Method of improving calling route selection in special network node interface network
A node and routing technology, applied in the field of data communication networks, can solve problems such as link congestion and return when busy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
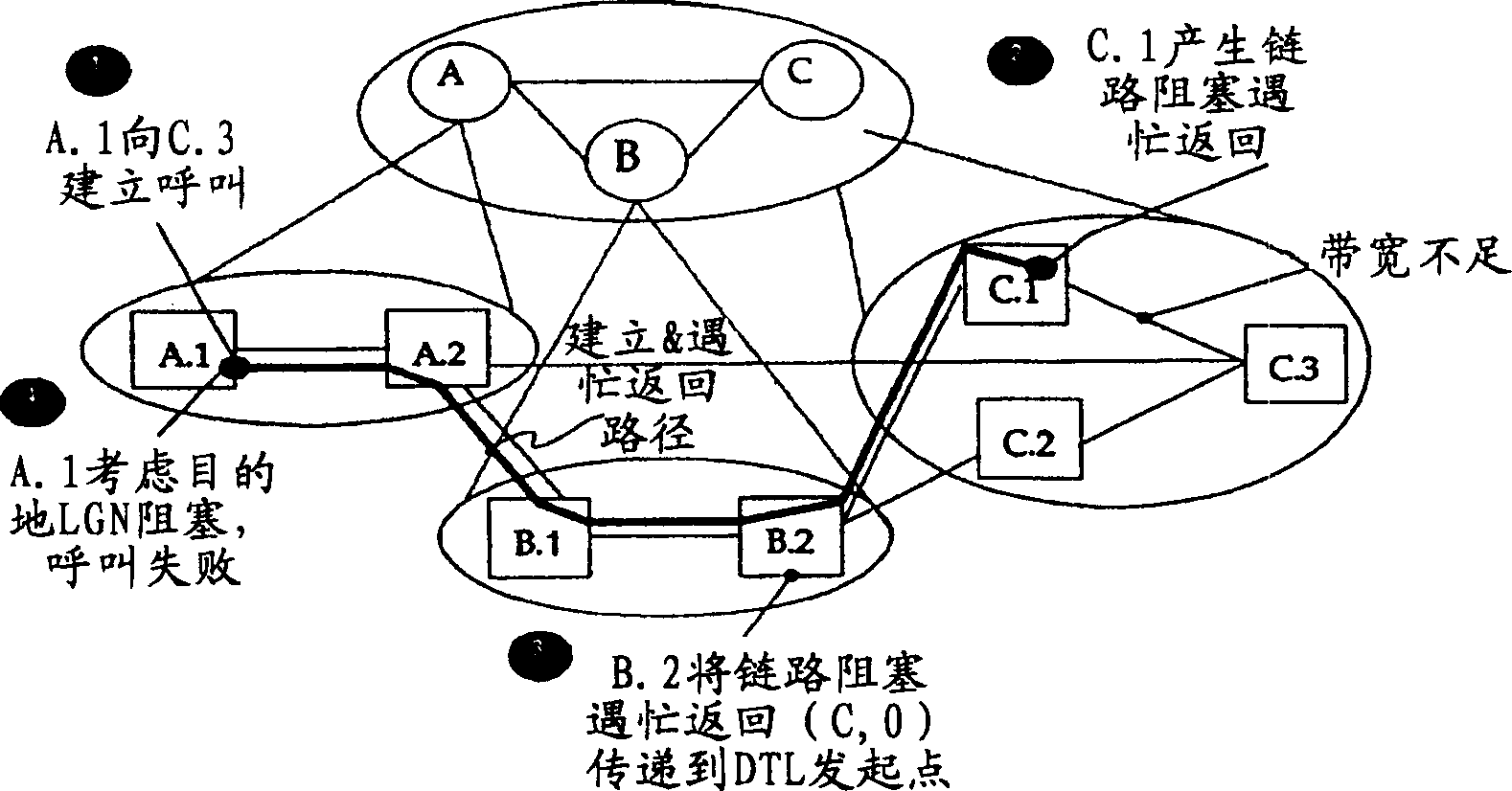
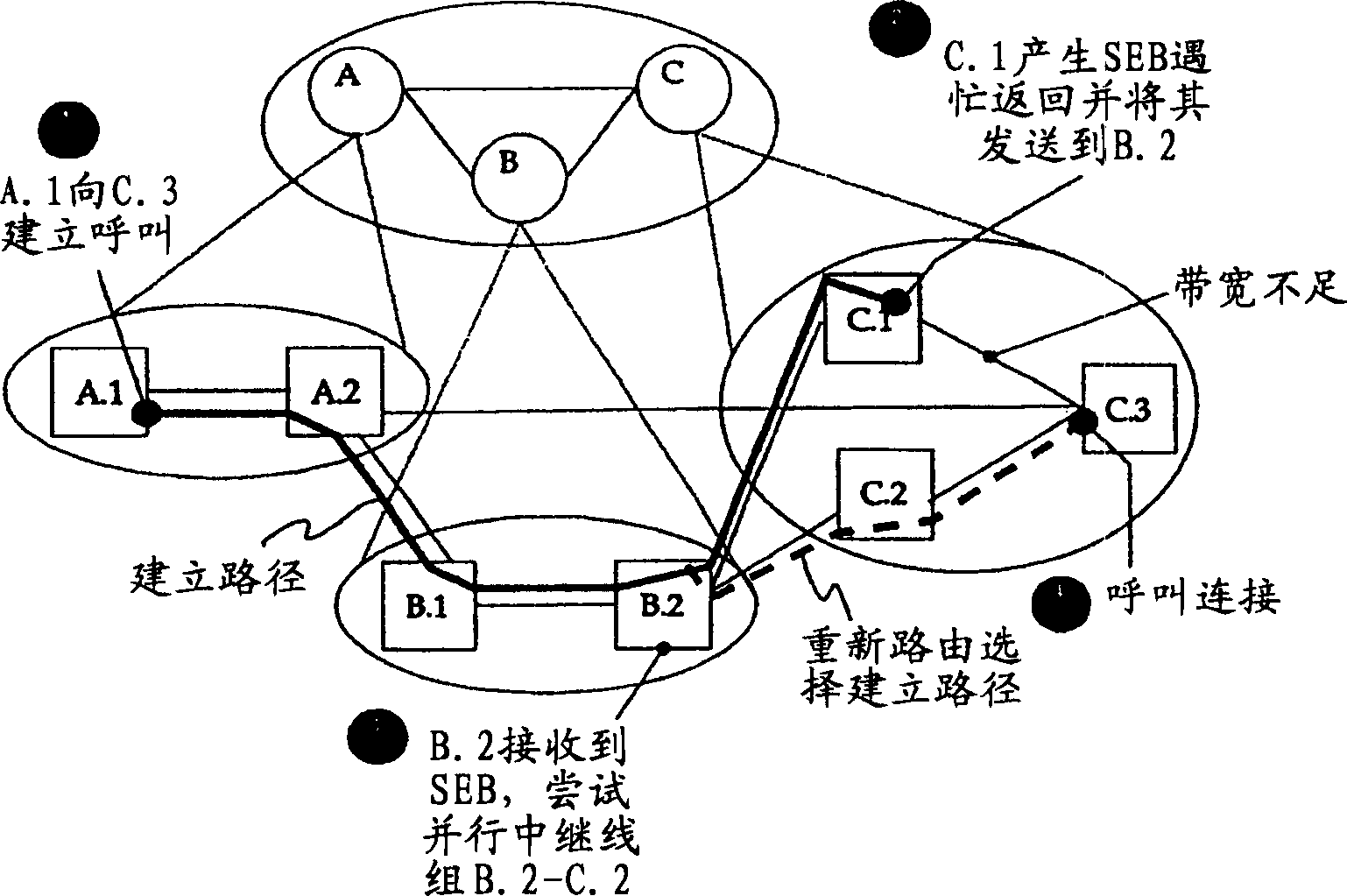
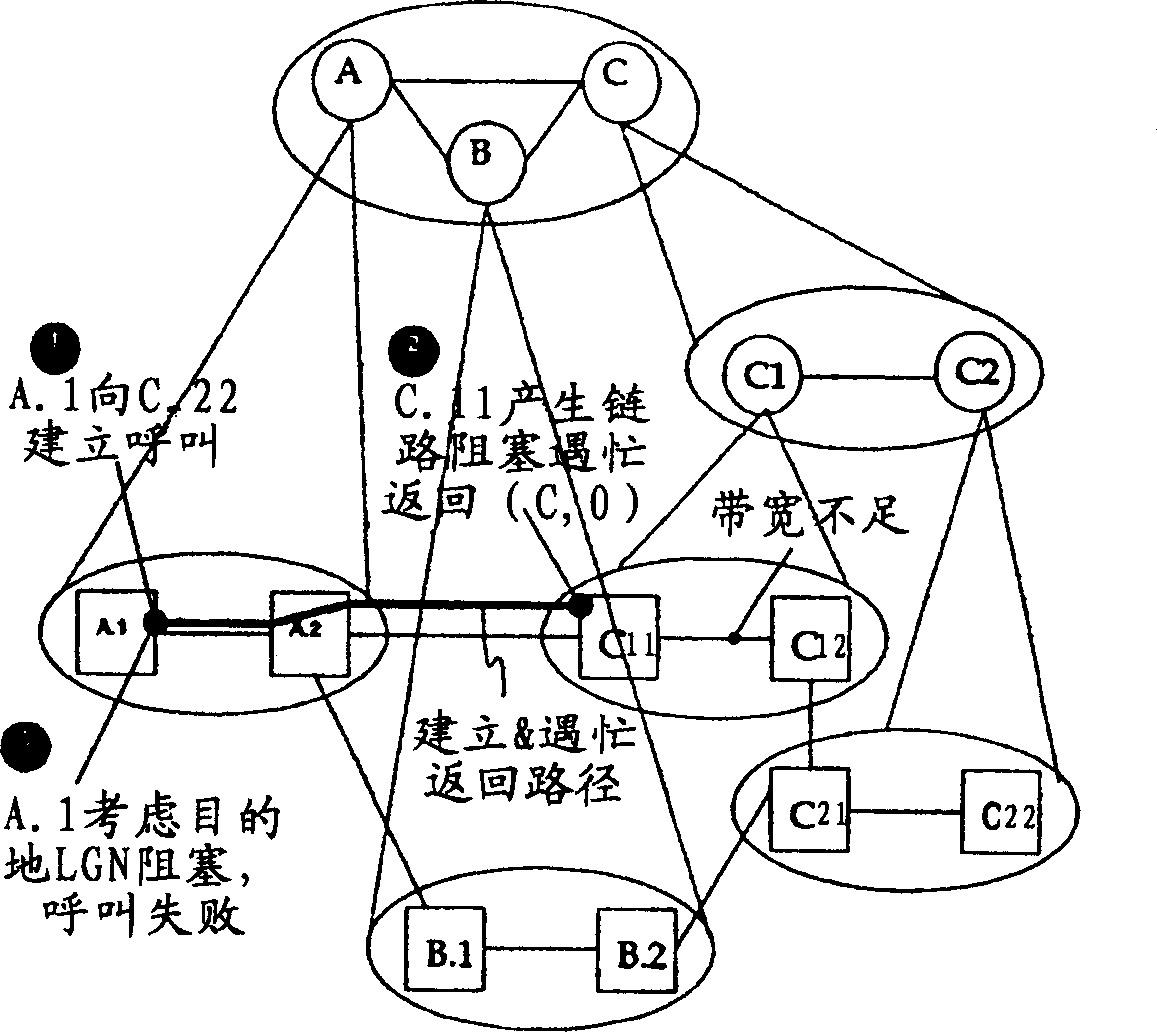
[0025] The busy return process of the present invention modifies the busy return process formulated in the PNNI specification. These procedures, referred to herein as the Destination LGN Blocking Busy Return procedure, are implemented by the ingress border node in the lowest-level destination peer group, the ingress border node in the last LGN in the DTL stack of the call (i.e. The ingress border node in the last LGN) and the DTL initiating node or the ingress border node with routing capability are used to make routing decisions based on the received busy return information.
[0026] The modified destination LGN blocking busy return process operates according to the following protocol.
[0027] Whenever an ingress border node in the lowest-level destination peer-group fails to route a call in the peer-group for any reason other than self-blocking of the physical destination node to the destination address, the lowest-level destination peer-group The ingress border node in wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com