Map matching algorithm based on deep learning
A map matching and deep learning technology, applied in the field of map matching to improve performance, enhance semantic expression ability, and improve effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
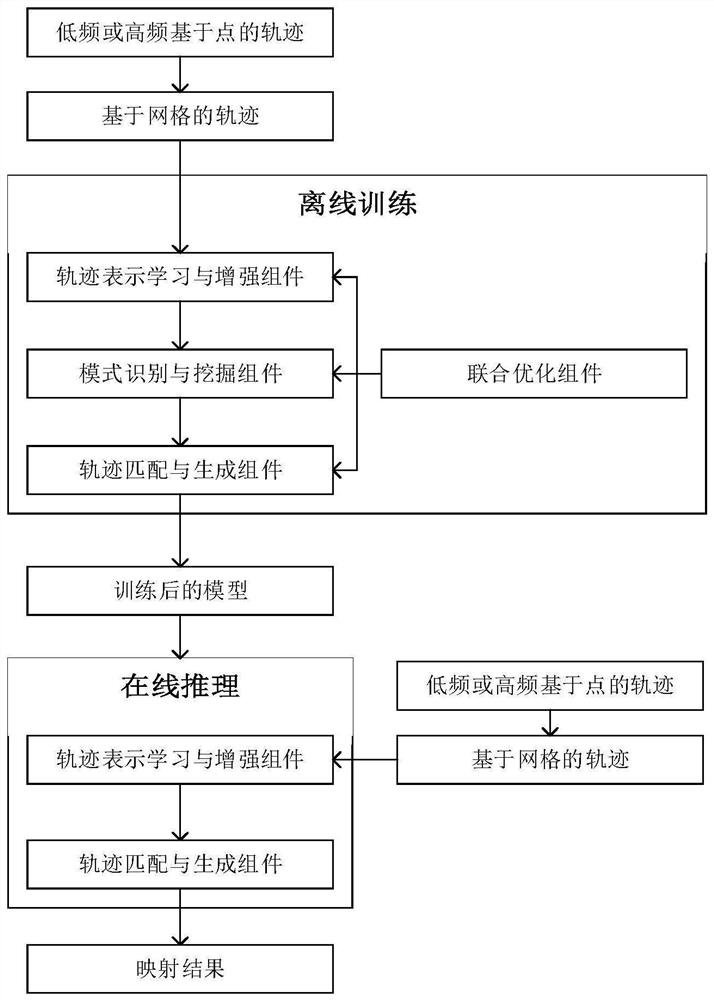
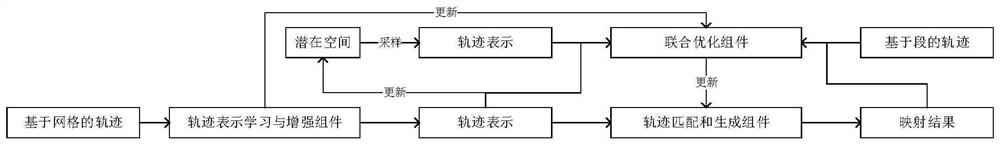
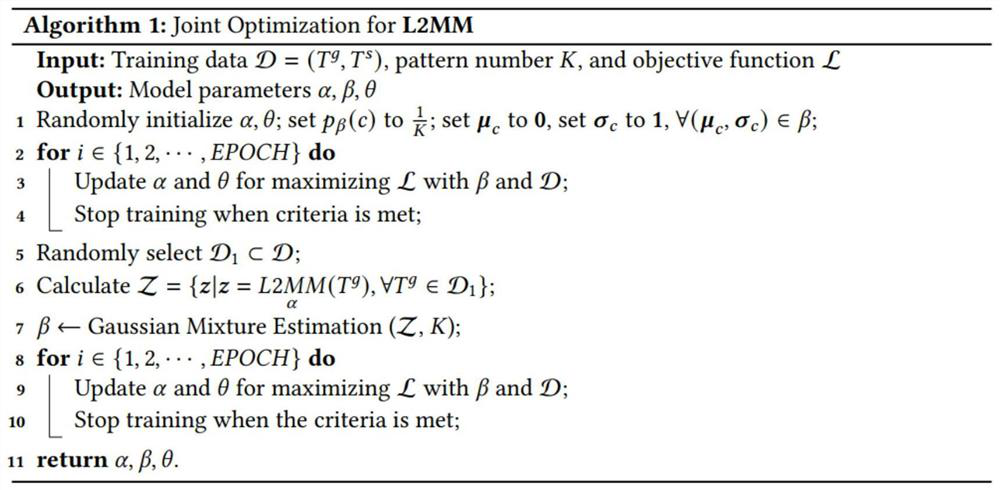
[0025] Embodiment one is basically as attached figure 1 As shown, a map matching algorithm based on deep learning (L2MM for short) is mainly composed of four components, namely, trajectory representation learning and enhancement component, pattern recognition and mining component, trajectory matching and generation component, and joint optimization component; L2MM includes Two working steps, offline training step and online inference step; in the offline training step, these four components work together to train a deep model for map matching; in the online inference step, the trained deep model is used , the trajectory representation learning and enhancement component, trajectory matching and generation component participate in the work and return the mapping result of a given trajectory based on test points.
[0026] In this embodiment, the offline training step includes the following steps:
[0027] A1. For a trajectory based on location points in the training data set, fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com