Cross-thread register sharing technique
A register and physical register technology, applied in memory systems, instruments, multiprogramming devices, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the number of free list entries, and achieve the effect of increasing hardware costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
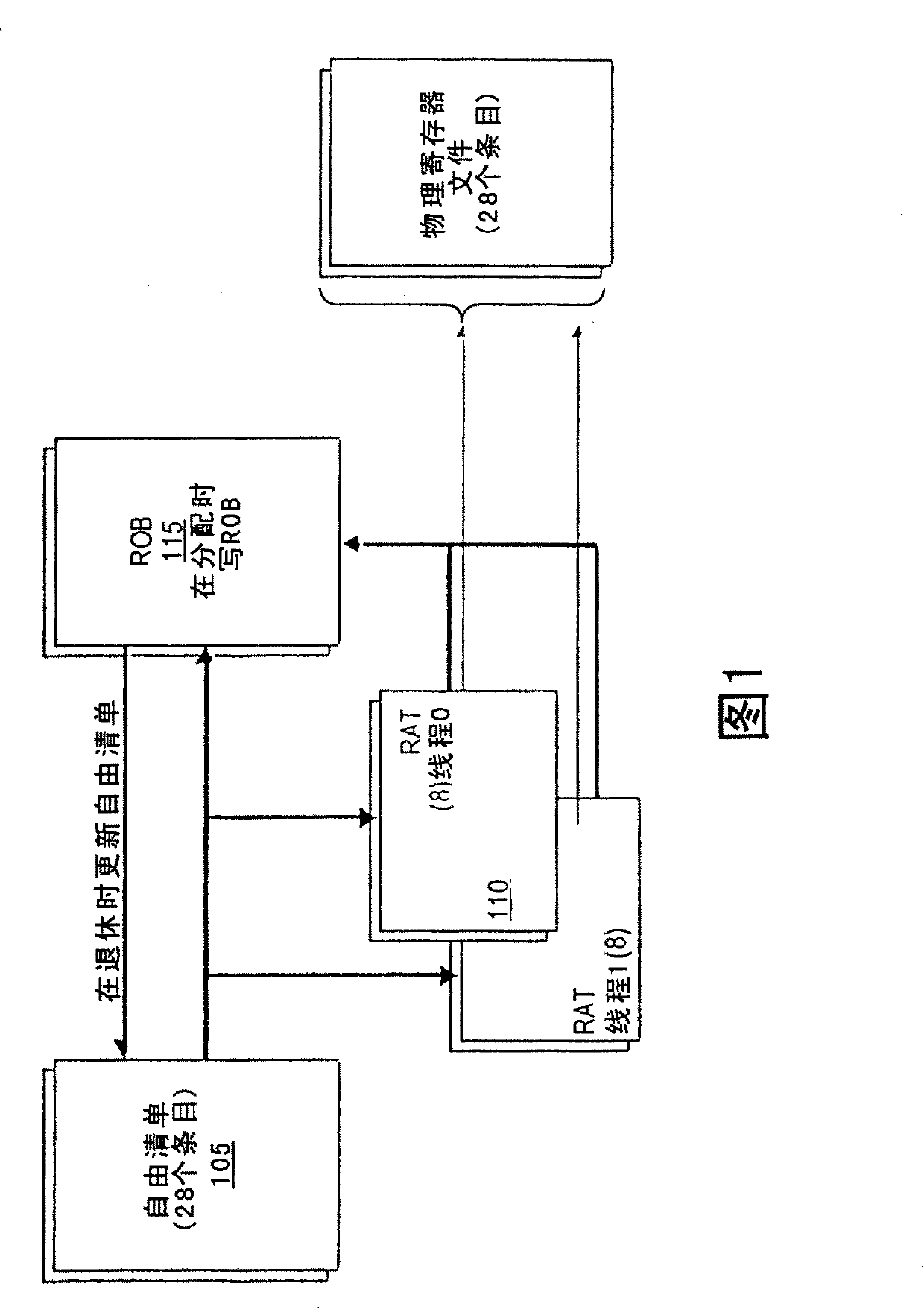
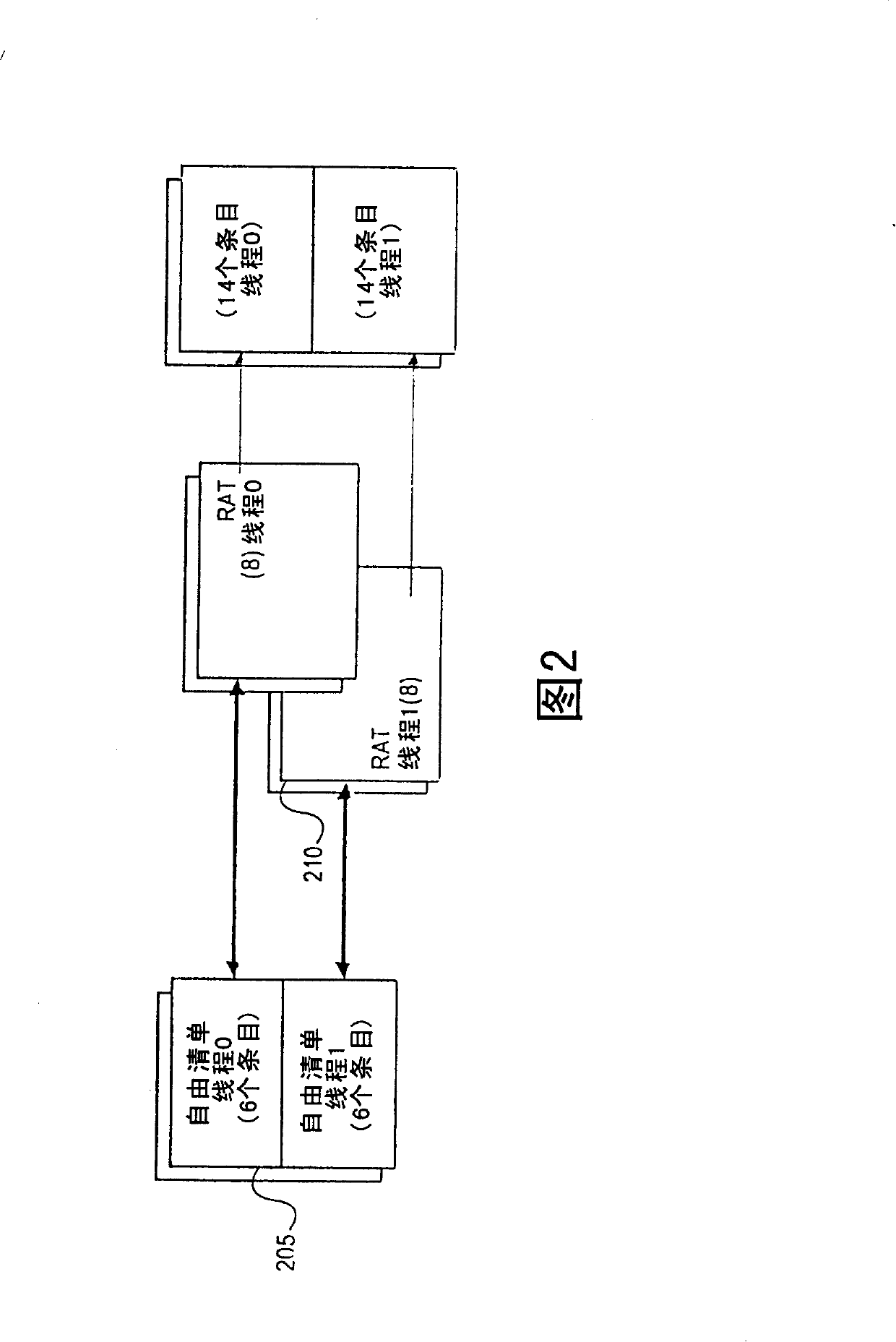
[0023] Embodiments of the invention relate to microprocessor architecture. More specifically, embodiments of the invention relate to register sharing techniques within microprocessors for multi-threaded instructions that facilitate mapping an optimal number of physical registers to a desired number of logical registers without incurring A lot of hardware overhead.
[0024] In at least one embodiment of the invention, a technique is used that incurs the hardware cost associated with the hard partition register sharing technique, but makes more registers available to another thread when one thread sleeps .
