Eddy-current probe
a technology of eddy current and probe, which is applied in the direction of magnetic property measurement, material magnetic variables, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the accuracy of the test results, the substrate is likely to be damaged by application, and the sticktion occurs more frequently, so as to reduce the probability of sticktion, the durability and lifetime performance is high, and the test results are high
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
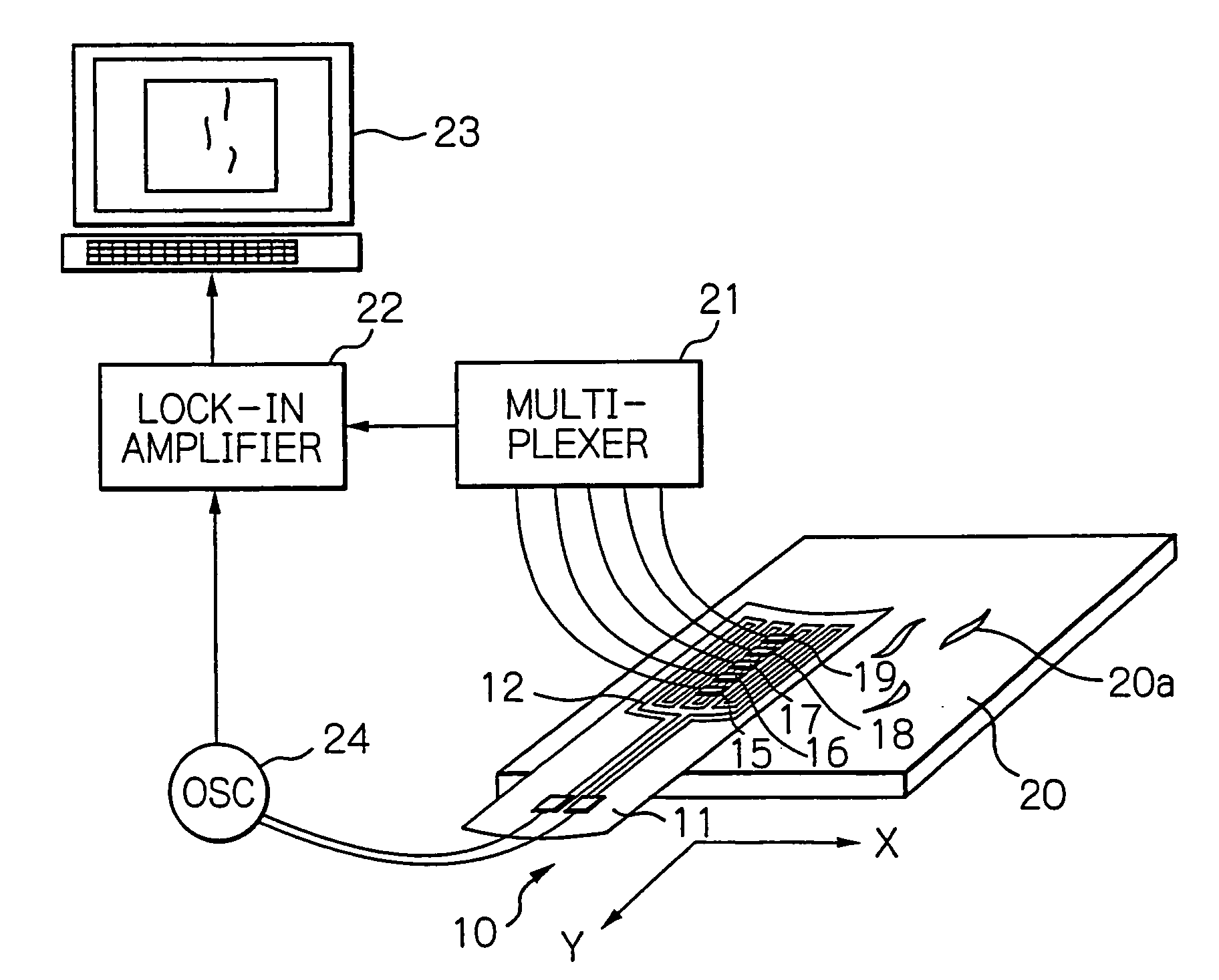
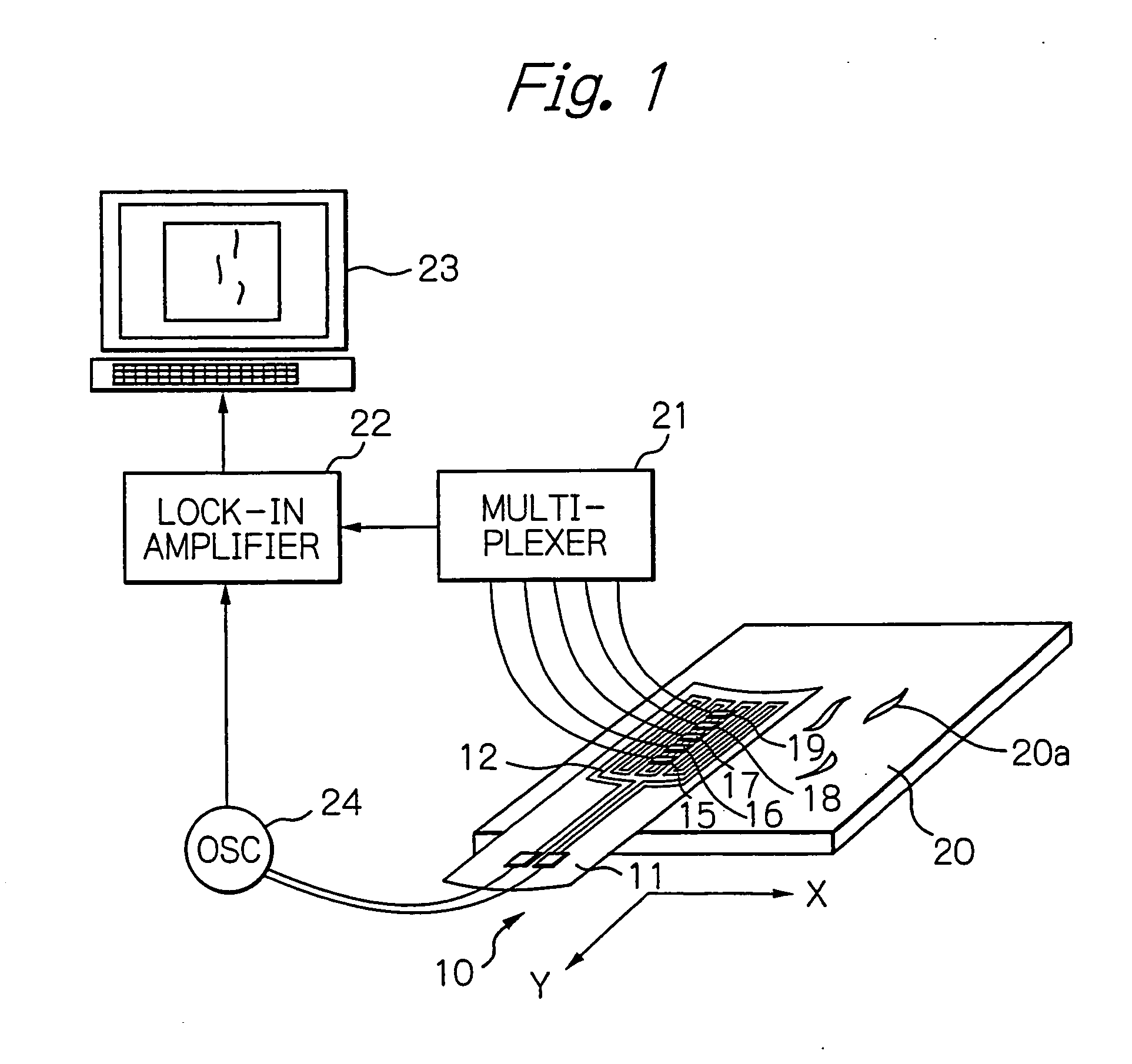
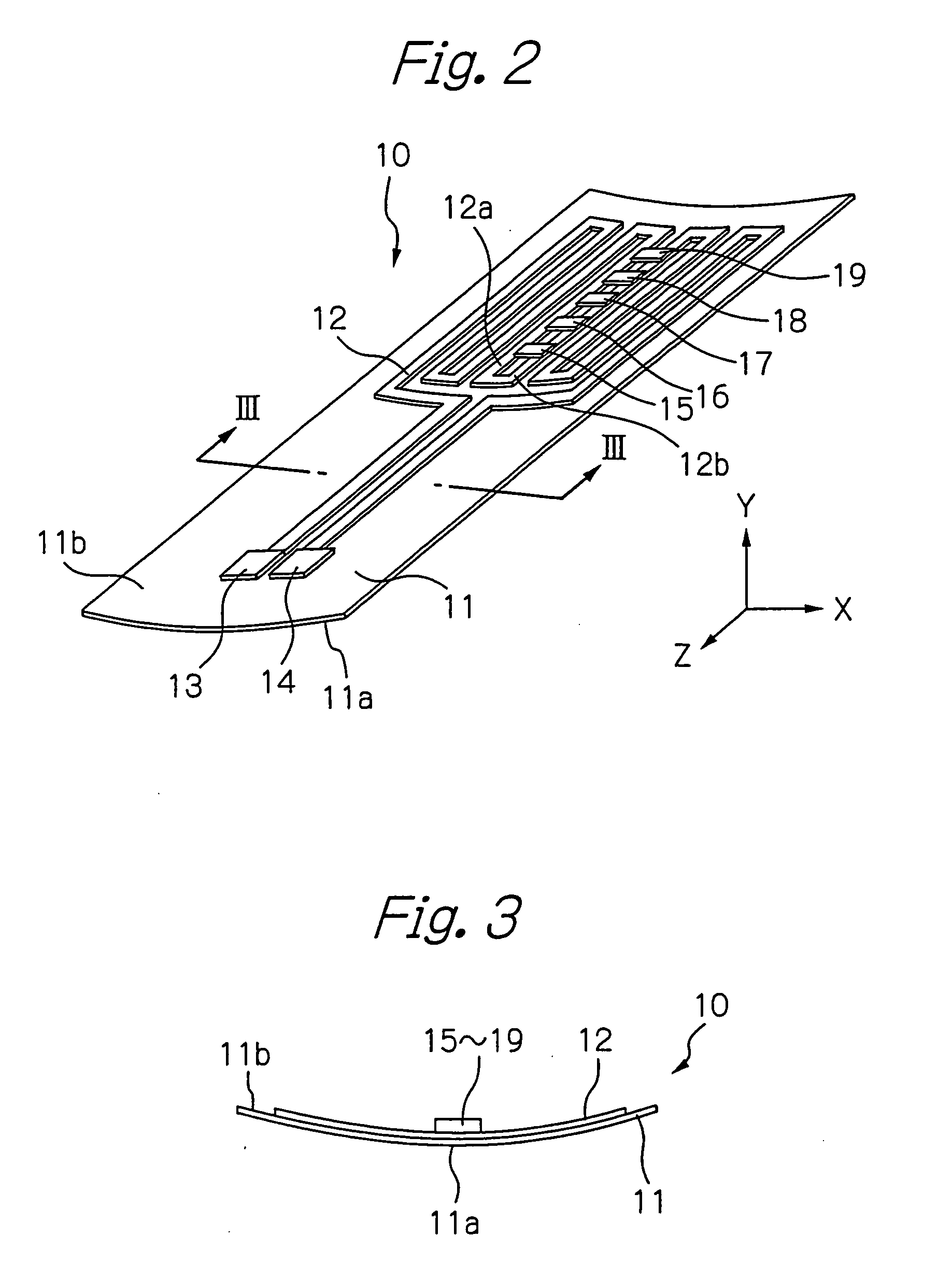
[0066]FIG. 1 shows a diagram schematically illustrating a configuration of an testing system using the eddy-current according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 2 shows a perspective view schematically illustrating a configuration of the ECT probe according to the embodiment in FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 shows a cross-sectional view taken along with line III-III in FIG. 2.
[0067] In these figures, reference numeral 10 indicates an ECT probe, 11 indicates its flexible substrate formed of an insulative material such as polyimide, 12 indicates a meander-type exciting coil including coil conductors formed as a planar pattern turned back on the opposite surface 11b to the measurement surface 11a of the substrate 11, 13 and 14 indicate a pair of electrode terminals formed on the substrate 11, which is connected electrically to both ends of the exciting coil 12, 15 to 19 indicate thin-film chips bonded on the exciting coil 12, each of which is mounted with a GMR element (eddy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| eddy-current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Eddy-current testing | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com