Method and system for obtaining a discovered price
a price and discovered technology, applied in the field of securities markets, can solve the problems of preventing accurate price formation and discouraging order entry, undesirable for traders, and inherent drawbacks of disparities in fill rate and price among participating traders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0040] Buyer A enters a priced order offering to buy 10,000 shares for ½.
[0041] Buyer B enters a priced order offering to buy 10,000 shares for ⅜.
[0042] Seller X enters a priced order offering to sell 10,000 shares for ⅜.
[0043] Seller Y enters a priced order offering to sell 10,000 shares for ⅜.
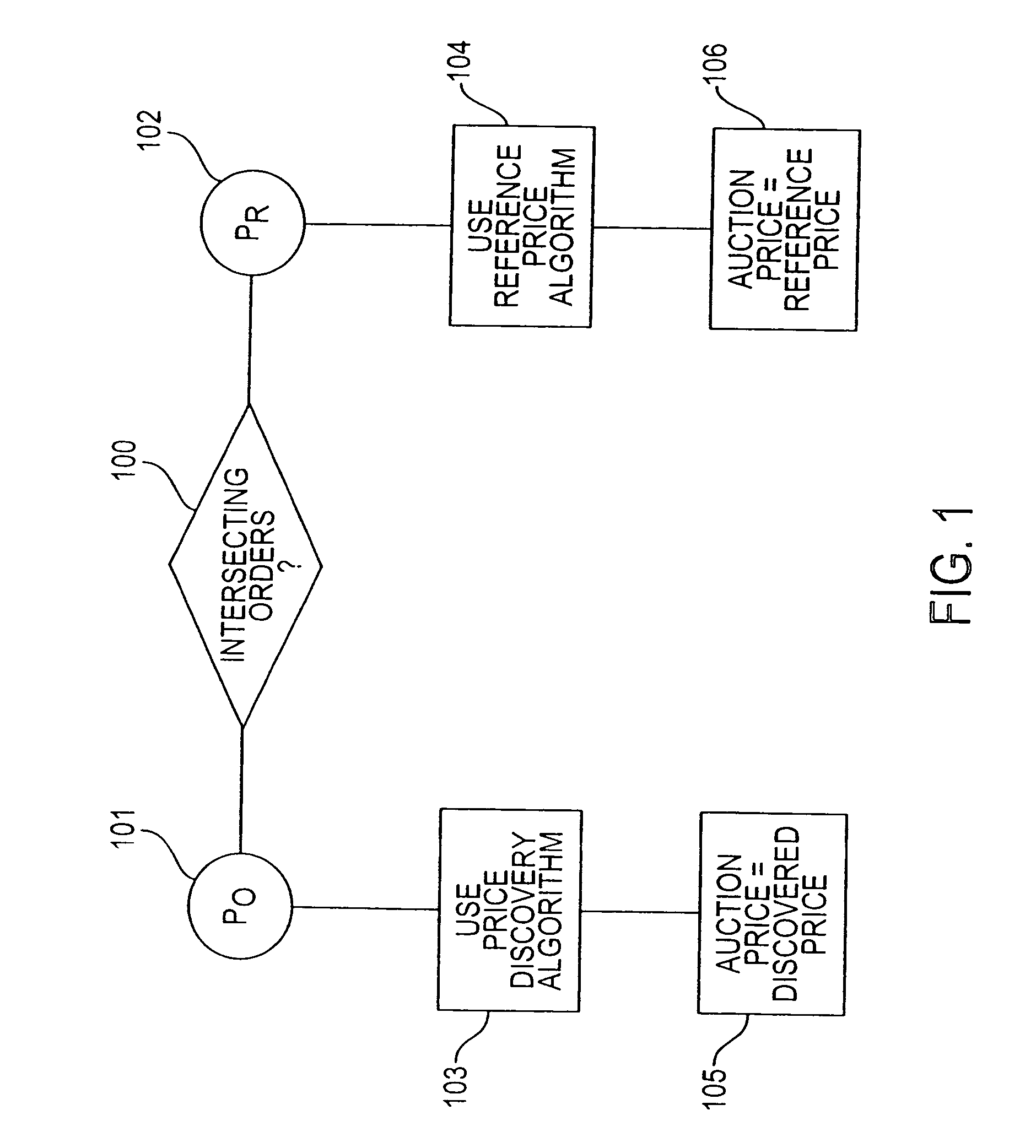
[0044] At a price of ½, only A is willing to buy, thus only 10,000 shares would be executed. At a price of ⅜, 20,000 shares would be executed as both A and B are willing to buy 10,000 apiece while X and Y are willing to sell 10,000 apiece. Since there is a single volume maximizing price, the discovered price equals ⅜.
