Sulphatization derivative of polysaccharide, its preparation method and use
A technology of polysaccharide sulfate and sulfate esterification, applied in the field of polysaccharides, can solve problems such as adverse reactions, large molecular weight of dextran sulfate, and difficulty in reaching blood drug concentration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
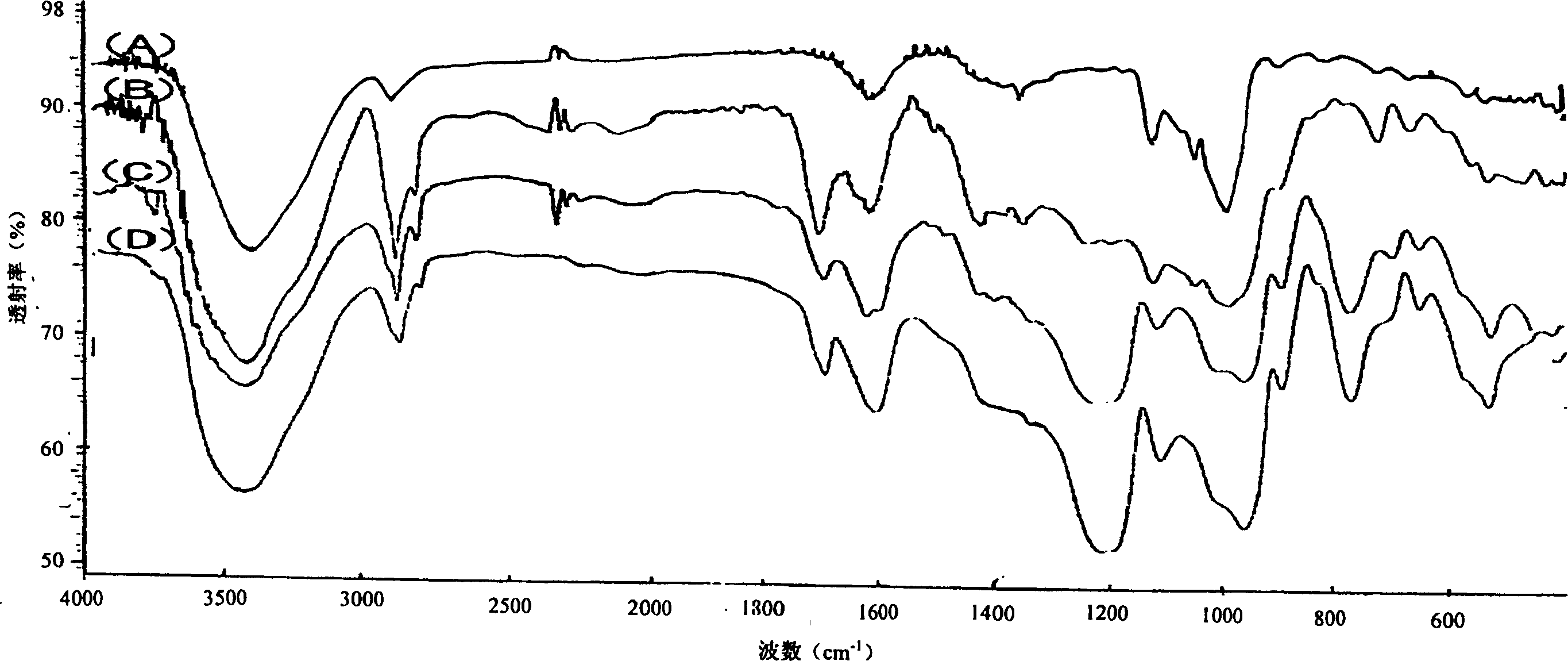
[0025] Embodiment 1. Preparation of polysaccharide YCP sulfated derivatives
[0026] Chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method was used. Place the round-bottomed flask with a condenser tube in an ice-salt bath, add 10 mL of anhydrous pyridine, and stir it magnetically to make it fully cooled. Slowly add 1.5 mL of chlorosulfonic acid with a dropper, and the dropwise addition is completed in about 15 minutes. Weigh 200 mg of refined polysaccharide YCP and suspend it in 10 mL of freshly steamed formamide, sonicate for 15 min, add to a round bottom flask, quickly transfer the flask to a 60°C oil bath, stir at constant temperature, the reaction is complete after 0.5 h, and cool to room temperature. The reaction mixture was poured into 100 mL of ice water, and the pH was adjusted to 7.5 with 2.5 mol / L NaOH solution. Add 5 times the volume of absolute ethanol and let stand at room temperature overnight. Centrifuge in a high-speed centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes, pour off the super...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2. Preparation of polysaccharide YCP sulfated derivatives
[0028] Chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method was used. Place the round-bottomed flask with a condenser tube in an ice-salt bath, add 12.5 mL of anhydrous pyridine, and magnetically stir to make it fully cooled. Slowly add 2.0 mL of chlorosulfonic acid with a dropper, and the dropwise addition is completed in about 20 minutes. Weigh 200 mg of refined polysaccharide YCP and suspend it in 20 mL of freshly steamed formamide, sonicate for 15 minutes, add to a round bottom flask, quickly transfer the flask to an 80°C oil bath, stir at constant temperature, and after 1 hour, the reaction is complete and cooled to room temperature. The reaction mixture was poured into 100 mL of ice water, and the pH was adjusted to 7.5 with 2.5 mol / L NaOH solution. Add 5 times the volume of absolute ethanol and let stand at room temperature overnight. Centrifuge in a high-speed centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes, pour of...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3. Preparation of polysaccharide YCP sulfated derivatives
[0030]Chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method was used. Place the round-bottomed flask with a condenser tube in an ice-salt bath, add 15 mL of anhydrous pyridine, and stir magnetically to make it fully cooled. Slowly add 3.0 mL of chlorosulfonic acid with a dropper, and the dropwise addition is completed in about 30 minutes. Weigh 200 mg of fine YCP and suspend it in 30 mL of freshly steamed formamide, sonicate for 15 min, add to a round bottom flask, quickly transfer the flask to a 100°C oil bath, stir at constant temperature, after 2 h the reaction is complete, and cool to room temperature. The reaction mixture was poured into 100 mL of ice water, and the pH was adjusted to 7.5 with 2.5 mol / L NaOH solution. Add 5 times the volume of absolute ethanol and let stand at room temperature overnight. Centrifuge in a high-speed centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes, pour off the supernatant, dissolve the preci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical rotation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com