Quantized matrix adjusting method for improving quality of video
A technology of quantization matrix and adjustment method, which is applied in image communication, image coding, image data processing, etc., can solve problems such as inability to generate enough bits, increase filling bits, and small quantization scale factor, so as to improve image quality and avoid Estimate the effect of quantization scale factor being too low, avoiding blockiness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
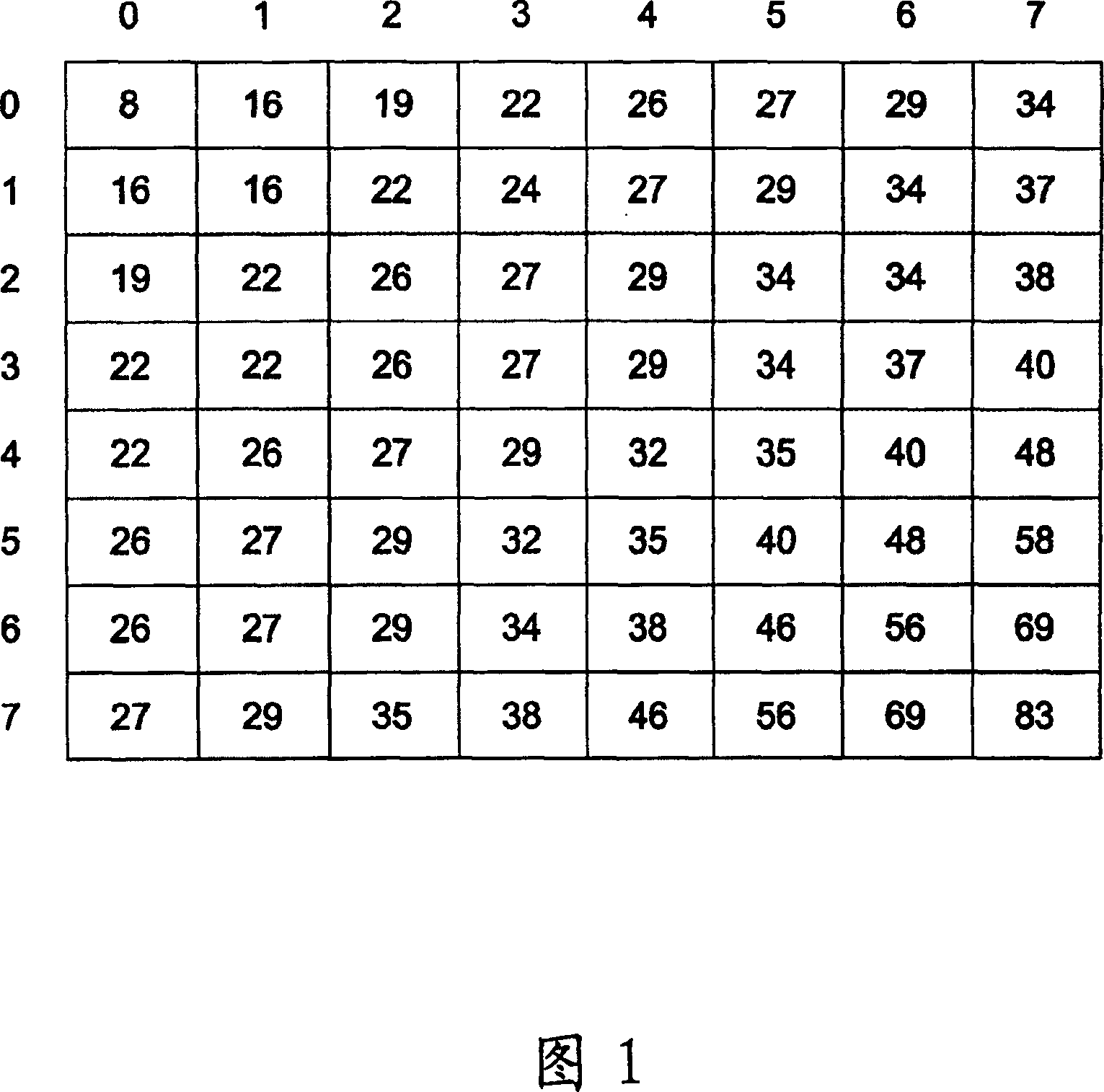
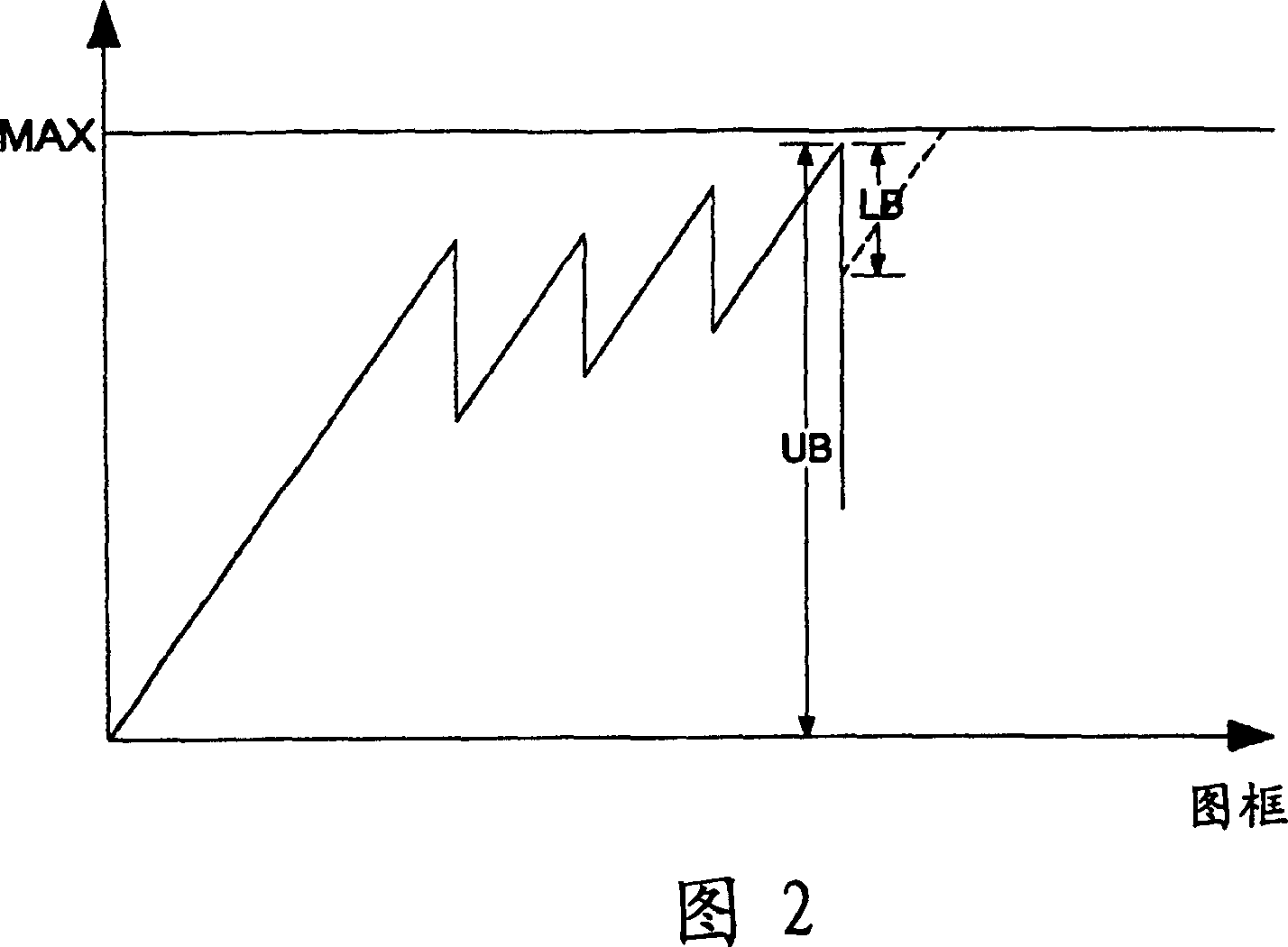
