Novel bits and cutting structures
a cutting structure and new technology, applied in drill bits, earthwork drilling and mining, construction, etc., can solve the problems of shortening the life of both natural and synthetic diamonds, affecting the cutting effect of pdc bit bodies, and difficult materials used in forming pdc bit bodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
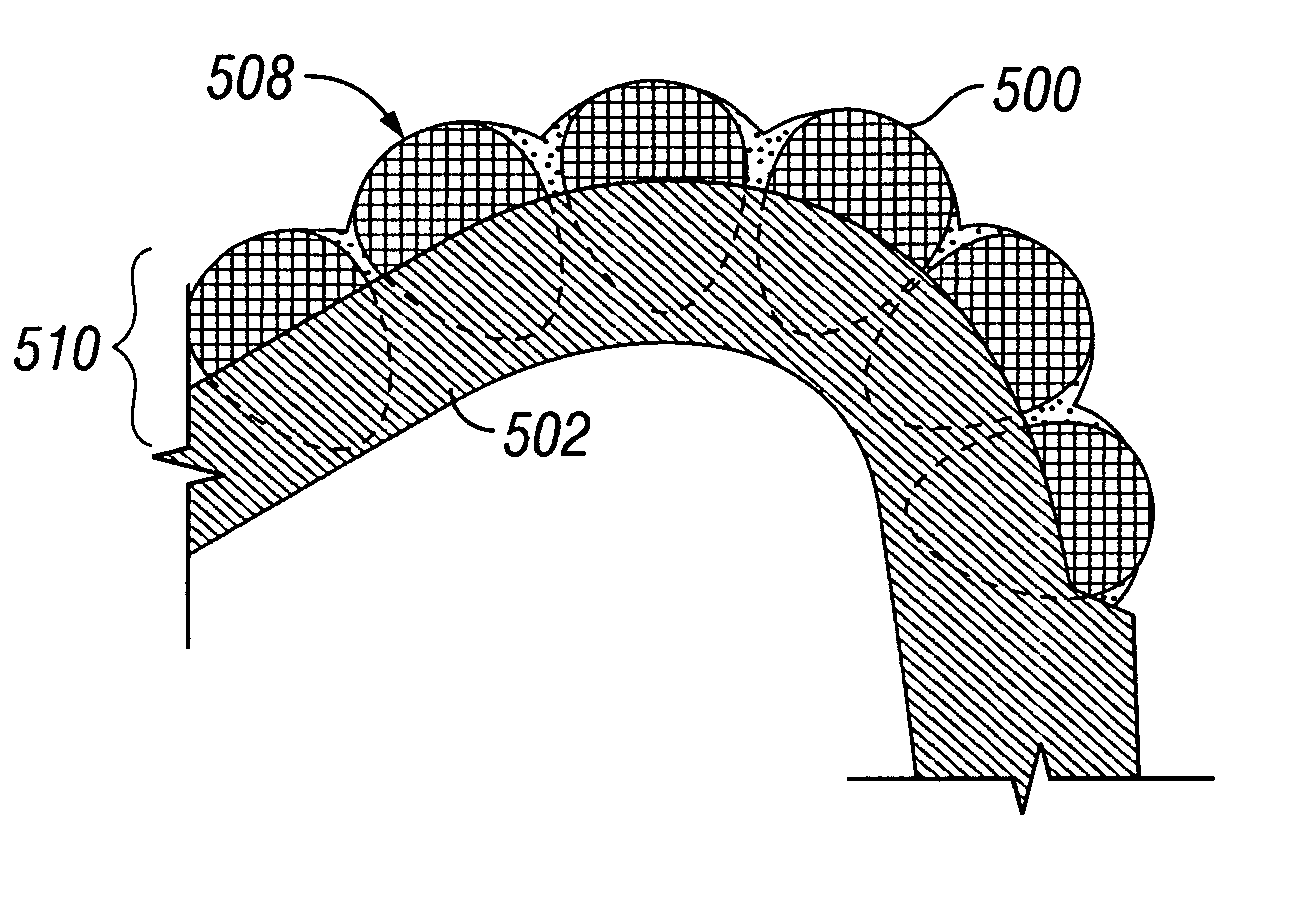
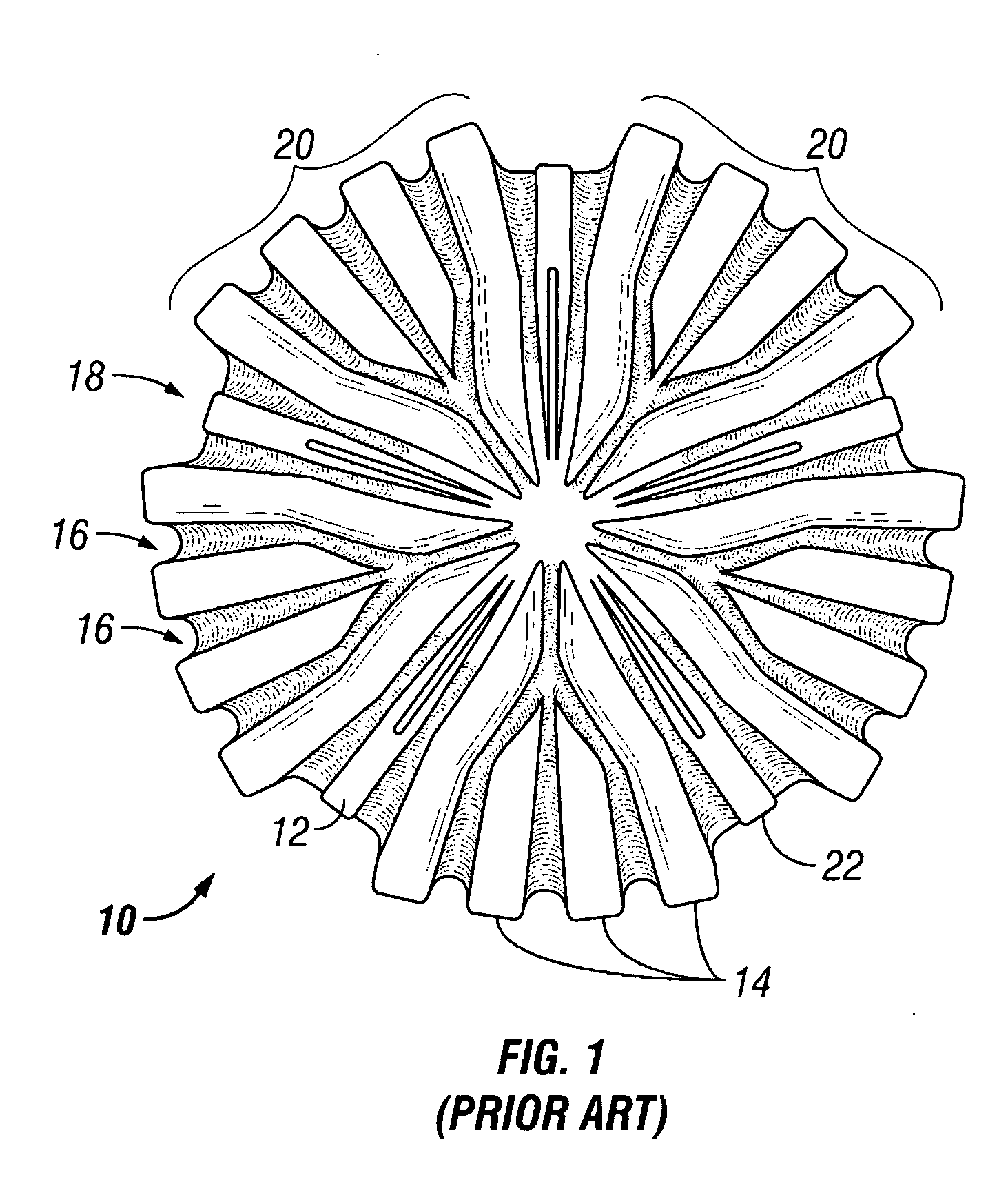
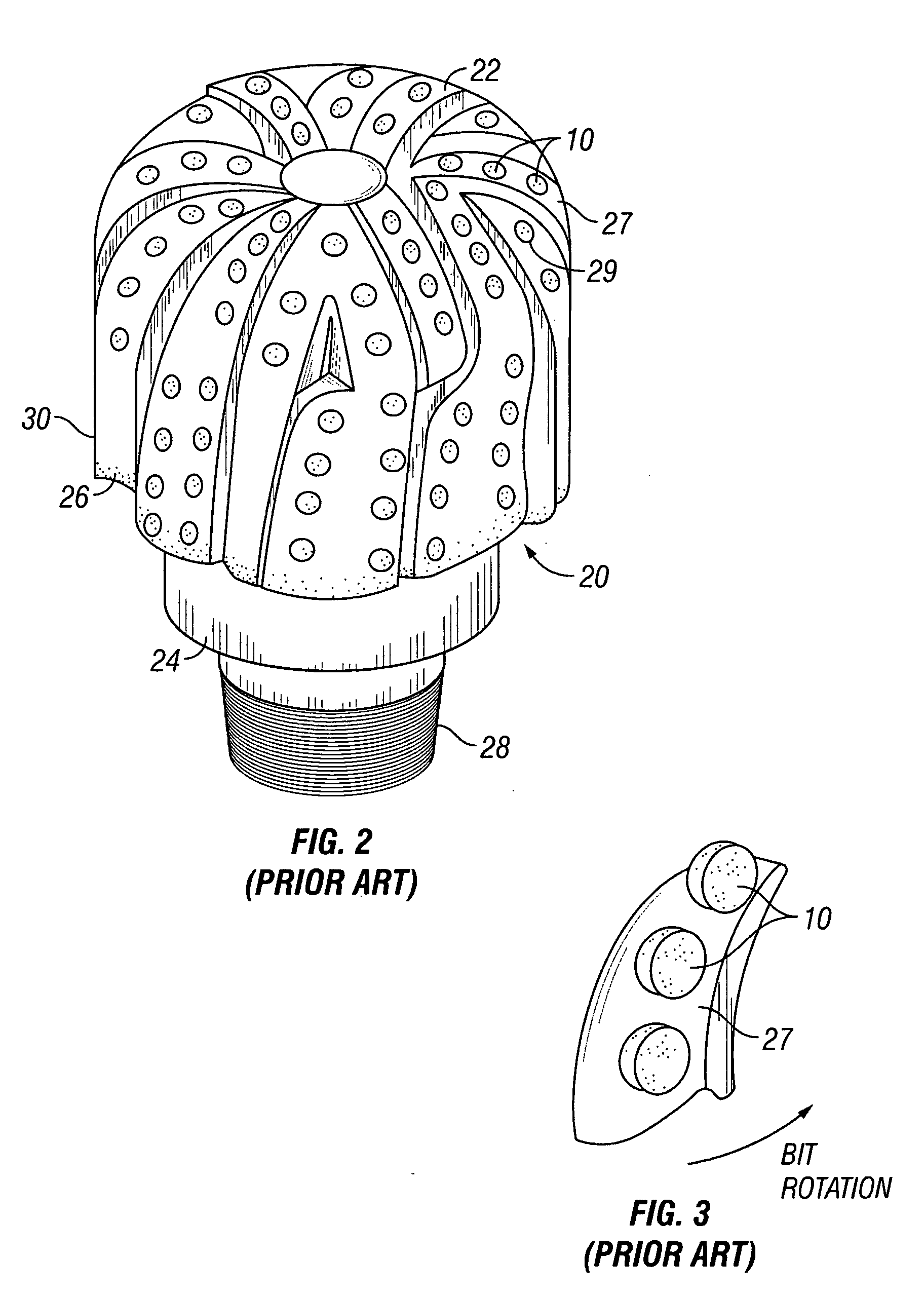
[0065] One aspect of the present invention relates to a cutting structure that uses a shearing element, disposed on a support. In particular, the present invention relates to a cutting structure for use in lieu of, or in combination with, PDC cutter elements to provide a shearing action. Embodiments of the present invention are particularly useful in high speed applications, such as applications that use a mud motor and / or turbines.
[0066] In another embodiment of the present invention, at least a portion of the shearing element is overlaid by a retaining element to provide an additional retention mechanism to prevent the shearing element from dislodging from the support. The retaining element may be integrally formed with the support, or may be discretely applied to the shearing element and formed from either the same composition as the support or a different composition.
[0067] In another embodiment of the present invention, diamond impregnated blades, which are used in lieu of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com