Stir-friction hot working control system
a technology of stirfriction and control system, which is applied in the direction of metal-working equipment, welding equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of inability to make small adjustments in the depth of penetration, inconvenient to change the penetration depth, and subject to error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
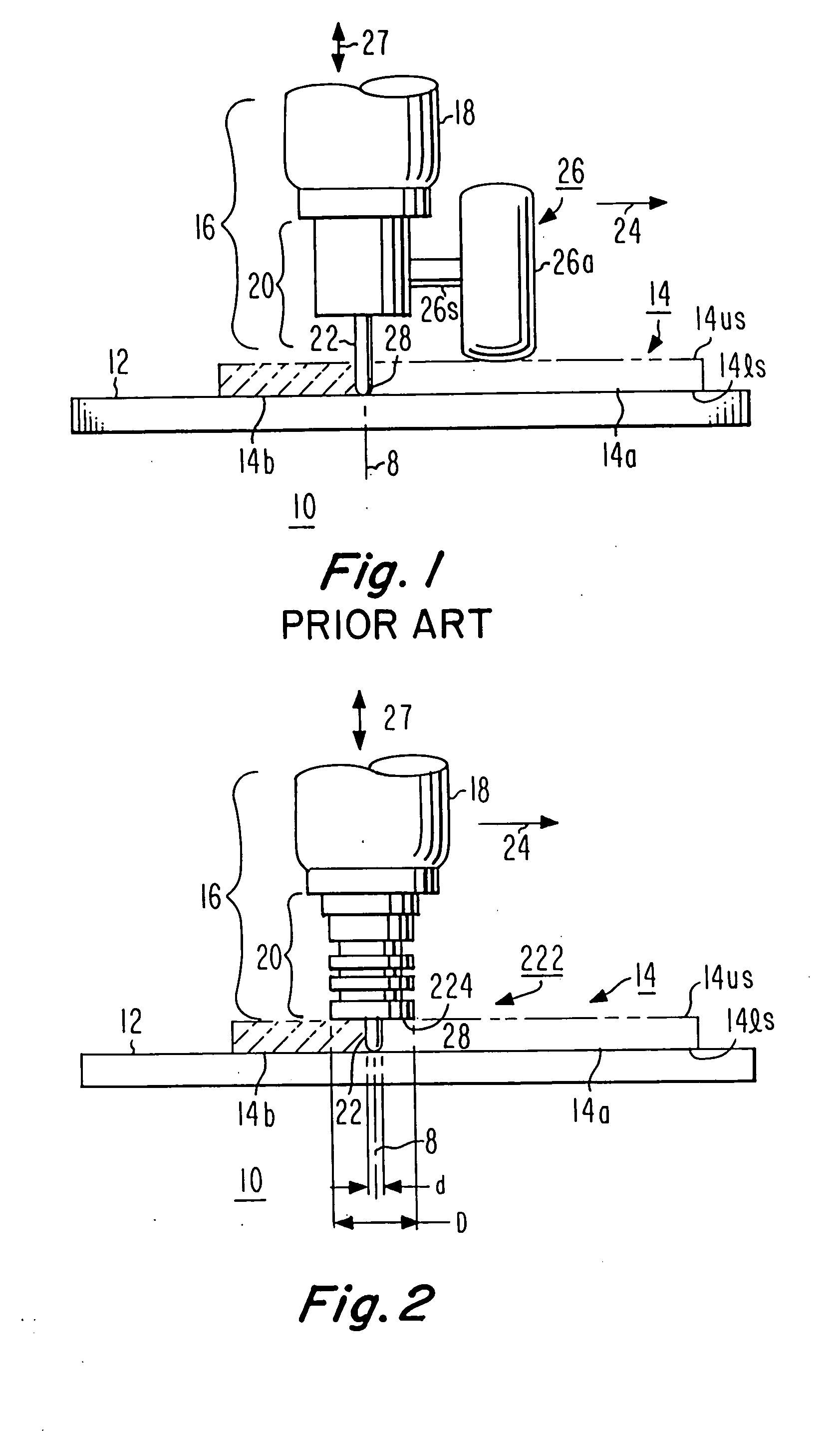
[0020]FIG. 2 is a simplified diagram, similar to FIG. 1, showing a pin tool 222 which includes a ligament 22 having a diameter d at locations away from the rounded tip, and also including a shoulder portion 224 having a larger diameter D than the diameter d of the ligament portion 22. As illustrated in FIG. 2, the shoulder portion 224 rides on the upper surface 14us of the workpiece 14 during operation, and the length of the ligament 22 in relation to the intended depth of hot-working or welding is selected to approximately equal the pin-tip-to-shoulder distance. Thus, the distance between the pin tip 28 and shoulder 224 in FIG. 2 is about equal to the depth of hot-working or welding.
