Semantic segmentation with soft cross-entropy loss
A cross-entropy and semantic technology, applied in the field of machine learning and computer vision, can solve the problem that the mobile training environment is not very useful
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
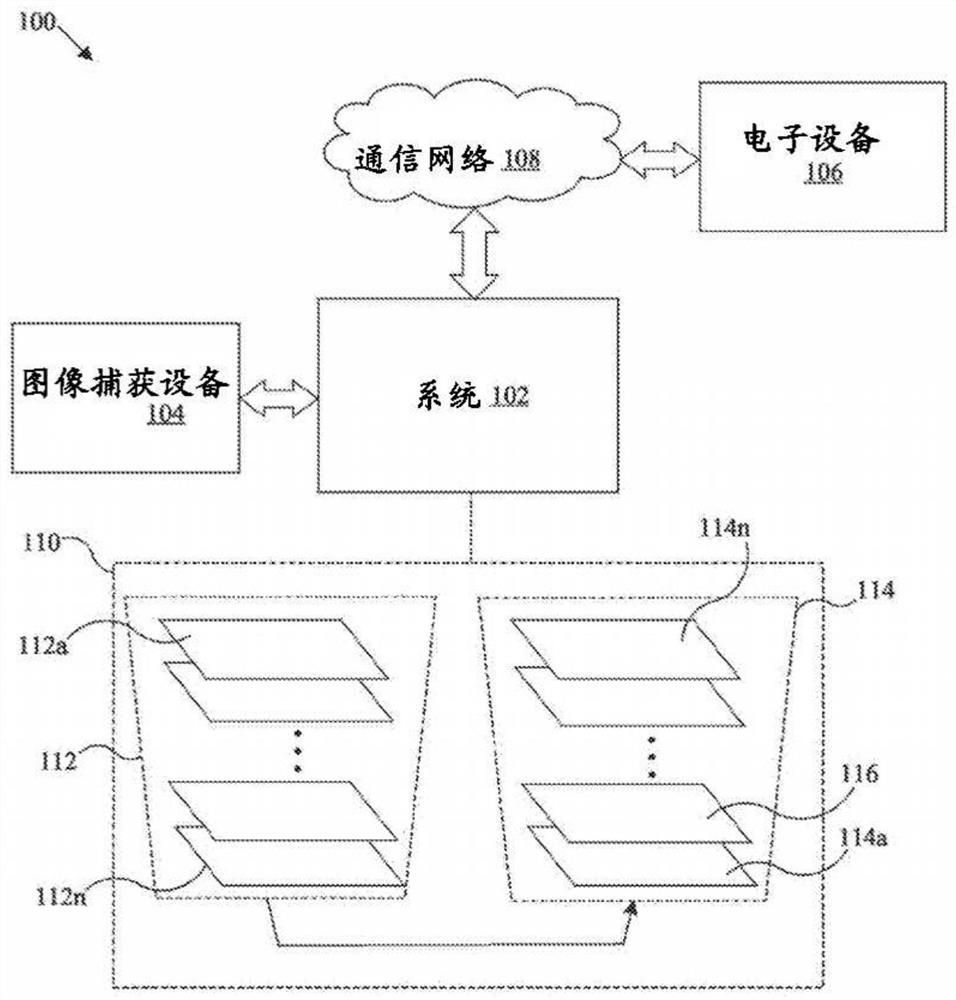
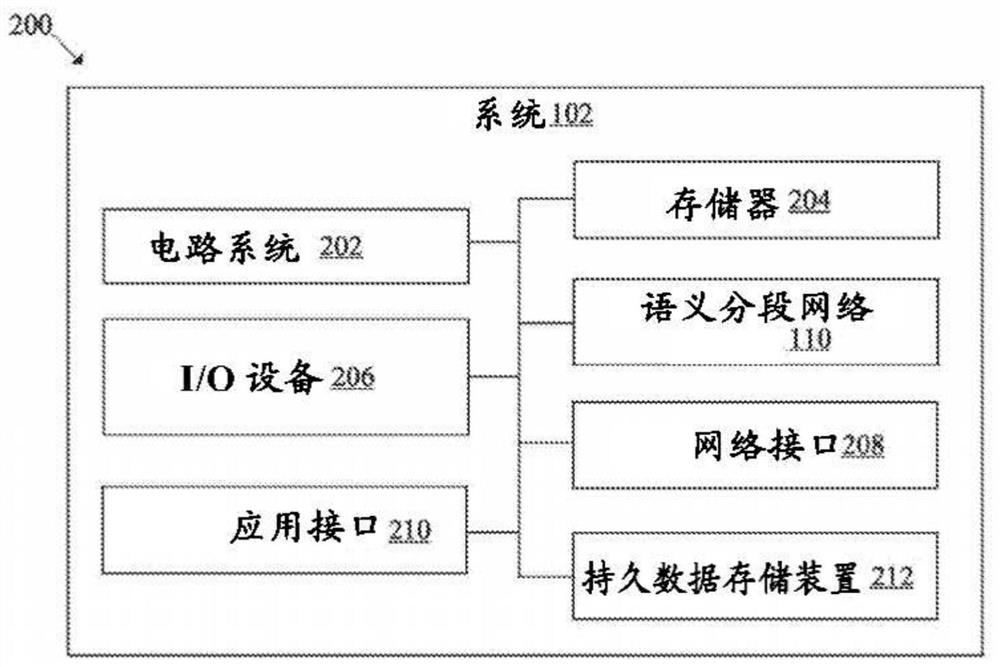
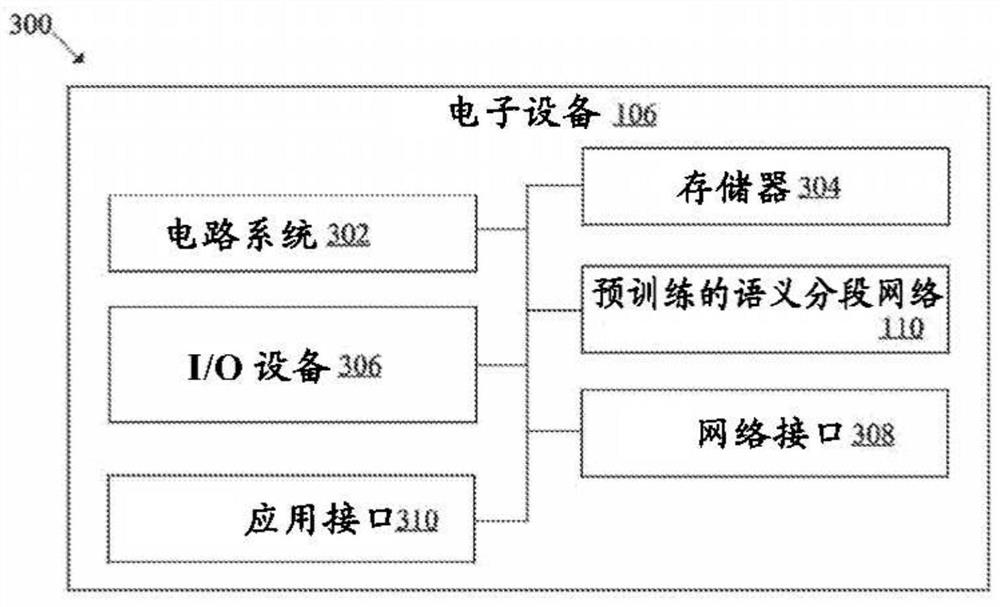
[0017] Embodiments described below can be found in the disclosed systems and methods for semantic segmentation with soft cross-entropy loss. Exemplary aspects of the present disclosure provide a system that trains a semantic segmentation network suitable for real-time inference while maintaining a balance between classification accuracy and compactness of the semantic segmentation network. The disclosed system utilizes a soft cross-entropy (CE) loss as an auxiliary loss to regularize the training of semantic segmentation networks and reduce memory usage during training time. In contrast to conventional hard-label assignment for classification tasks, the disclosed system generates soft-assigned labels as a probability distribution at each auxiliary stride, and applies cross-entropy as an auxiliary loss function on soft targets. Here, soft assignments may differ from typical hard assignments, where each value of a feature map is assigned one of binary values (0 or 1). In soft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com