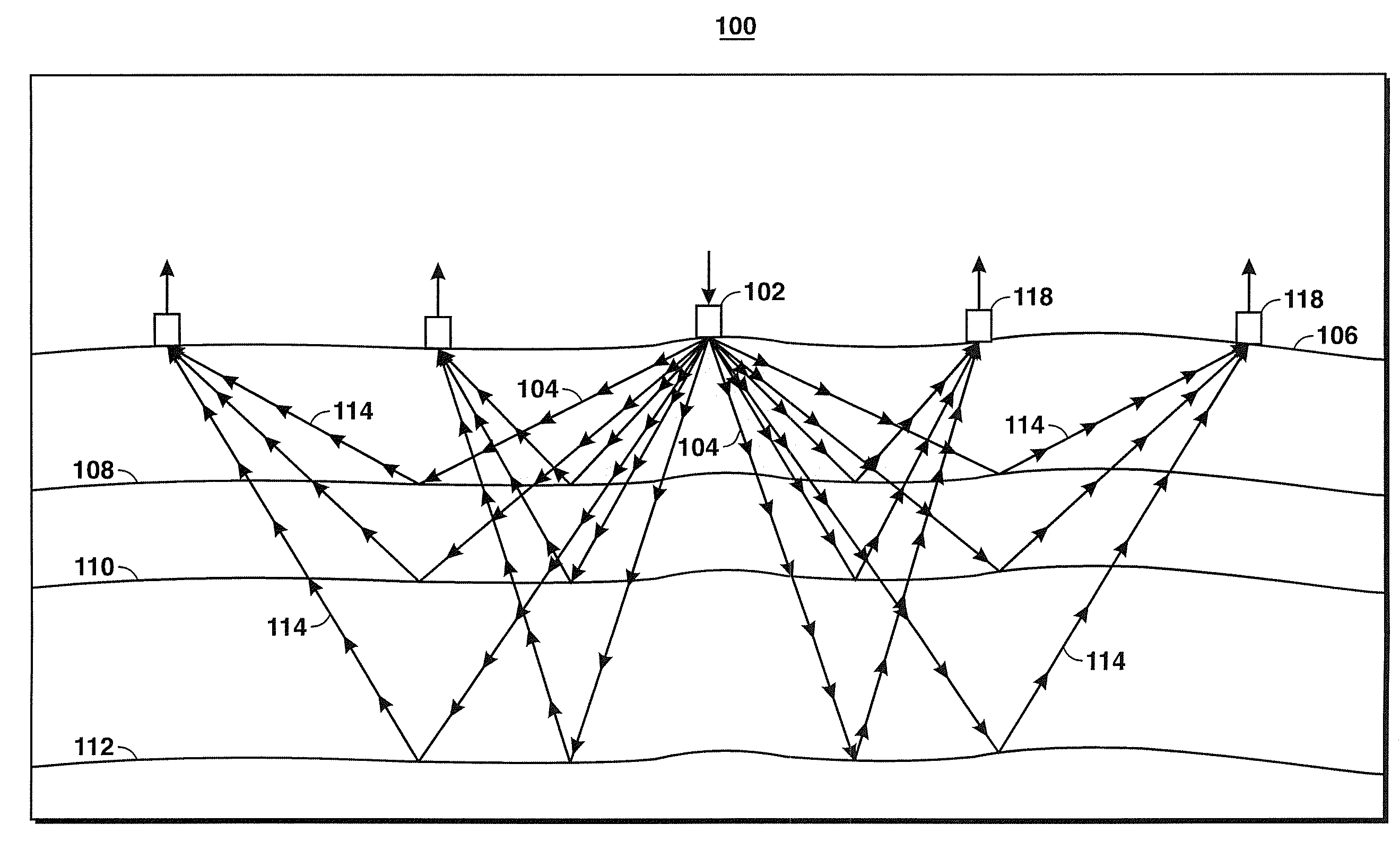