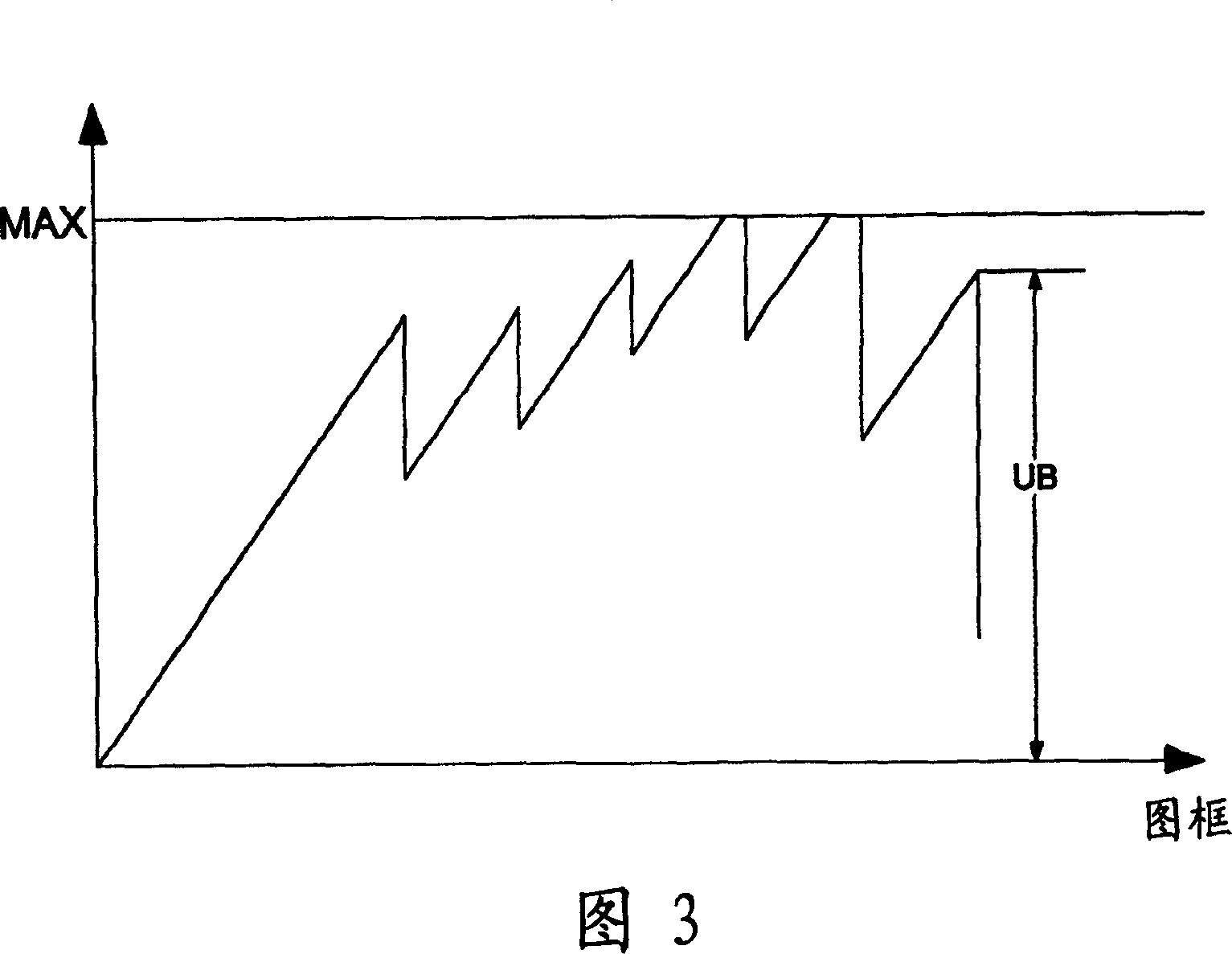
[0052] When the calculated estimated quantization scale factor EstQ_C of the current image becomes very small and the current image is coded with a preset quantization matrix, a slight visible block effect will occur in the flat image area. To solve this problem, the encoder of the present invention reduces the weighting of the quantization matrix to adjust the estimated quantization scale factor EstQ_C to a larger value. For example, as shown in formula (1), when the preset quantization matrix W[v][u] is reduced to 1 / 4, the average quantization scale factor Avg_Q can be enlarged from 1.5 to 6, and the quantization scale factor Q can be increased at this time 7 or 8 to reduce bit rate consumption, or lower to 5 or 4 to increase bit rate consumption. Therefore, the quantization error of adjacent macroblocks can be greatly reduced.
[0053] In the MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 specifications, a sequence header must be configured at the beginning of each coded bitstream, and the sequence he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com