Masonry block constructions with polymeric coating
a technology of masonry block and polymeric coating, which is applied in the direction of structural elements, building components, construction materials, etc., can solve the problems of high level of skill required in the laying of blocks with mortared joints, the difficulty of achieving the effect of reducing the difficulty of laying blocks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
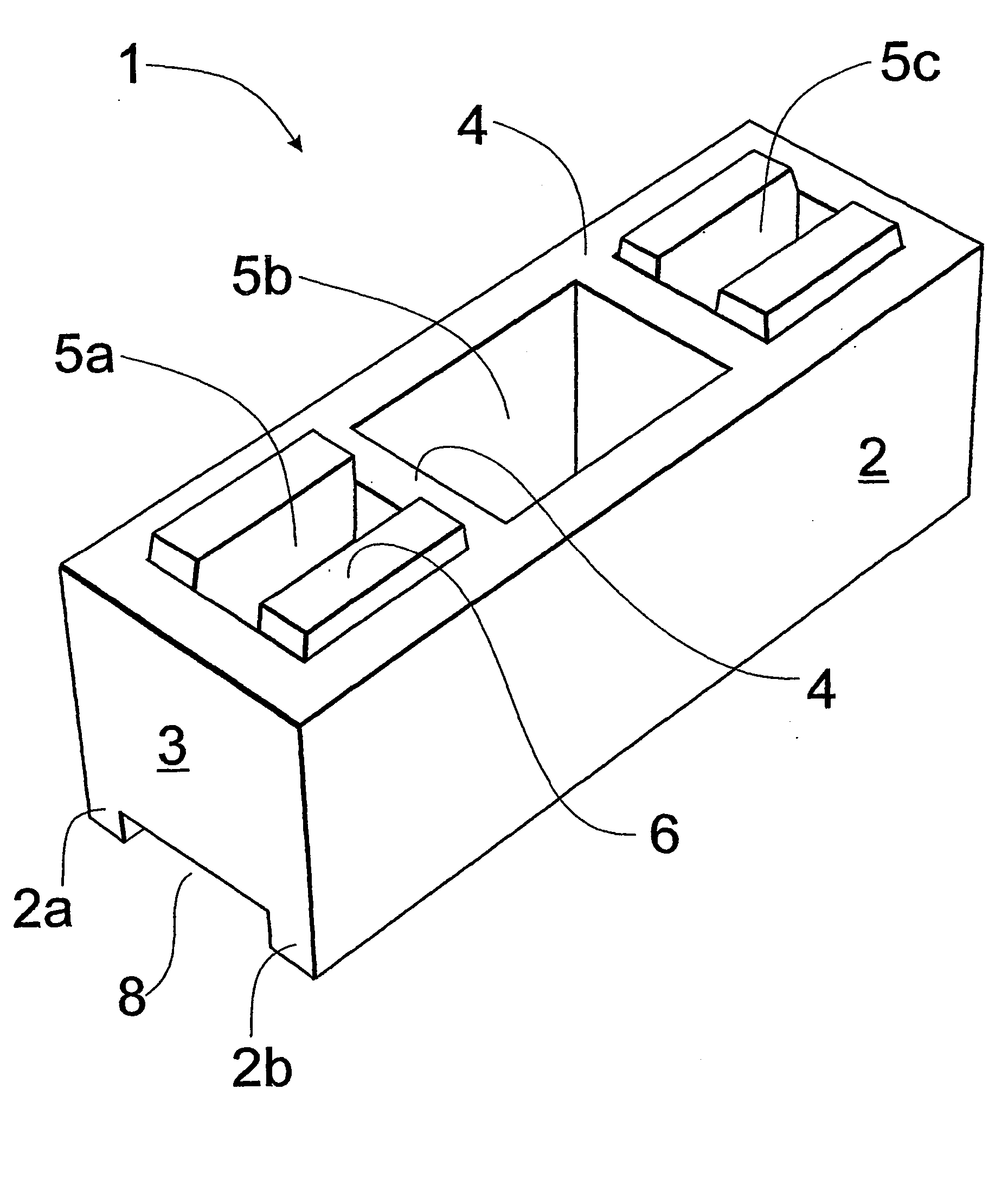
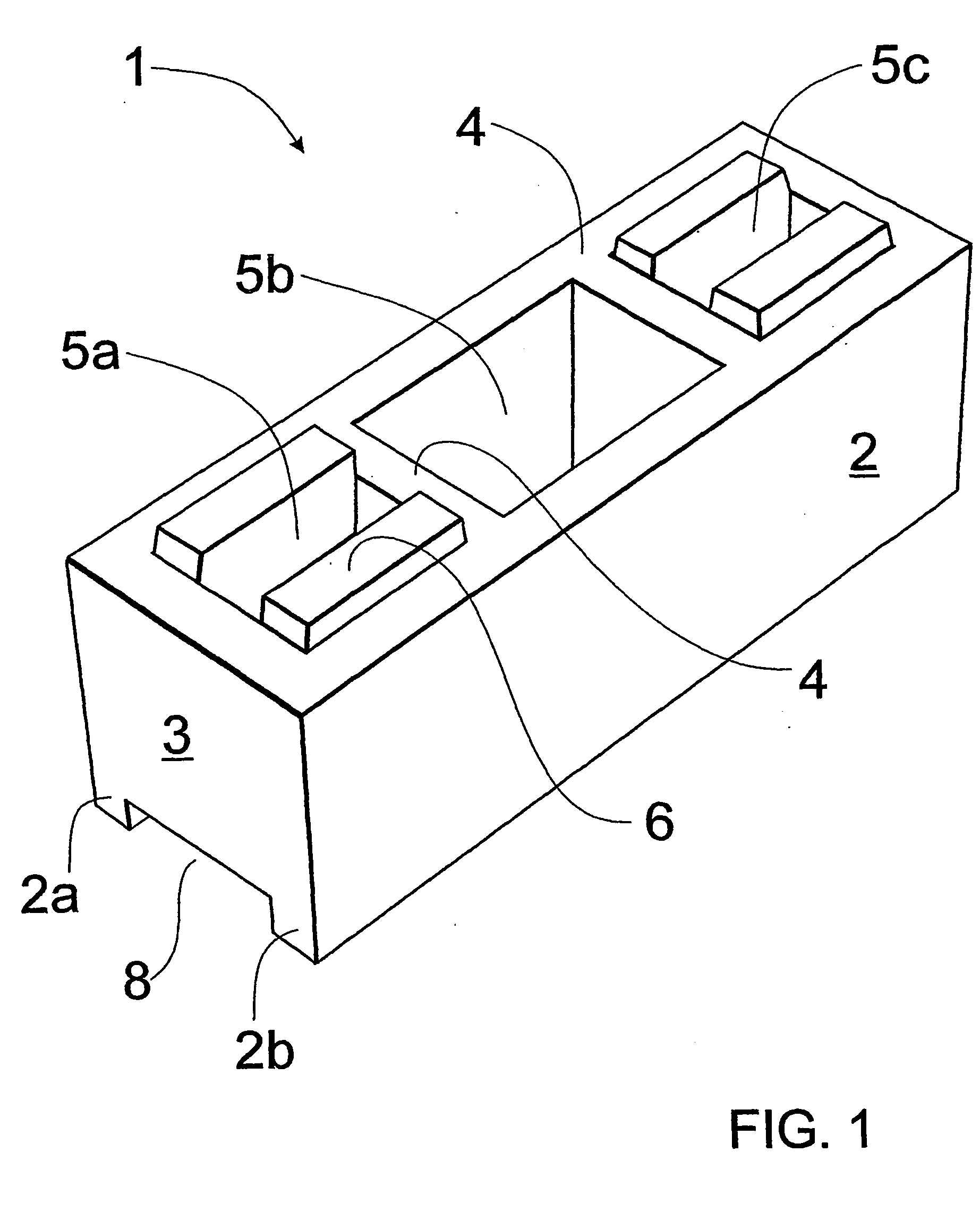
[0050] In FIGS. 1-4 there is shown a masonry block suitable for building “dry-stacked” or mortarless wall structures.
