Method of automatic grading program design language editor topic
A programming language and automatic scoring technology, applied in the field of program writing and verification, can solve problems such as shallow processing depth, failure to reflect the correctness of students' program semantics, knowledge and concept application, and failure to faithfully reflect the correctness of programs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
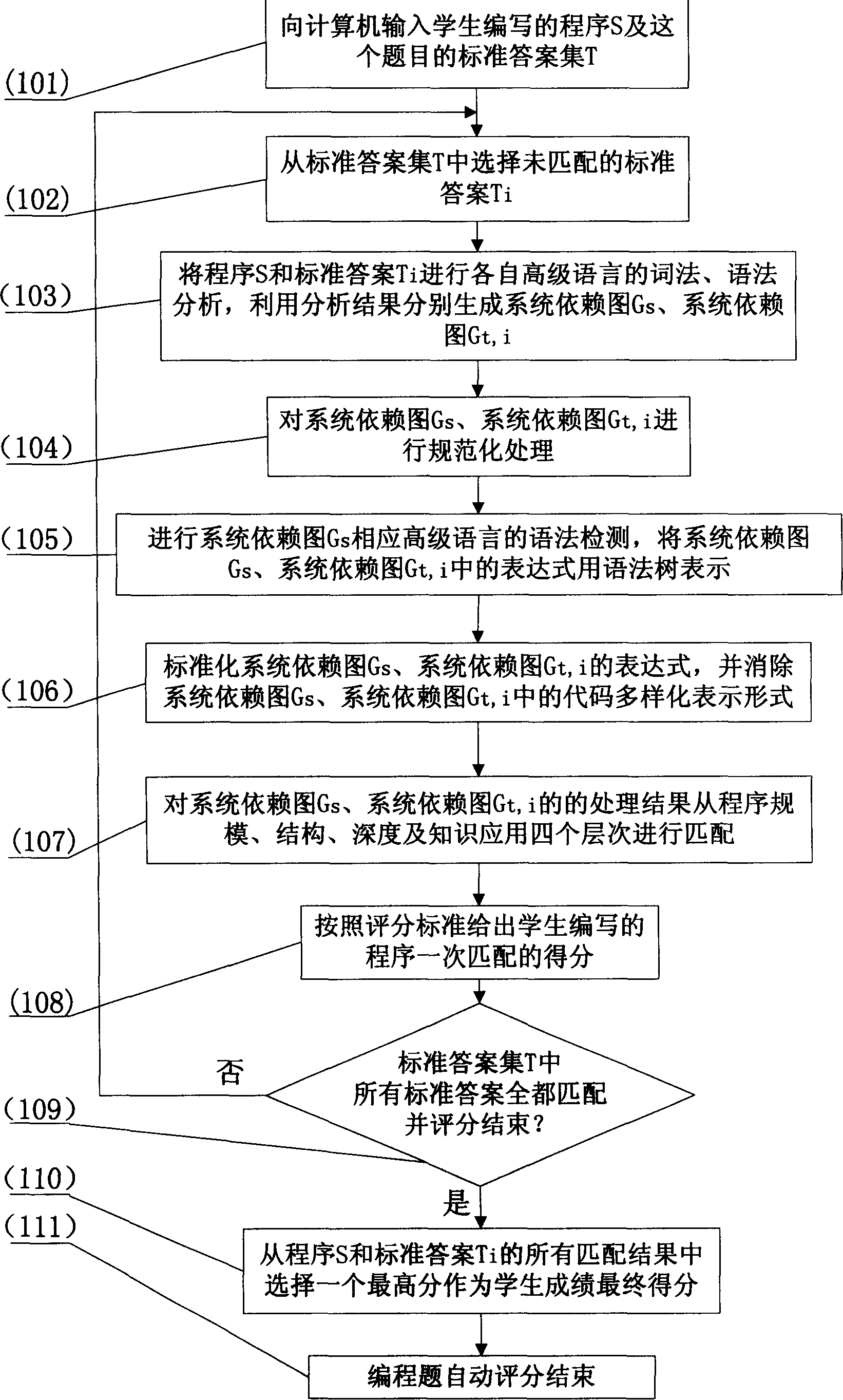
[0005] Specific implementation mode one: what this specific implementation mode describes is the step of automatic scoring method for programming questions: the following combination figure 1 This embodiment will be specifically described. Input the program S written by the students and the standard answer set T101 of this question into the computer, and select the unmatched standard answer Ti102 from the standard answer set T; carry out the lexical and grammatical analysis of the program S and the standard answer Ti in their respective high-level languages, and use the analysis As a result, the system dependency graph G is generated respectively s , system dependency graph G t,i 103; System dependency graph G s , system dependency graph G t,i Perform normalization processing 104 and perform system dependency graph G s Syntax detection of the corresponding high-level language, the system depends on graph G s , system dependency graph G t,i The expressions in 105 are repr...
