Charge transfer device
a technology of charge transfer and discharge device, which is applied in the direction of radiation control devices, semiconductor devices, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of transfer failure, ccd discharge capacity reduction, and more likely, and achieve the effect of lowering power source voltage and channel potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
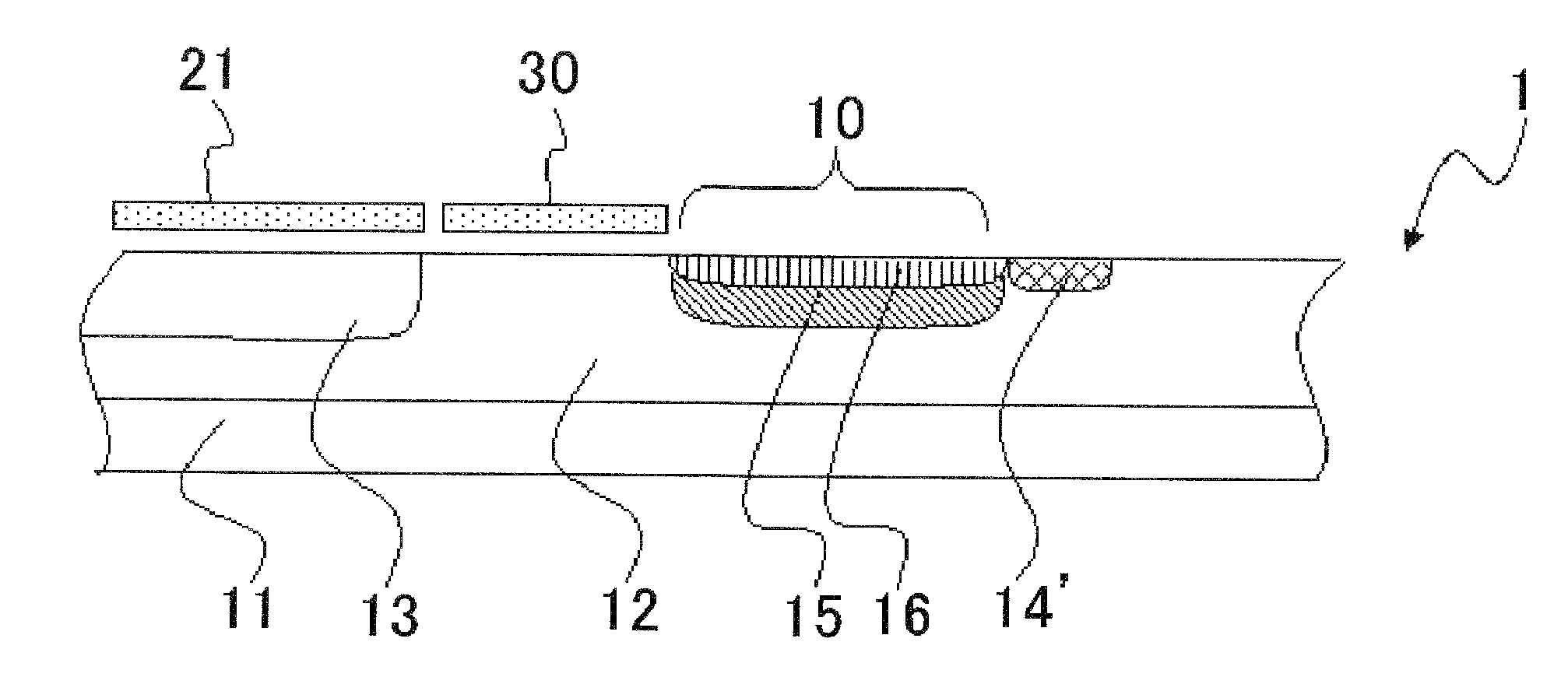
