Halophilic archaea for degrading nitrite and application of halophilic archaea
A technology of halophilic archaea and nitrite, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as not being screened
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Screening of Halophilic Archaea
[0020] Take the farmhouse's homemade salted mustard lumps sold in the farmers' market in Anda City, Heilongjiang as the sample, weigh 10g of the sample, add 90mL of normal saline after crushing, fully shake for 1h and then let stand for 2h, take the supernatant for 10-fold gradient dilution to 10 -1 ~10 -7 , 100 μL of each was applied to NHM solid medium, and after culturing in a 37°C incubator for 7 days, single colonies with pink, round, neat edges were selected and streaked three times on NHM solid medium to obtain pure colonies. The strain JB33.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: Preliminary identification of denitrification function of halophilic archaea
[0022] The screened strain JB33 was activated in NHM medium, inoculated into a screw-cap tube (Durham tube) of liquid denitrification medium with 1% inoculum, and cultured at 37°C to observe whether the screw-cap tube produced gas. , to test whether the strain can metabolize nitrite to produce gas. It was observed that after culturing for 7 days, there were bubbles in the screw cap tube, indicating that the strain JB33 could metabolize nitrite to generate gas.
Embodiment 3
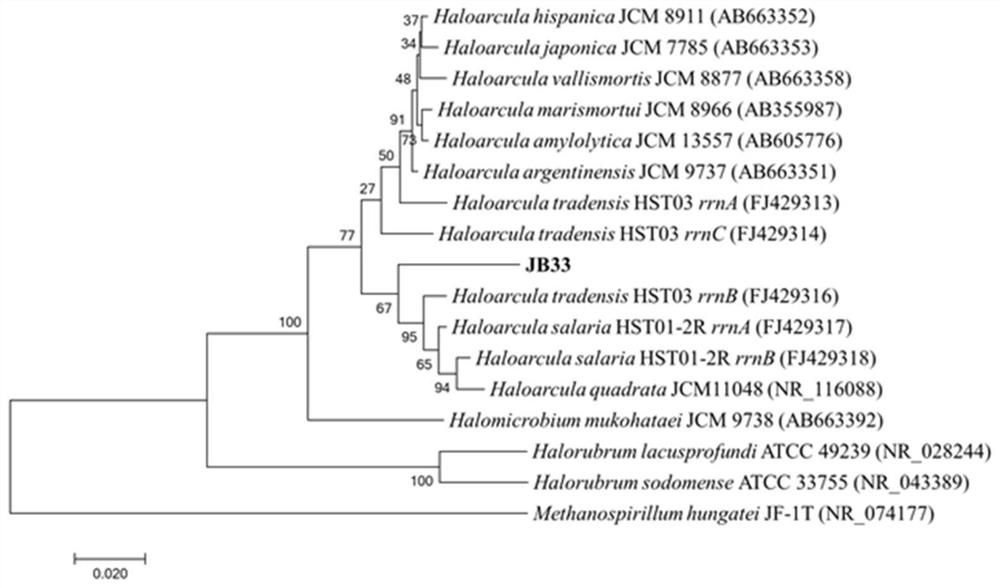
[0023] Example 3: Morphology and molecular biology identification of halophilic archaea
[0024] The strain JB33 was inoculated into solid NHM medium and cultured at 37°C for 7 days. After a single colony was grown, the morphological characteristics and color of the colony were observed, and then a single colony was picked for Gram staining: smear, fixation, crystal violet After primary staining, iodine mordant staining, ethanol destaining, water washing, and safranine counterstaining, drying and microscopy were performed. Its biological characteristics are: Gram staining negative, the colonies on the NHM plate are pink, round, translucent, with neat edges.
[0025] According to conventional methods, genomic DNA was extracted from the pure culture of strain JB33 for molecular biological identification: PCR amplification was carried out with the strain 16S rDNA sequence as the template. The upstream primer for PCR amplification is 20F, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com