specific Embodiment approach 2
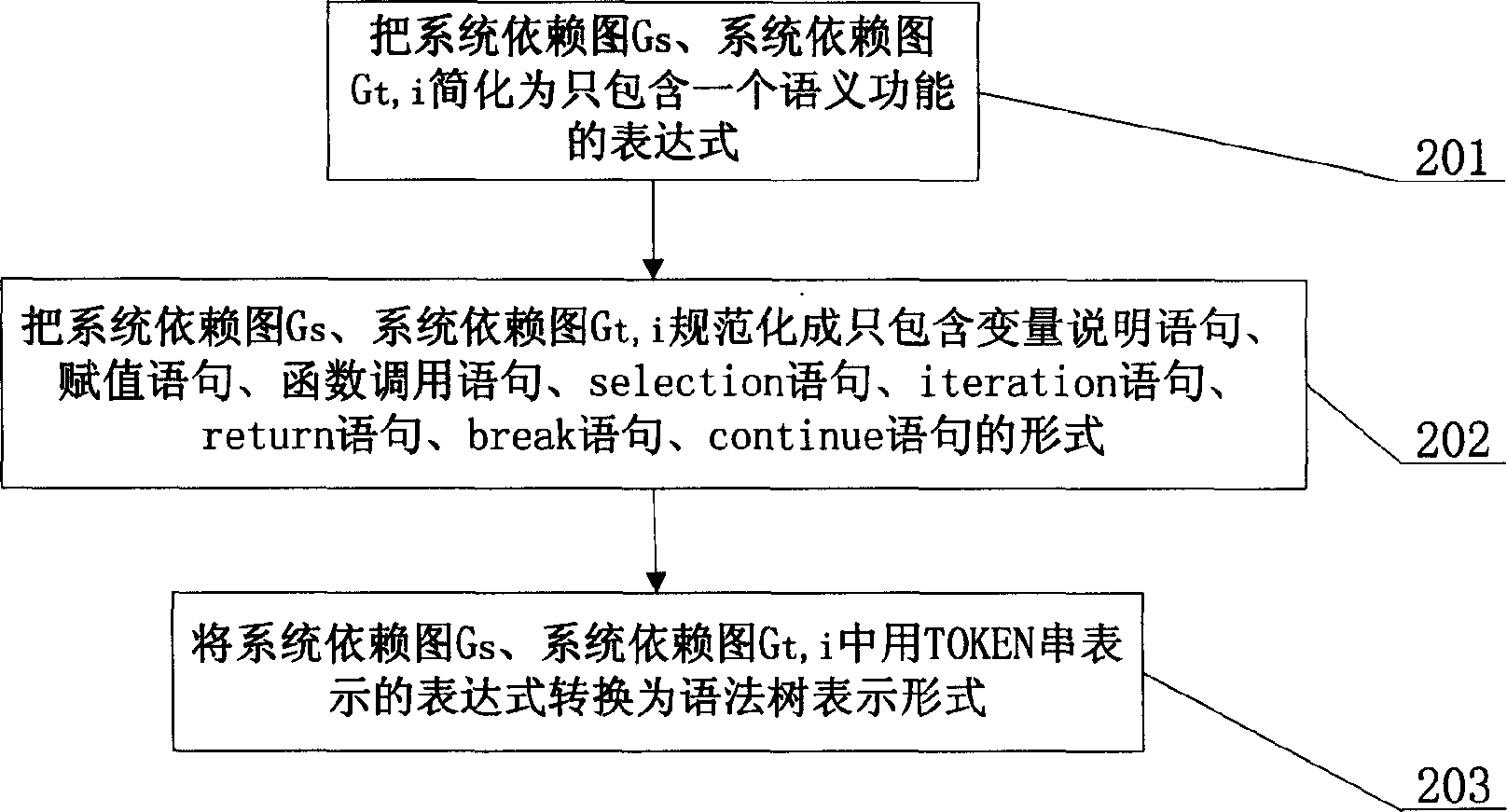
[0011] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 2 This embodiment will be specifically described. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that step 104 is divided into the following steps: (after the lexical and grammatical analysis of the source program and the representation of the system dependency graph, the program contains two or more than two semantic functions. Under the condition that the semantics of the program remain unchanged but the grammatical form of the expression changes), the system dependency graph G s , system dependency graph G t,i Simplified to an expression 201 that only includes a semantic function (for example: the C program statement "n=m++;" can be simplified to "n=m; m++;"; then, the special statement, selection and loop structure in the normalized system dependency diagram ), put the system dependency graph G s , system dependency graph G t,i The specification is simplified to a form that only incl...
