Method for detecting risk of torsades de pointes
A state-of-the-art technology for ventricular tachycardia, used in medical automation diagnosis, medical informatics, health index calculation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
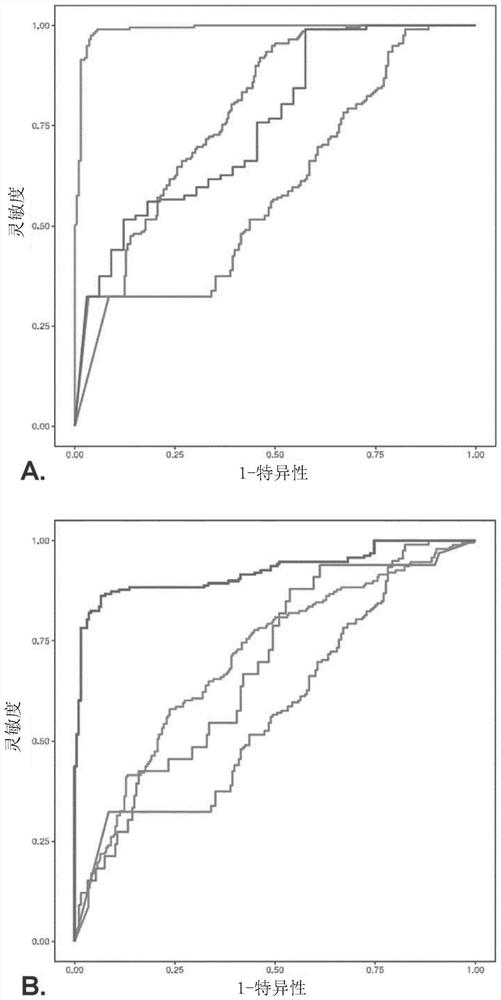
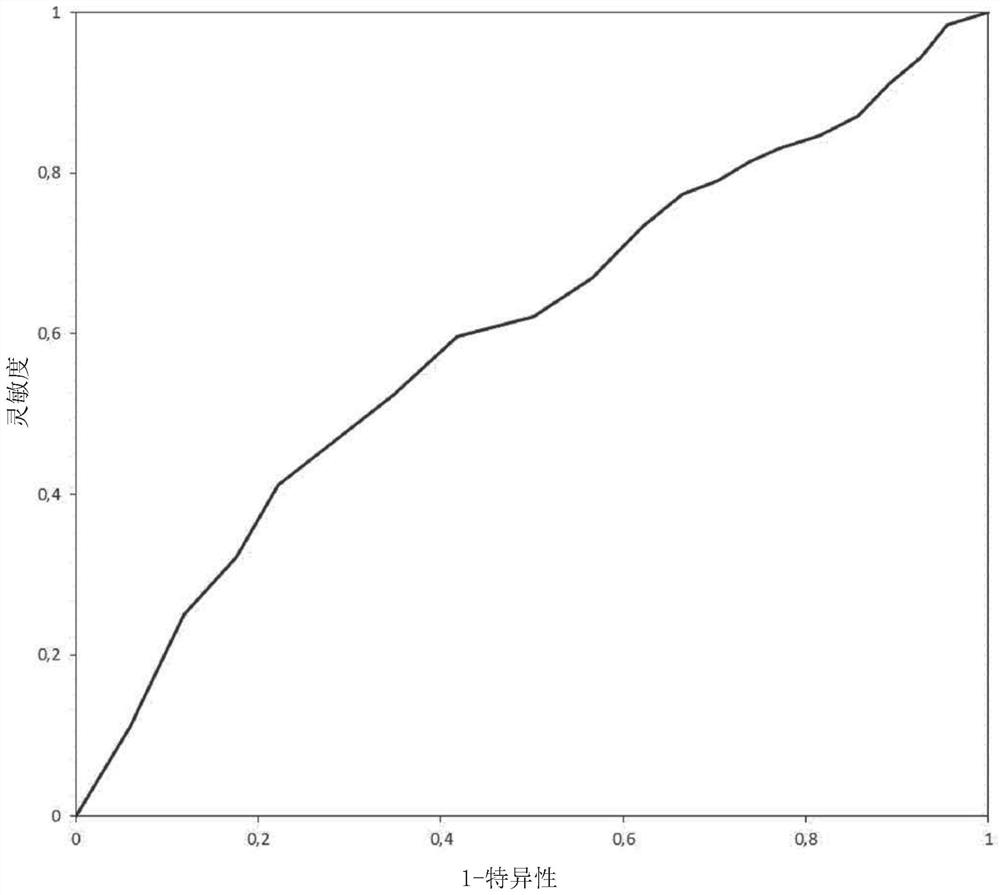
[0169] experimental design
[0170] The training database included 9014 ECG signals from 792 healthy patients before (n=4014; Sot-) and after (n=5000) sotalol intake (80 mg orally, Sot+). ECGs were taken at different time points (1, 2, 3 and 5 hours after sotalol ingestion).
[0171] A subset of the dataset was split to test the trained model consisting of 198 healthy patients with ECGs before (n=999) and after (n=1238) sotalol ingestion.
[0172] In addition, a third dataset consisting of long congenital QT patients was used to test the trained model, specifically LQT-1 (n=266 patients and n=560 ECGs), LQT-2 ( n=188 patients and n=456 ECGs) and LQT-3 (n=33 patients and n=67 ECGs) constituted.
[0173] group description
[0174] Two cohorts of patients were utilized.
[0175] The first cohort contained ECGs from 990 healthy subjects before and after consumption of 80 mg of sotalol at different time periods (i.e., 2, 3, 4 and 5 days after sotalol ingestion). Hour). Each...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com