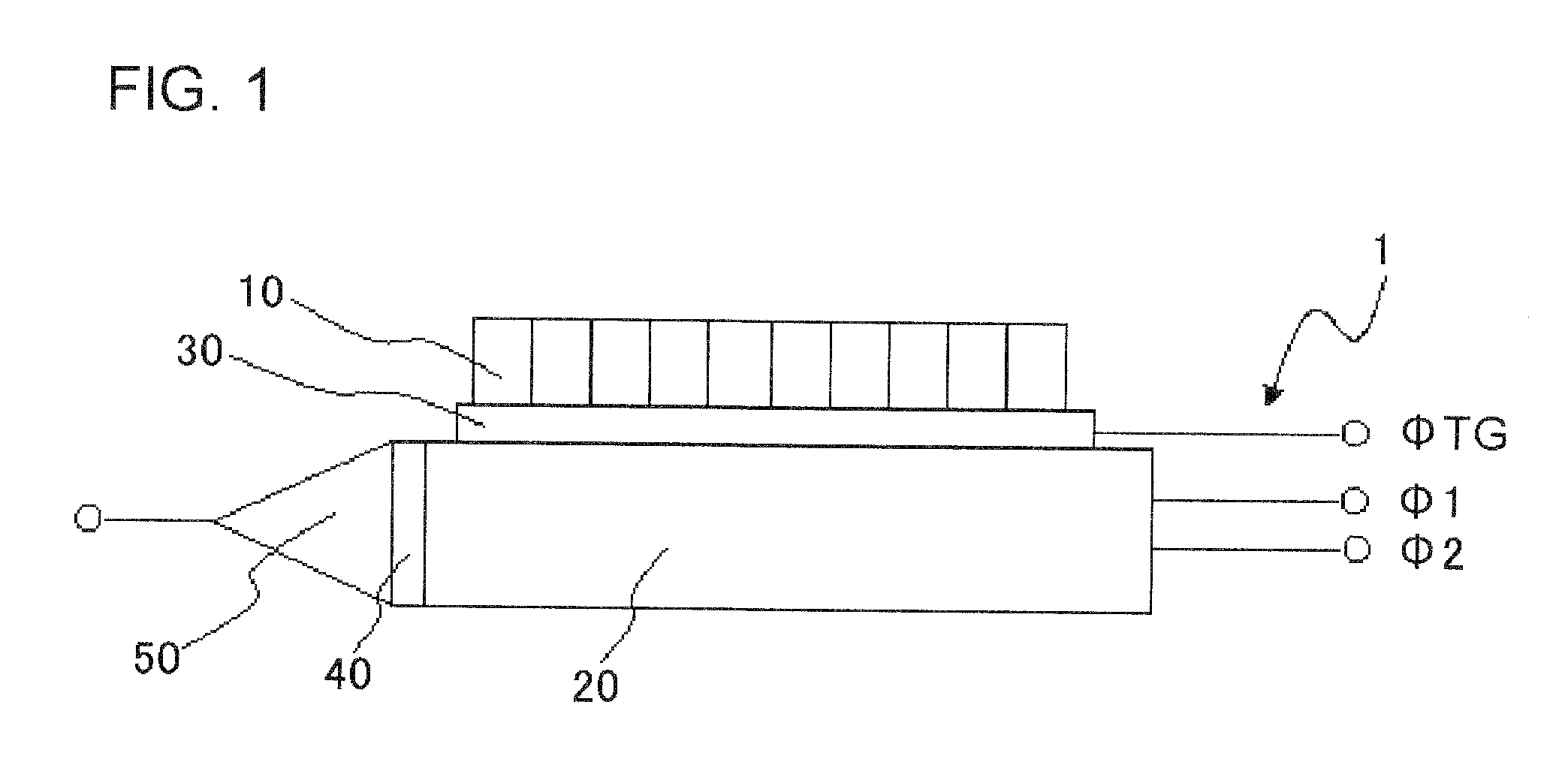
[0042]FIG. 1 is a schematic drawing of a CCD image sensor (charge transfer device) according to a first embodiment of the present invention. A CCD image sensor 1 has photodiodes 10, a CCD register 20, and a transfer gate electrode 30. On one end of the CCD register 20, there are provided a charge detecting unit 40 and an output circuit 50. The transfer gate electrode 30 is provided between the photodiodes 10 and the CCD register 20.