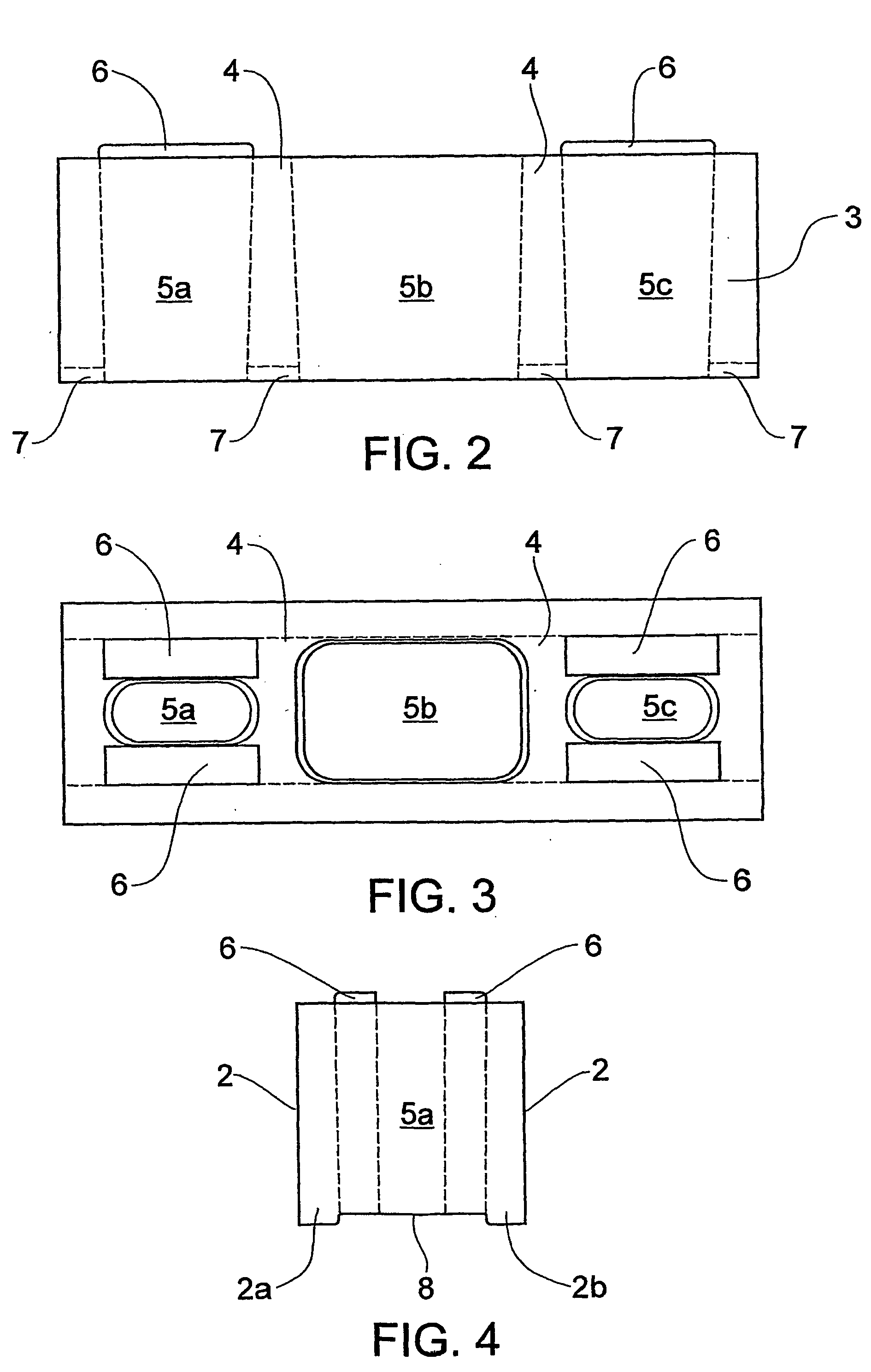
[0051] Masonry block 1 includes opposed side walls 2, opposed end walls 3 and intermediate webs 4 defining apertures 5a, 5b and 5c extending along upright axes through block 1.
[0052] On the upper face of block 1 there are formed projections 6 adapted to locate in complementary recesses 7 formed in an adjacent block. Recesses 7 are formed in the lower opposite wall portions of apertures 5a and 5c whereby a channel-like recess 8 extends over the lower face of block 1 between the lower portions 2a, 2b of opposed side walls 2.
[0053] The structure of the block permits quick, accurately aligned stacking of blocks in a conventional manner wherein the blocks of one course overlap the end joints between blocks of an underlying course, the end joints being located centrally of central aperture 5b. Part blocks (not shown) are utilised for wall ends, wall openings and joints b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| alkaline resistant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com