[0045] The volume of unpriced orders will be included in the cumulative supply and demand of volume. For example, if there are 50,000 units of unpriced buy orders and 25,000 units of unpriced sell orders, these shares will be added to volume of priced buy and sell orders, respectively, at each price. If unpriced orders meet priced orders that do not intersect, these unpriced...
example 2
[0047] Buyer A enters a priced order offering to buy 10,000 shares at a price of 50.00, and an unpriced order offering to buy 50,000 shares at the determined price.
[0048] Buyer B enters a priced order offering to buy 5,000 shares at a price of 50.10.
[0049] Seller X enters a priced order offering to sell 20,000 shares at a price of 50.30, and an unpriced order offering to sell 25,000 shares.
[0050] Seller Y enters a priced order offering to sell 15,000 shares at a price of 50.20.
[0051] Between A, B, X, and Y there are unpriced and non-intersecting priced buy and sell orders on for the particular auction cycle. At a price of 50.00, buyer A would be willing to buy a total of 60,000 shares and buyer B would be willing to buy a total of 5,000 shares. Thus, aggregate demand at a price of 50.00 is 65,000 shares. At this price, neither of seller X's or seller Y's priced orders would be executed. Thus, aggregate supply would equal the total number of unpriced order shares, 25,000.
[0052] ...
example 3
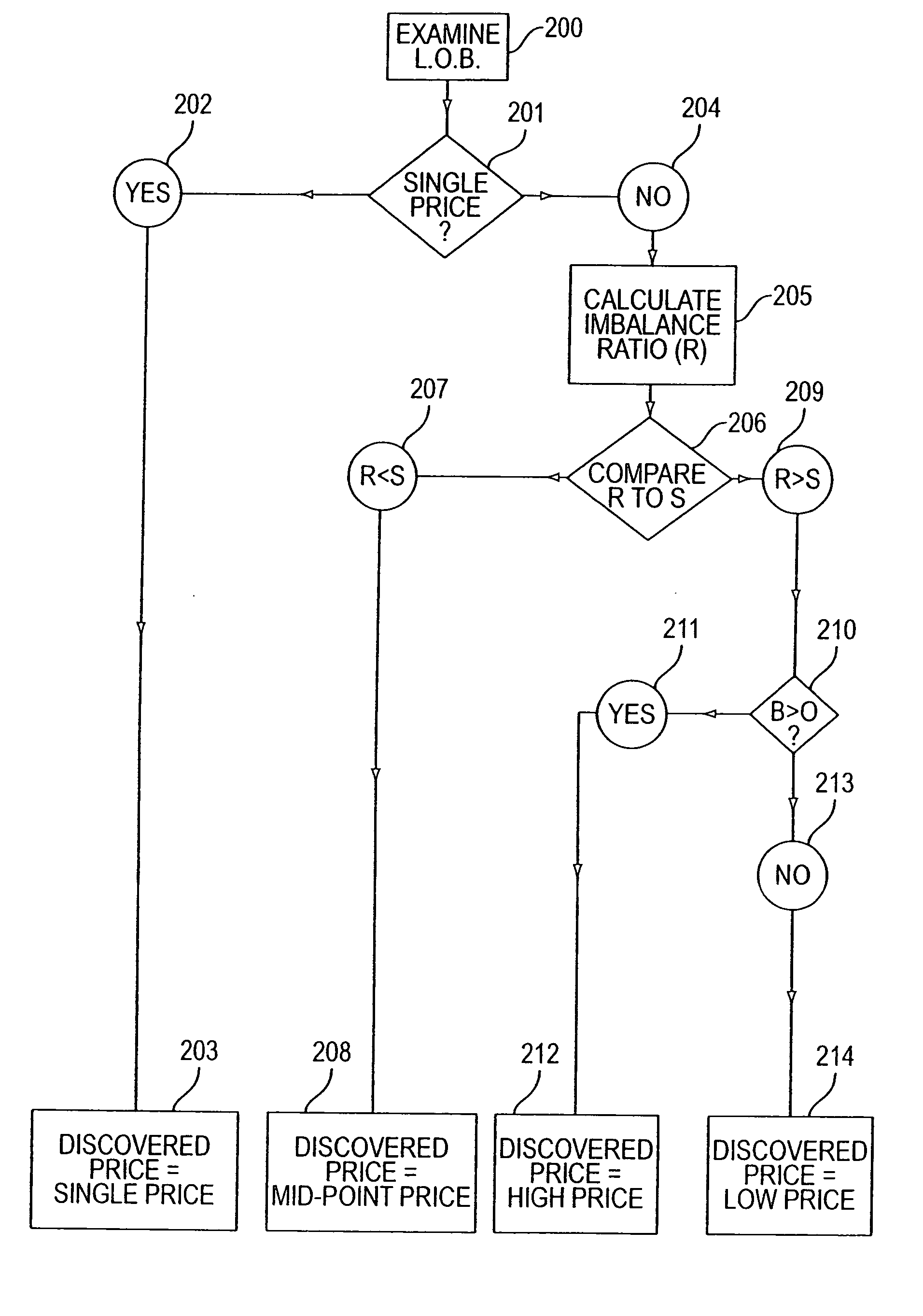
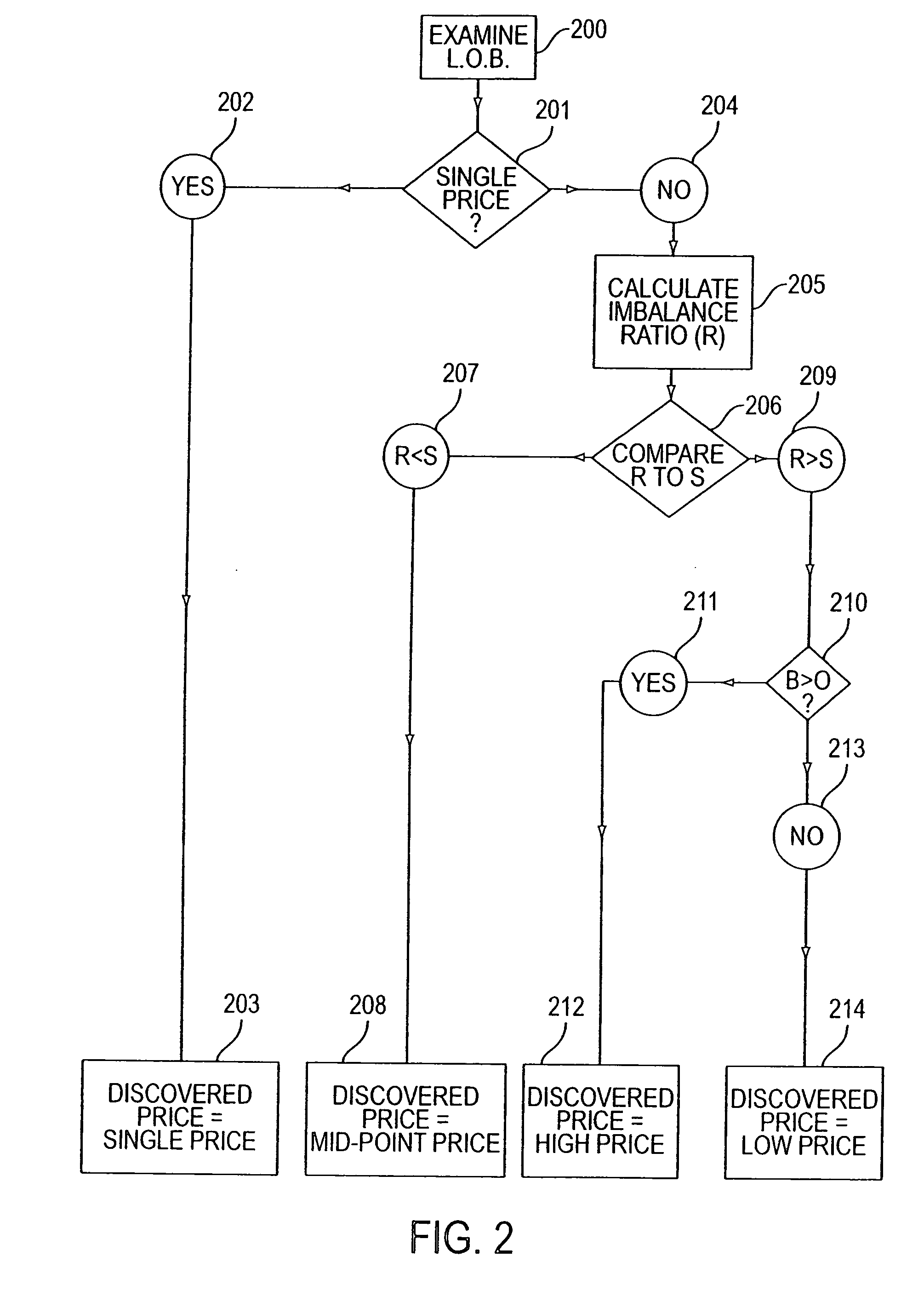
[0059] Same facts as example 1, except that X and Y only wish to sell 5,000 shares apiece for ⅜.
[0060] The standard “S” for the particular stock in question is 0.25 (representing a belief that a 25% excess of supply over demand, or vice versa, would constitute a large enough net order imbalance to significantly impact price).
[0061] Using equation 1, B is 10,000, O is 10,000, and L is 10,000, thus R is calculated to equal 0.00 (i.e., no net order imbalance). Since R is less than S, the net order imbalance is deemed to not significantly impact price.
[0062] Given that X and Y will sell 5,000 shares apiece (10,000 total) whether the price is ½ or ⅜ (there is no single volume maximizing price) and that R is less than S, the discovered price will be the mid-point of the volume maximizing range (⅜ to ½). Thus, the price is 7 / 16.
[0063] If the imbalance ratio is greater than the appropriate standard 209, the imbalance of supply and demand of the particular stock within the volume maximiz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com