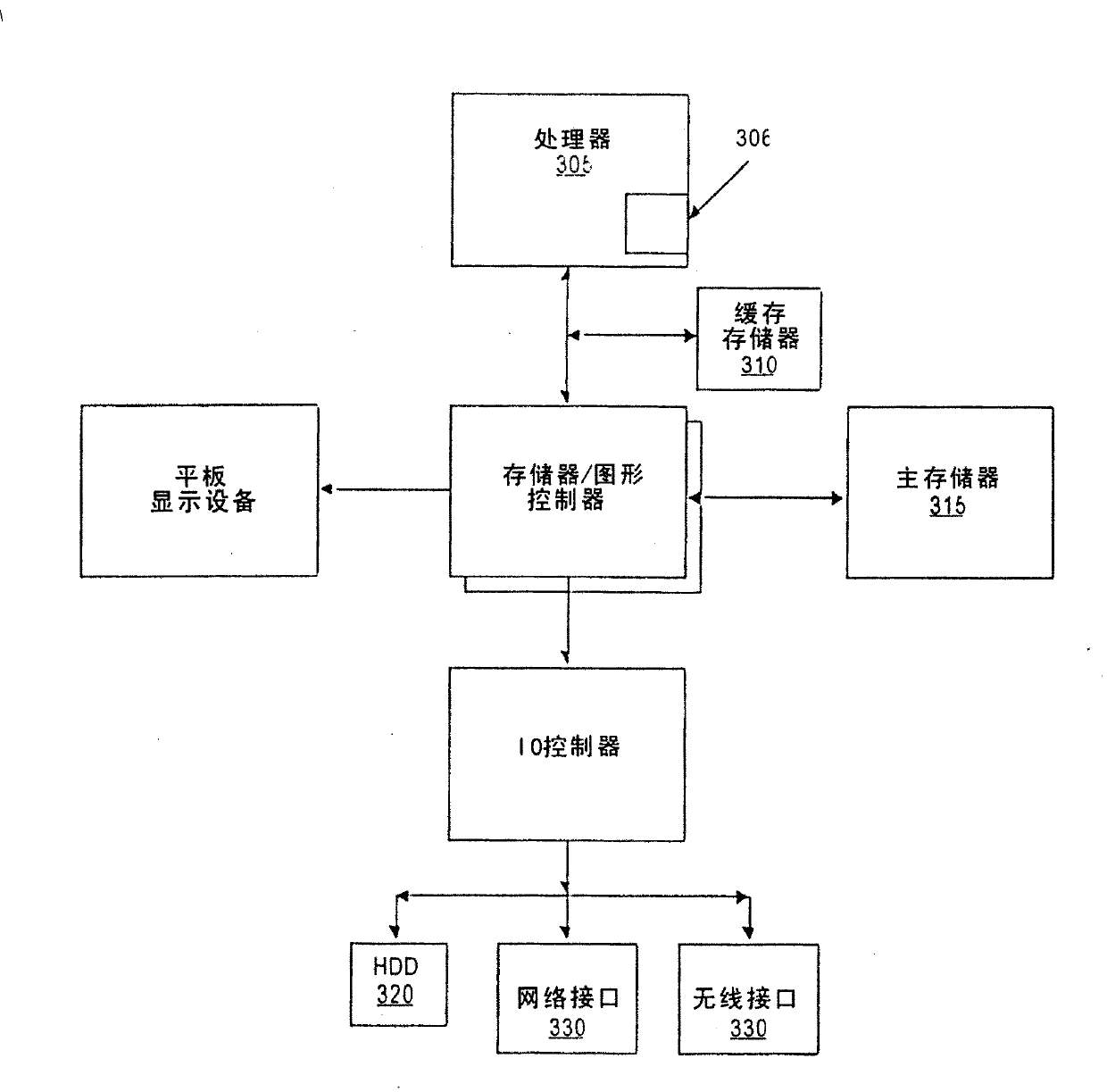
[0025] image 3 A computer system is shown in which at least one embodiment of the invention can be used. Processor 305 accesses data from cache memory 310 and main memory 315 . exist image 3 Shown in the processor 306 is an embodiment of the present invention. However, other embodiments of the invention may be implemented in other devices within the system, such as i...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap