Match System that Uses a Non-Indexed Collection of Orders
a non-indexed collection and order technology, applied in the field of financial instruments trading, can solve the problems of insufficient efficiency in aggregating and retrieving trading data, substantial chip clock cycles, and insufficient efficiency in storing and searching large amounts of data, and achieve efficient processing, storage and searching, and efficient storage and searching of large amounts of data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Exemplary Operating Environment
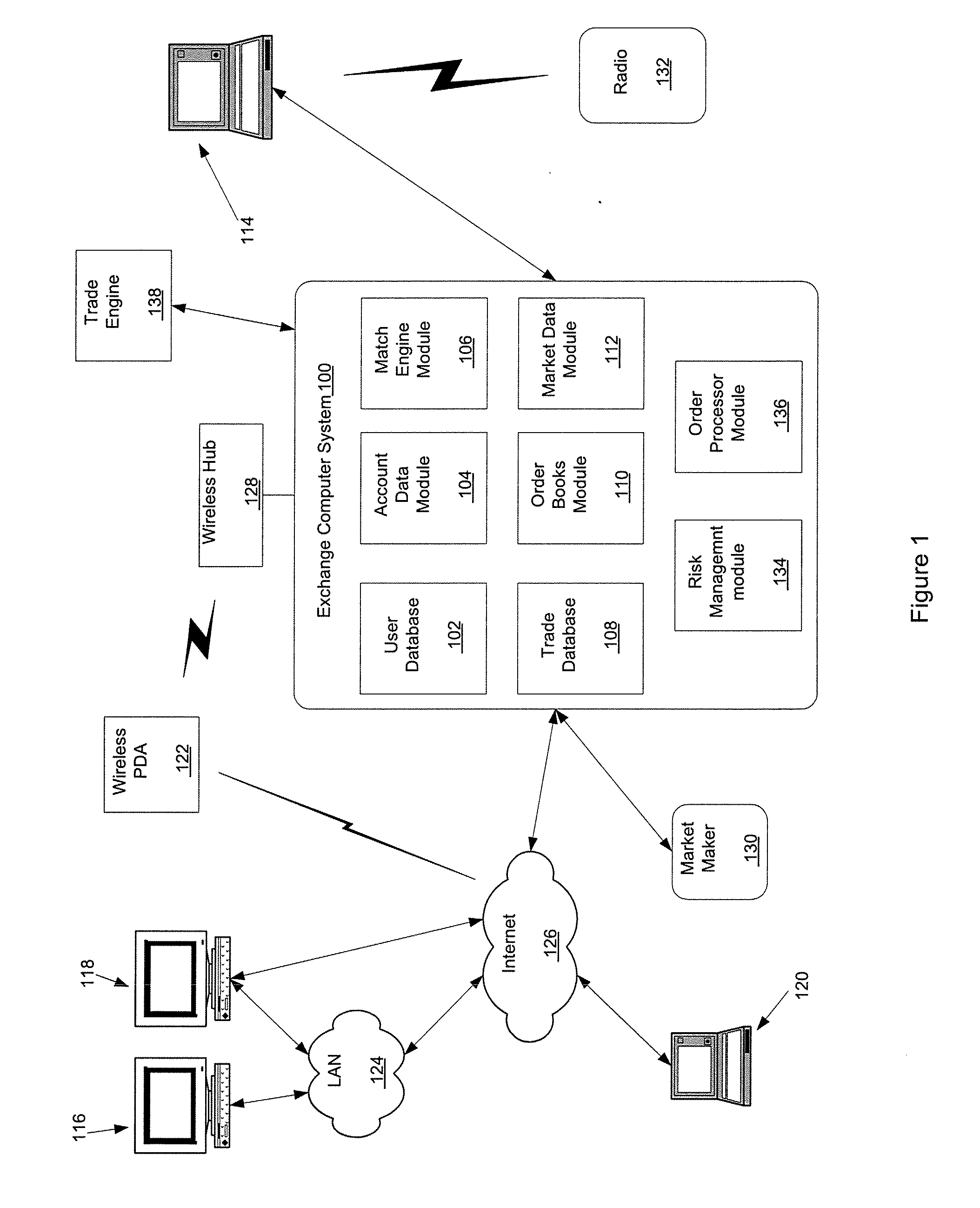
[0020] Aspects of the present invention are preferably implemented with computer devices and computer networks that allow users to exchange trading information. An exemplary trading network environment for implementing trading systems and methods is shown in FIG. 1.
[0021] An exchange computer system 100 receives orders and transmits market data related to orders and trades to users. Exchange computer system 100 may be implemented with one or more mainframe, desktop or other computers. In one embodiment, a computer device uses a 64-bit processor. A user database 102 includes information identifying traders and other users of exchange computer system 100. Data may include user names and passwords. An account data module 104 may process account information that may be used during trades. A match engine module 106 is included to match bid and offer prices. Match engine module 106 may be implemented with software that executes one or more algorithms for m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com