specific Embodiment approach 3
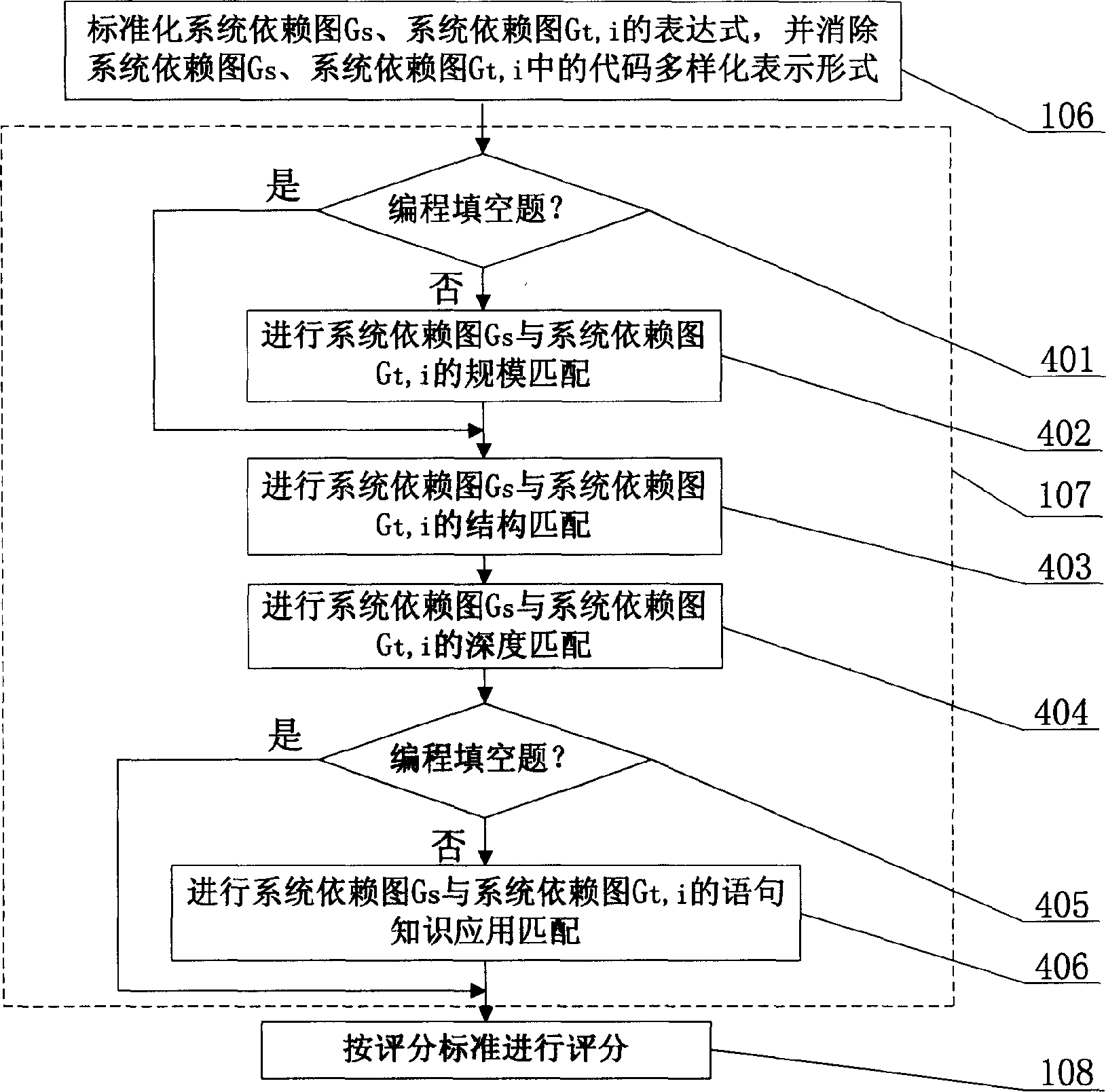
[0012] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination image 3 This embodiment will be specifically described. This specific embodiment describes the system dependency graph G s , system dependency graph G t,i The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that step 106 is divided into the following steps: firstly, use standardized rules to process the system dependency graph G s , system dependency graph G t,i expression 301; determine whether the standardization rules are not applicable 302; the result is no, then return to step 301 (expression standardization is mainly to apply the standardization processing rules to the expression in the syntax tree form, until these rules are not applicable to the expression formula); if the result is yes, delete the system dependency graph G s, system dependency graph G t,i Redundant code 303 in (that is, delete the code that cannot be executed under any conditions or the code that can be executed but does...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com