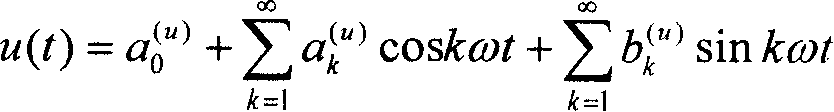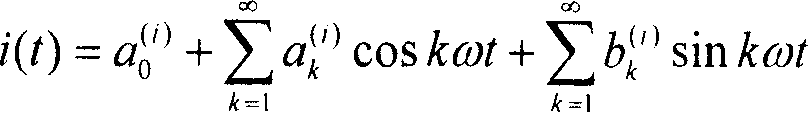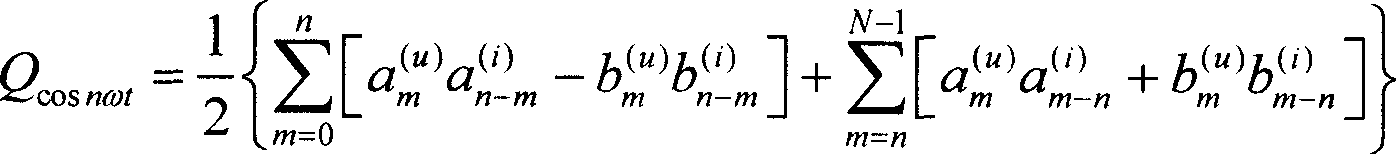Method for metering reactive electric energy
A measurement method and technology of electric energy, which is applied in the measurement of electric variables, electric power measurement through current/voltage, and electrical devices, etc., and can solve problems such as incorrect or insufficient reactive energy measurement methods, and inability to fully meet the requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0165] The present invention comprises the following steps:
[0166] (1) Data collection to obtain voltage and current signals at the load end
[0167] Transform the voltage and current signals at the load end into a low level that can be collected and measured through the voltage and current transmitters. If it is a three-phase load, send the voltage and current signals of each of the three phases to the voltage and current conversion Transformer, the transformed voltage and current signals are sampled synchronously and uniformly, and the number of sampling points in one power frequency cycle is N, where N≥50 and For example, take N=1024 to get the voltage sequence {u in the time domain (n)} and the current sequence {i (n)}, where 0≤n≤N-1, the Fourier expressions of the voltage and current signals transformed by the transmitter are
[0168] u ( t ) = a 0 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com