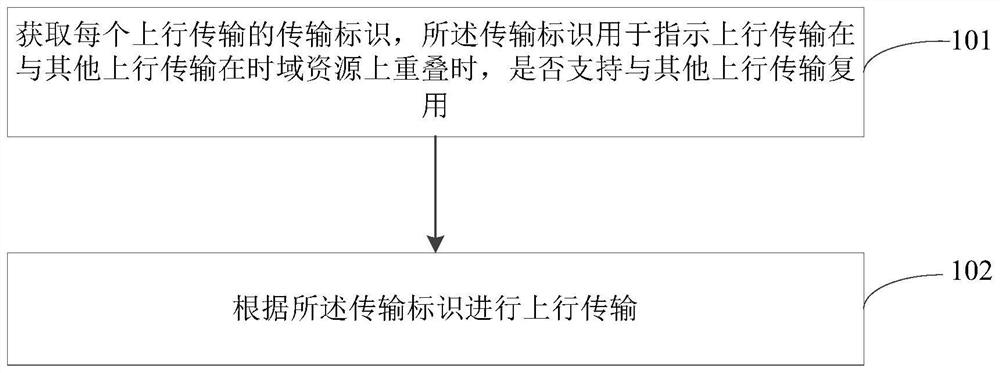
Uplink transmission processing method, device, and terminal
A processing method and a technology of a processing device, applied in the communication field, can solve problems such as discarding of low-priority channels and affecting transmission performance of low-priority channels, so as to improve effectiveness and ensure transmission performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
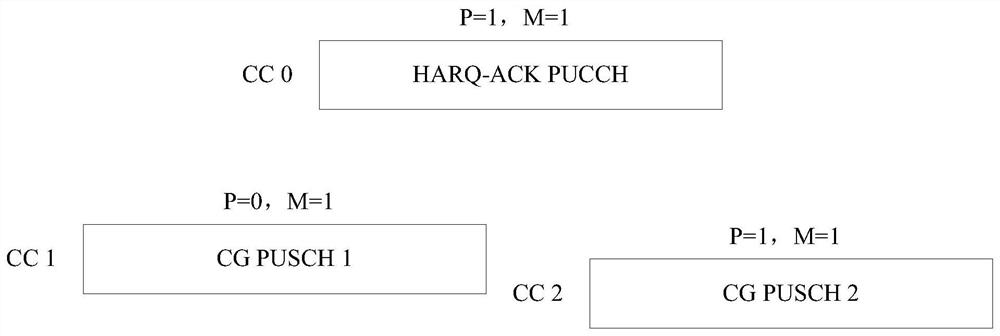
[0083] Such as image 3 As shown in the figure, P represents priority indication, P=0 represents low priority, P=1 represents high priority; M represents transmission indication multiplexing indicator, M=0 represents no multiplexing support, and M=1 represents multiplexing support. According to the priority indication, the HARQ-ACK PUCCH (that is, the PUCCH carrying HARQ-ACK) is a high-priority channel, and CG PUSCH1 and CGPUSCH2 are different configuration authorization PUSCHs, and their priorities are low priority and high priority respectively. At the same time, all three channels are configured or indicated with corresponding M / P identifiers, where M=1 (or 'Multiplexing') means that multiplexing with other channels is allowed, and M=0 (or 'Prioritization') means Does not support multiplexing with other channels, but supports priority transmission (priortizaition), by image 3 It can be seen that all three channels support multiplexing. The resources of the HARQ-ACK PUCCH...
Embodiment approach 1
[0084]Embodiment 1: UE processes the multiplexing between channels with the same priority first, that is, first processes the multiplexing between HARQ-ACK PUCCH and CG PUSCH2 with the same priority, and the UE multiplexes HARQ-ACK on CG PUSCH2 for transmission. Since the time domain resources of CG PUSCH1 and CG PUSCH 2 do not overlap, the UE transmits CG PUSCH 1 and CG PUSCH2 respectively.
Embodiment approach 2
[0085] Embodiment 2: The UE assumes that all transmissions have the same priority or no priority. image 3 The figure shows HARQ-ACK PUCCH and multiple PUSCHs. According to related technologies, when PUCCH and multiple PUSCH time domain resources overlap, UE selects the way of multiplexing PUSCH. Assuming that the subcarrier space (subcarrier space, SCS) of different serving cells CC0, CC1 and CC2 is the same, then PUSCH 1 and PUSCH 2 are in the same slot, and the UE selects the corresponding CG with a smaller serving cell index for multiplexing on PUSCH 1 according to the serving cell index HARQ-ACK transmission. Since the time domain resources of CG PUSCH 1 and CG PUSCH 2 do not overlap, the UE transmits CG PUSCH 1 and CG PUSCH 2 respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com