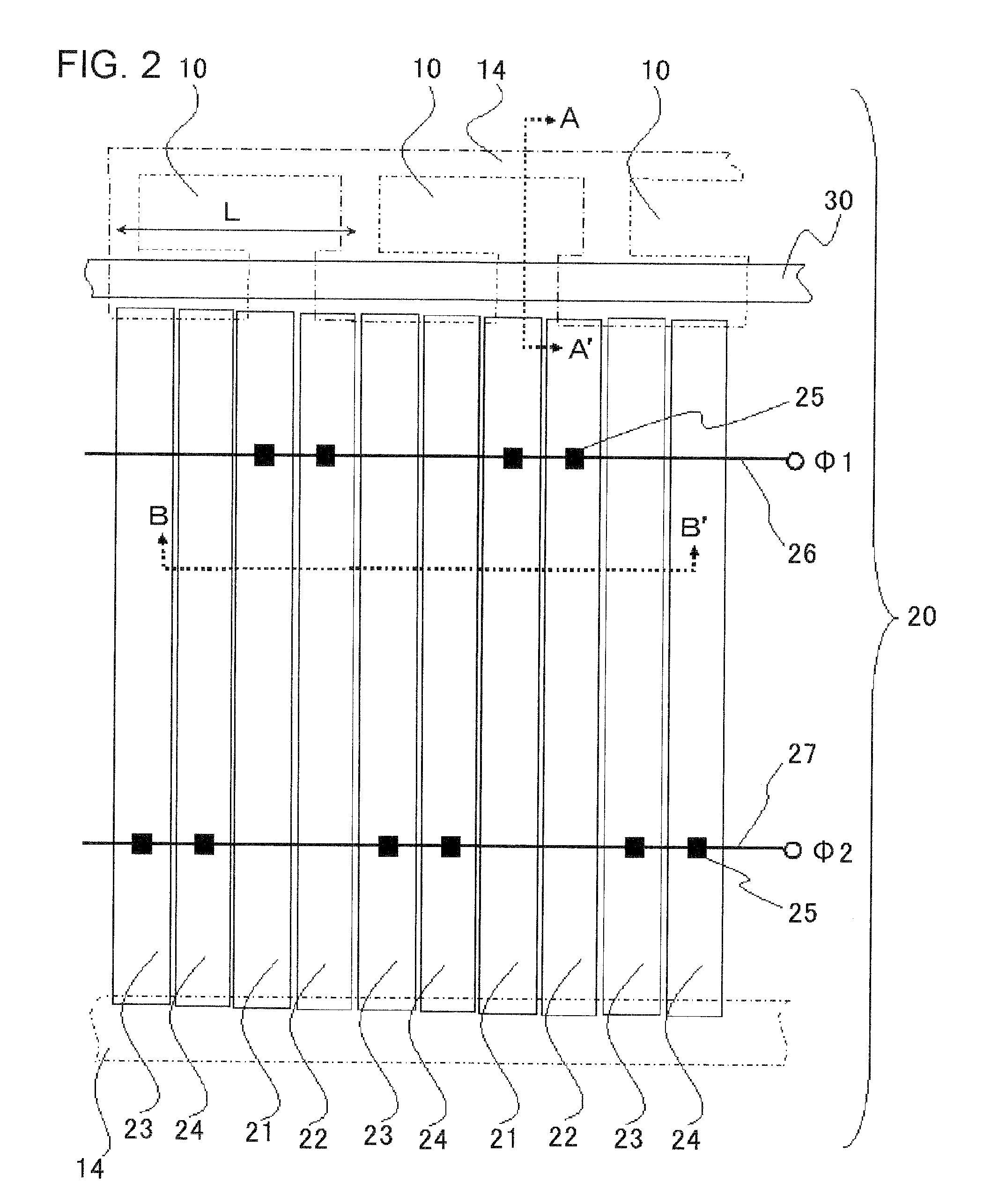
[0043]FIG. 2 is a plan view of a CCD image sensor 1. The photodiodes 10 are isolated from each other by a device isolation region 14 formed of a P+-type diffusion layer, for example. The CCD register 20 contains four types of electrodes 21 to 24. The electrodes 21 are Φ1 storage electrodes. The electrodes 22 are Φ1 barrier electrodes. The electrodes 23 are Φ2 storage electrodes. The electrodes 24 are Φ2 barrier electrodes. These electrodes 21 to 24 are repetitively arranged in this order. The electrodes 21 to 24 are connected via contacts 25 to metal inte...
second embodiment
[0060]FIG. 7 is a plan view of a CCD image sensor according to a second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 8A and FIG. 8B are sectional views respectively taken along E-E′ and line F-F′ in FIG. 7.
[0061]As shown in FIG. 7, two types of electrodes are arranged in the CCD register. Electrodes 29 are Φ1 electrodes formed of P-type polysilicon. Barrier regions 19 are N−-type diffusion layers formed by ion implantation into the N well under the electrodes 29. Electrodes 28 are Φ2 electrodes formed of P-type polysilicon. Barrier regions 18 are N−-type diffusion layers formed by ion implantation into the N well under the electrodes 28. The electrodes 29, 28 are connected via contacts 25 to metal interconnects 26, 27, respectively, and are supplied with drive pulse Φ1 or Φ2. Assuming now pitch of unit cell in the direction of electron transfer as L, the configuration herein is such as making two electrodes 29 and 28 corresponded to L.
[0062]FIGS. 9A and 9B are a timing chart of drive p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com