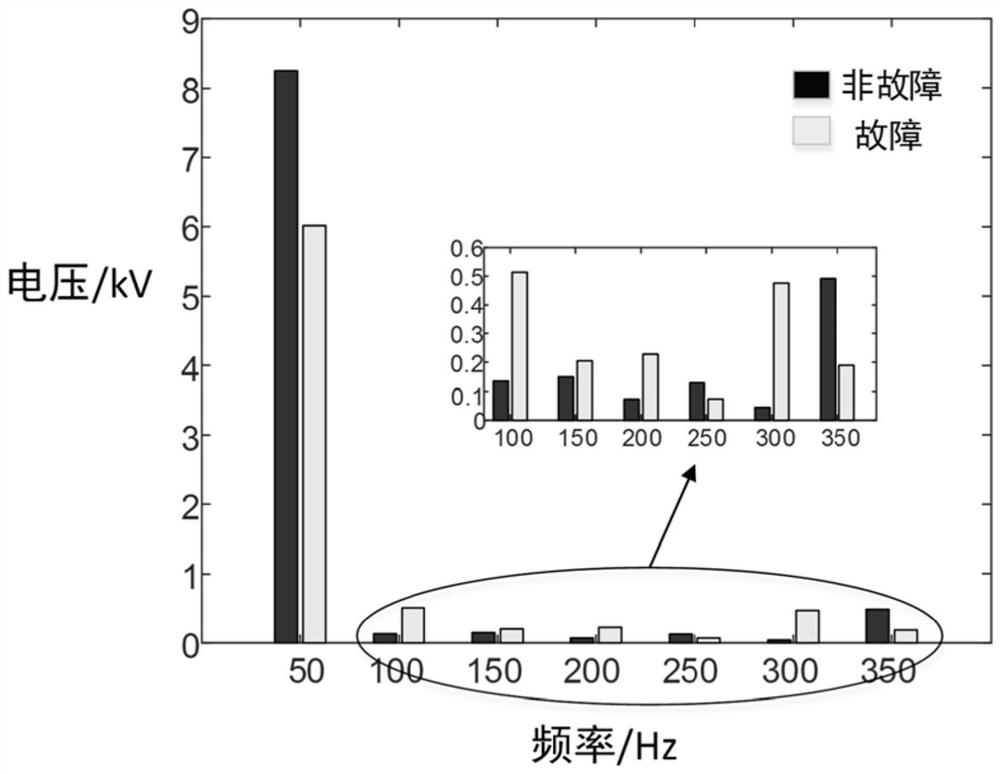
[0115] Extract the phase voltages of each measurement point in one cycle after multiple groups of faults and under normal operating conditions, and obtain the fundamental wave and 2-7th harmonics of the phase voltage of each measurement point through Fourier analysis of the data in each state. components, forming the original feature ...
Embodiment 3
[0196] A specific calculation example is given below.
[0197] Based on PSCAD / EMTDC software, such as Figure 9 IEEE 33 node active distribution network model shown. Measurement points are set at the head end of each line and the DG access point. The measurement point serial number is set to be the same as the serial number of the end node of the line. The measurement point serial numbers at the DG1 and DG2 access points are 33 and 34 respectively, so there are 34 measurement points in total. Point, measure the three-phase voltage, and the two DGs are grid-connected inverter-type direct-drive wind turbines.
[0198] Step 21: Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
[0199] Five fault types, namely AB, AC, AB-G, AC-G, ABC, are simulated at 50% of the 32-segment lines of the PSCAD model of the active distribution network, and the three-phase voltage of each measurement point in one cycle after the fault is extracted. , through Fourier analysis, the A-phase fundamental frequency an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com