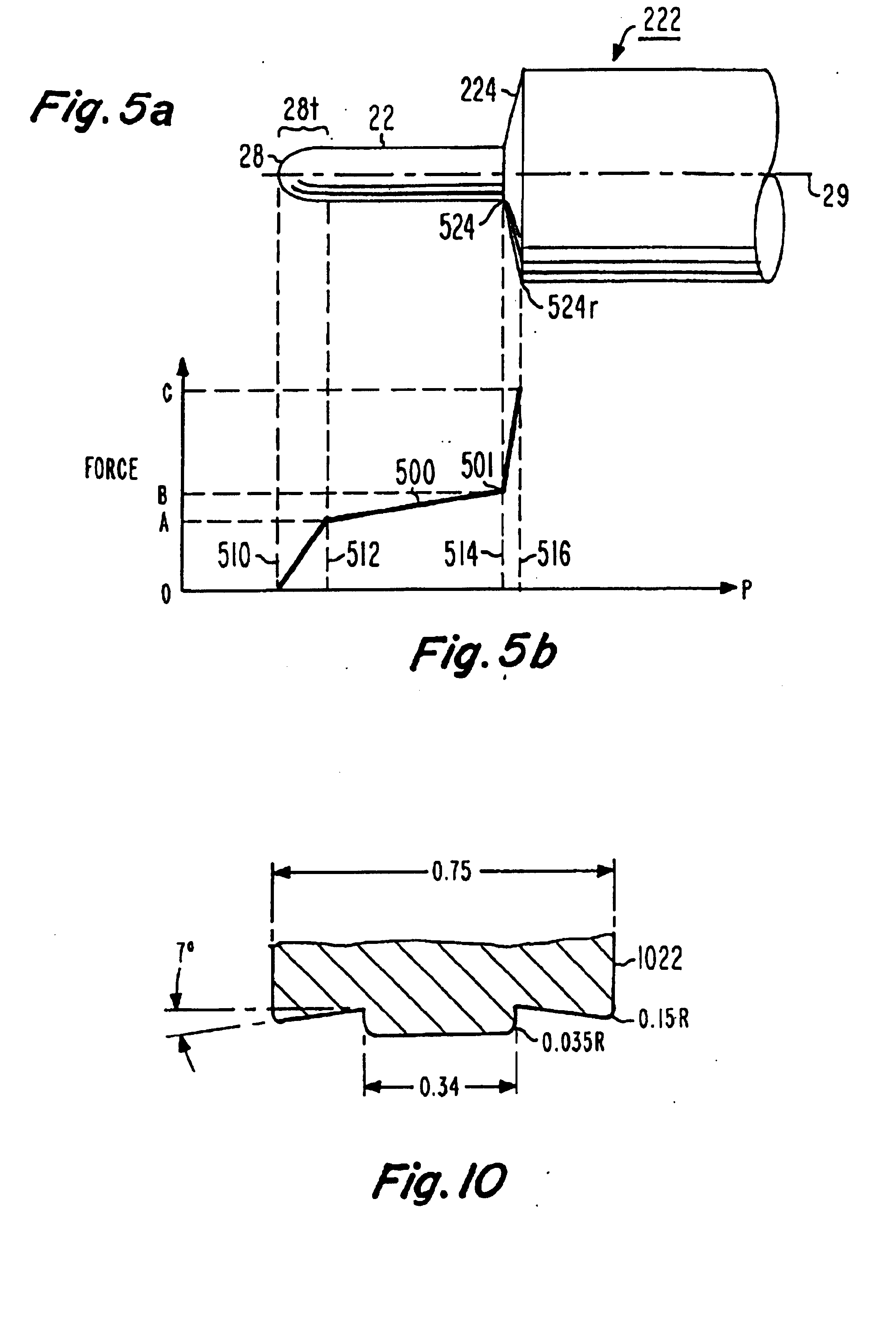
[0021]FIG. 3 illustrates the pin tool 222 of FIG. 2 separate from the spindle 18. As illustrated in FIG. 3, the pin tool 222 includes a shank 310 in addition to the shoulder portion 224 and pin or ligament 22. The grooves cut into the pin support in FIG. 3 are for ______.
