High-precision offline control method of flexible wire-driven surgical instruments for minimally invasive surgical robots
A surgical instrument and minimally invasive surgery technology, applied in the field of medical robots, can solve the problems of limited control accuracy, rough operation, inconvenient use, etc., and achieve the effects of high accuracy, convenient use, and improved control accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
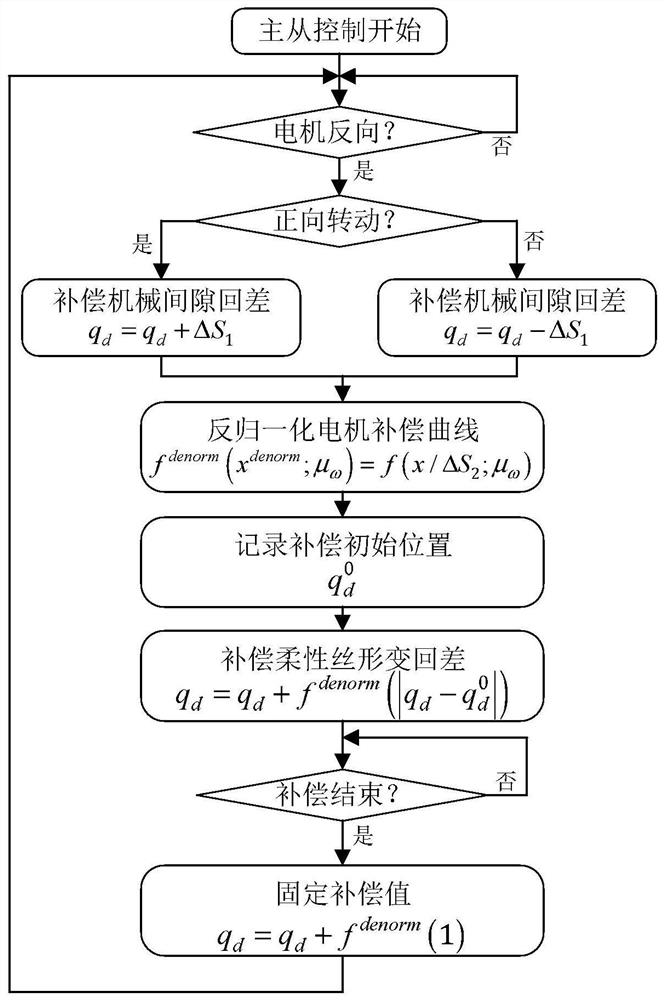
[0055] Embodiment 1: Combining figure 1 Illustrating this embodiment, a high-precision offline control method for a minimally invasive surgical robot flexible wire-driven surgical instrument described in this embodiment, the specific steps are as follows:
[0056] Step 1. The minimally invasive surgical robot system starts master-slave control, and cyclically determines whether the actuating motor moves in reverse in each control cycle;
[0057] Step 2. After actuating the motor to move in the reverse direction, determine the direction of the motor after the reverse movement. If it rotates in the forward direction, set the target position of the motor q d
[0058] q d =q d +ΔS 1 (1)
[0059] Use the motor target position q d to compensate for the mechanical backlash;
[0060] If it rotates in the opposite direction, let the motor target position q d
[0061] q d =q d -ΔS 1 (2)
[0062] Use the motor target position q d To compensate for the mechanical backlash,...
specific Embodiment approach 2
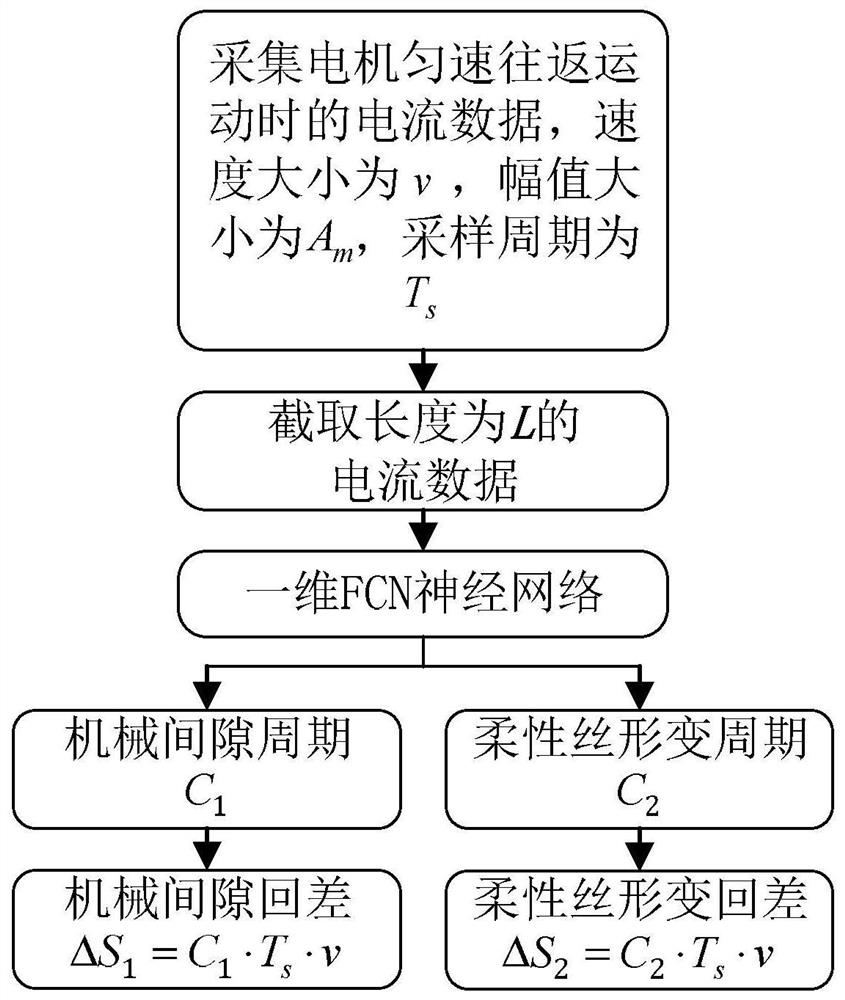
[0073] Specific implementation mode 2: Combining figure 2 This embodiment will be described. This embodiment is a further limitation of the control method described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, a high-precision offline control method for a flexible wire-driven surgical instrument for a minimally invasive surgical robot is described. Mechanical clearance difference ΔS of the surgical instrument in step 2 1 is calculated as follows:
[0074] Step 21. Before the master control starts, make the actuating motor move back and forth at a constant speed v, and the amplitude is A m , the sampling period is T s , collect the current data when the actuator motor moves back and forth at a constant speed;
[0075] Step 22: Intercept the current data of length L from the current data, and use it as the input of the one-dimensional FCN neural network;
[0076] Step 2 and 3, the one-dimensional FCN neural network uses the current data of length L to calculate the mechanical gap p...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0081] Specific implementation three: combination figure 2 This embodiment will be described. This embodiment is a further limitation of the control method described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, a high-precision offline control method for a flexible wire-driven surgical instrument for a minimally invasive surgical robot is described. The flexible wire deformation return difference ΔS of the surgical instrument in step 3 2 The calculation scheme is as follows: before the main control starts, the actuating motor is made to move back and forth at a constant speed v, and the amplitude is A m , the sampling period is T s , collect the current data when the actuator motor moves back and forth at a constant speed; intercept the current data of length L from the current data and use it as the input of the one-dimensional FCN neural network; the one-dimensional FCN neural network uses the current data of length L to calculate the flexible wire Deformation period size C 2 ; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com