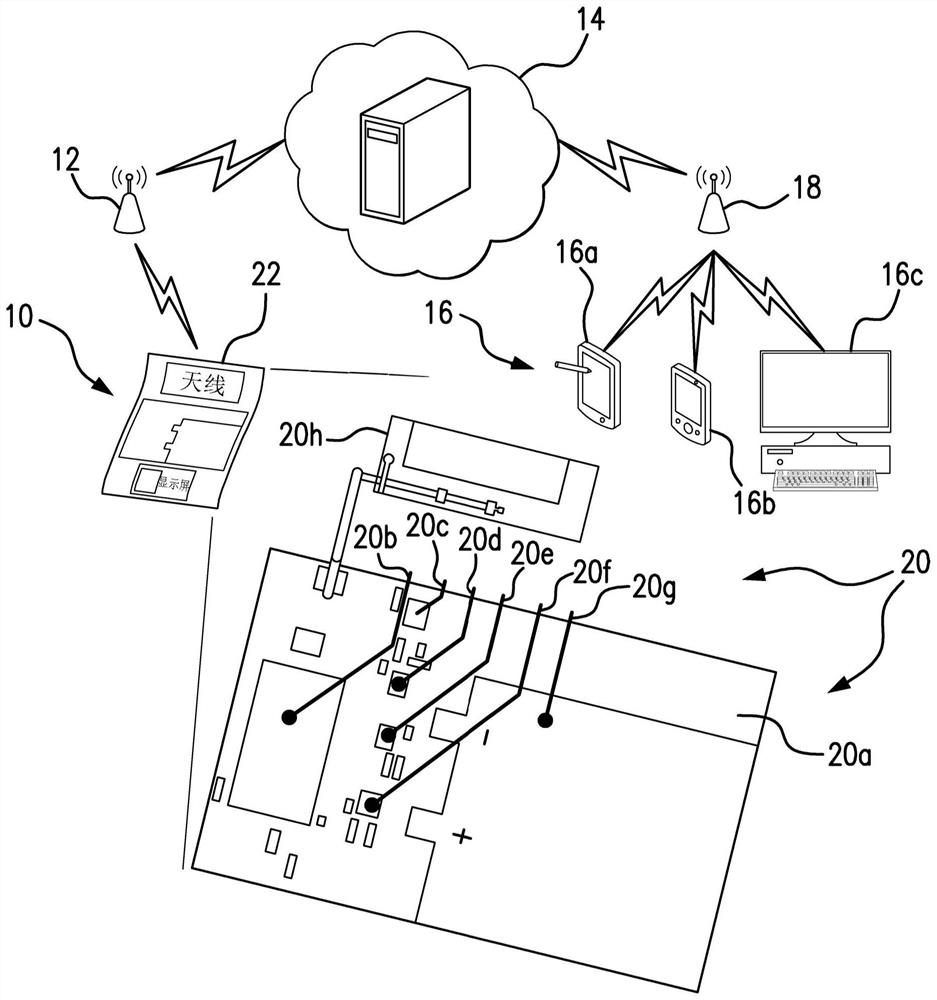
Internet of things tags for factory and warehouse applications
A label, standard technology, applied in the field of IoT labeling in factories and warehouses, which can solve problems such as restricting tracking of large and bulky items, package tampering, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
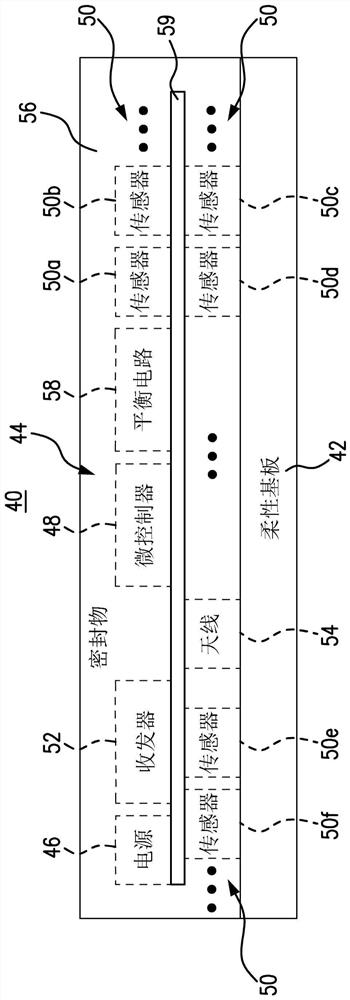
[0063] Example 1. A tag comprising: a flexible substrate; and a flexible circuit coupled to the flexible substrate, the flexible circuit comprising a power supply, a microcontroller, a plurality of sensors, one or more a transceiver and an antenna, wherein the microcontroller: identifies sensor readings in one or more signals from the plurality of sensors, and communicates via one or more standard wireless transmission protocols to the central computer and computer network One or more of the sensor readings are sent, wherein at least one of the sensor readings is sent in push communication.
example 2
[0064] Example 2. The tag of example 1, wherein the sensor readings indicate one or more of a temperature measurement crossing a temperature threshold, a humidity measurement crossing a humidity threshold, a vibration event, an impact event, and a tamper event.
example 3
[0065] Example 3. The tag of any one of examples 1-2, wherein the microcontroller generates the push communication in response to an event associated with the sensor reading.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com