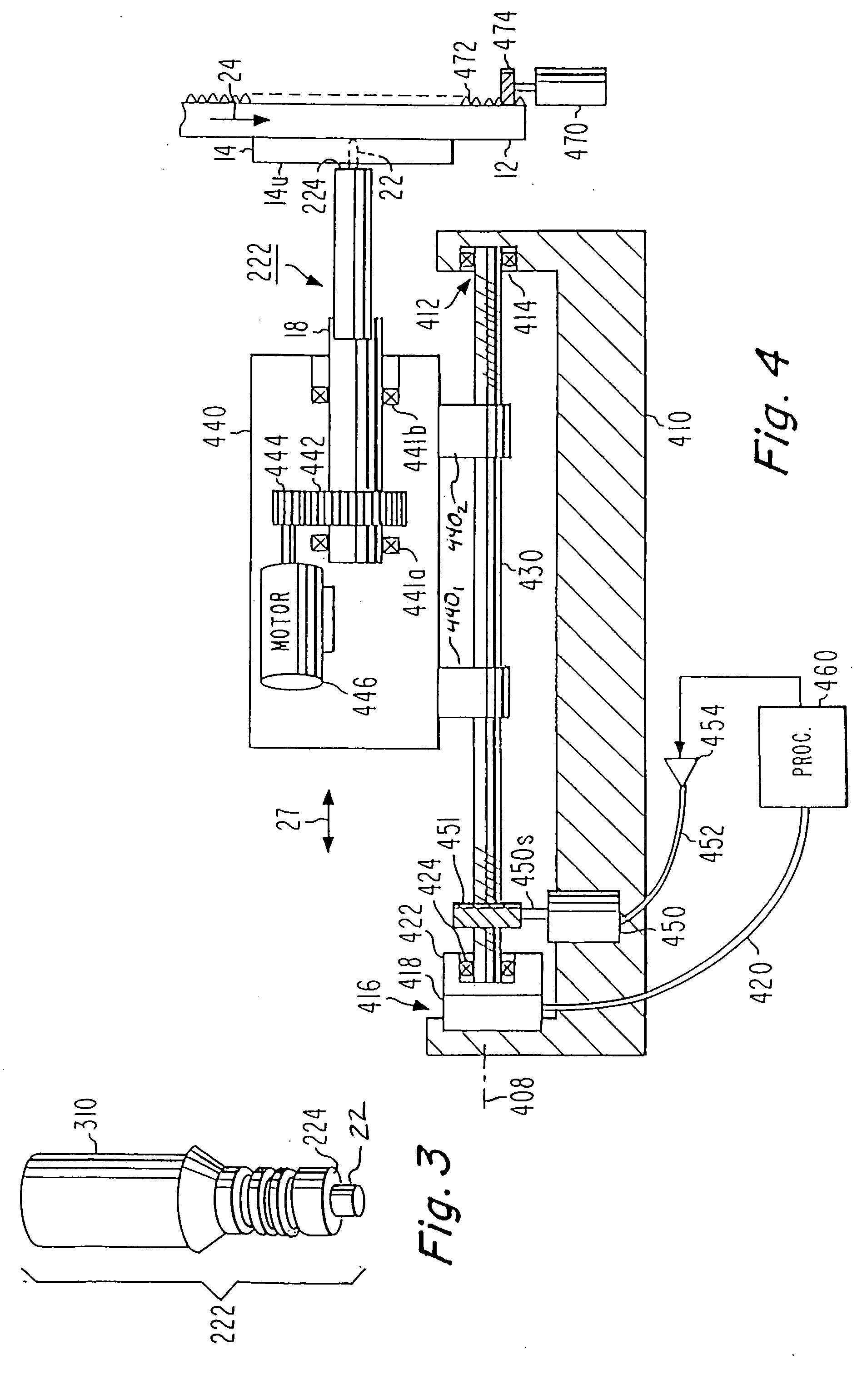
[0022]FIG. 4 is a simplified d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| plunge depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| friction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com