Automatic segmentation of tissues by dynamic change characterization
A technology of image segmentation and segmentation steps, applied in image analysis, instruments for radiological diagnosis, image data processing, etc., can solve the problem of difficult segmentation of tissues of interest or other substances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
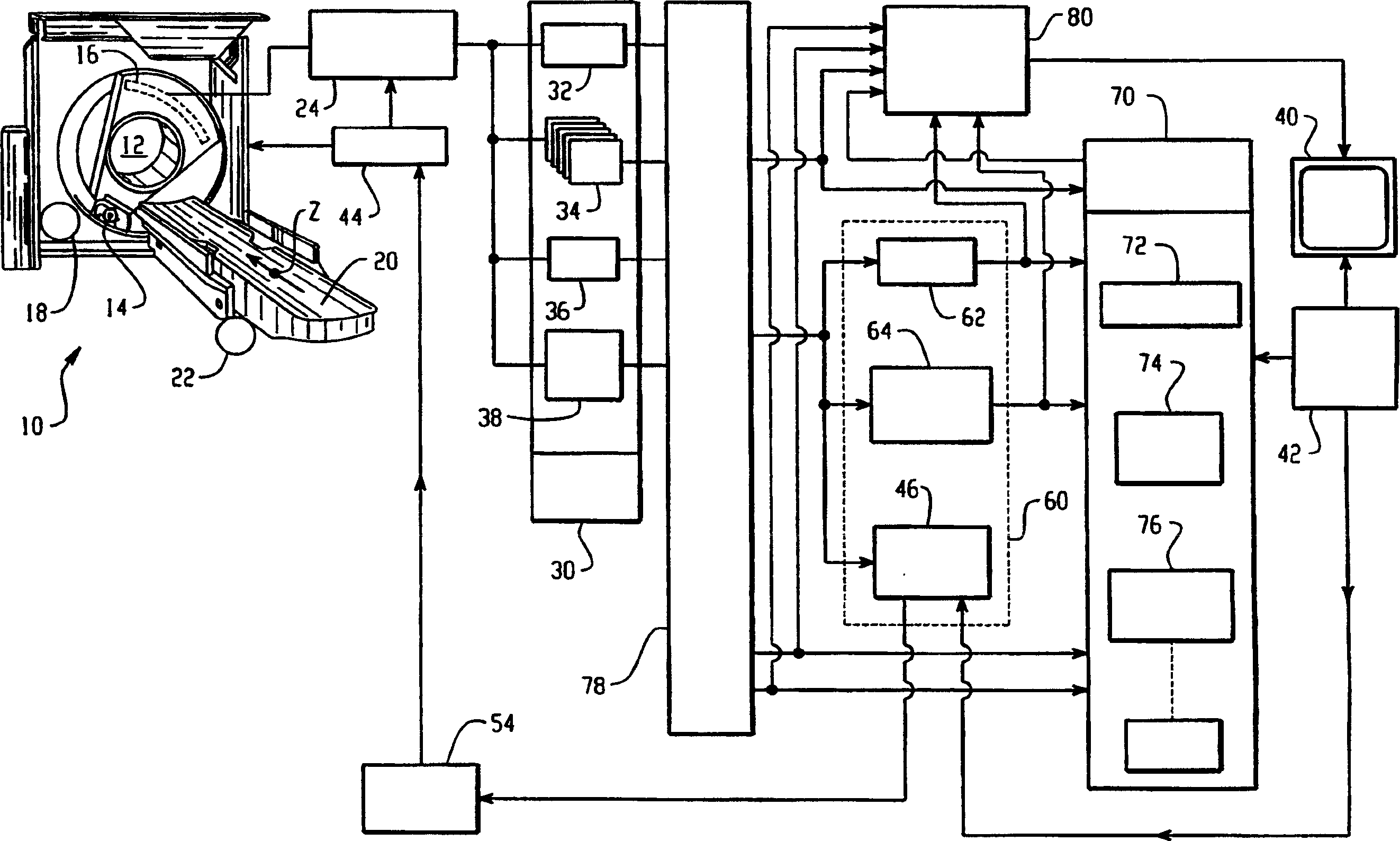
[0015] refer to figure 1 , a diagnostic imaging apparatus, such as a CT scanner 10, non-invasively examines a subject located in an imaging region 12 and generates diagnostic image data representing a region of interest of the subject placed in the examination region. In the described CT scanner embodiment, an x-ray tube 14 or other radiation source generates a beam, preferably a multilayer or cone beam, which is directed towards a radiation detector 16 through an examination region 12 . A motor 18 and associated drives (not shown) rotate the x-ray beam around the examination region, typically by rotating the x-ray source and detectors. The subject is supported on a patient support 20 such as a subject couch. A motor 22 and associated engagement and coupling means (not shown) propels the subject longitudinally through the examination region such that the subject's region of interest passes through the examination region. For a helical scan, while the motor 18 rotates the x-r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com