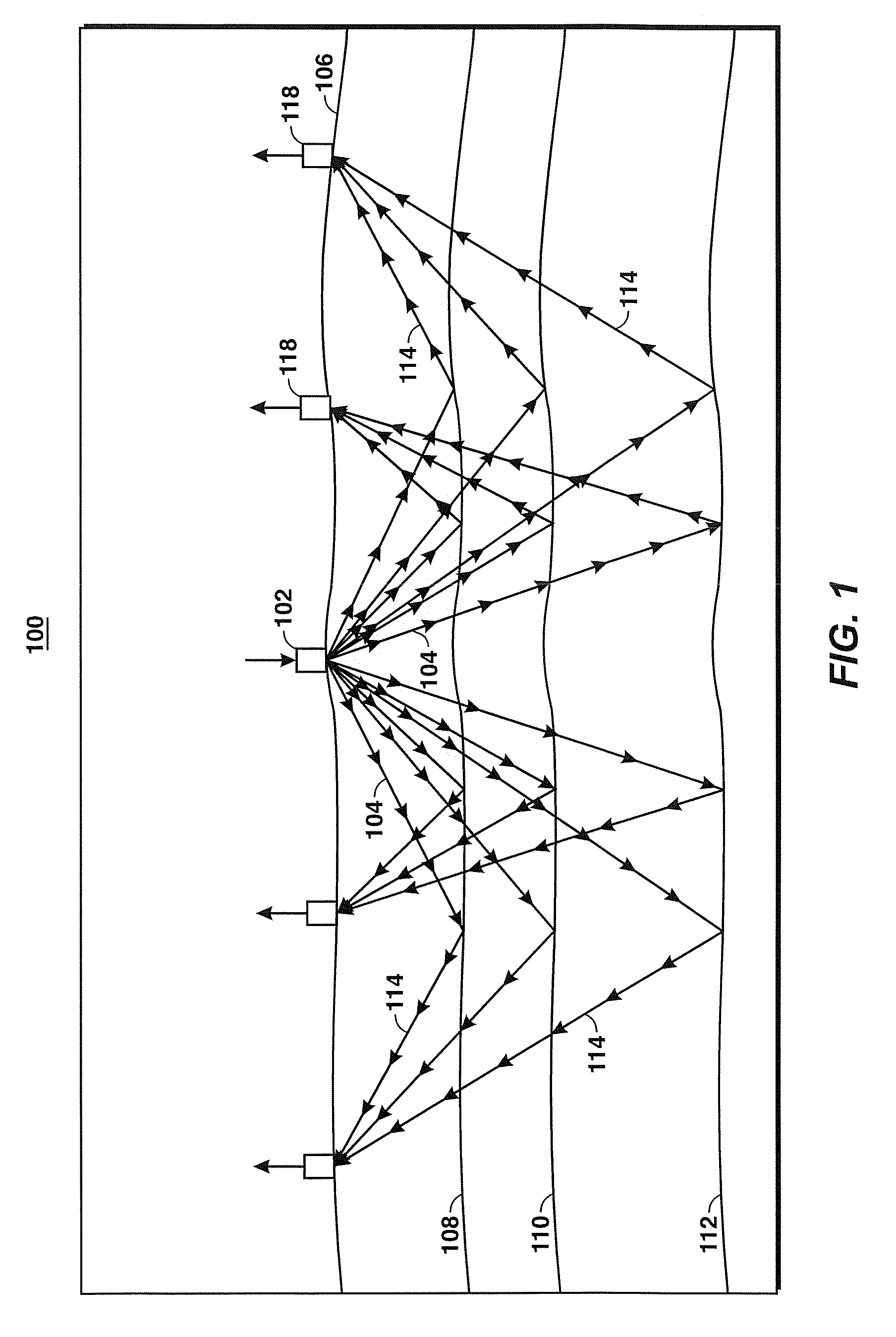
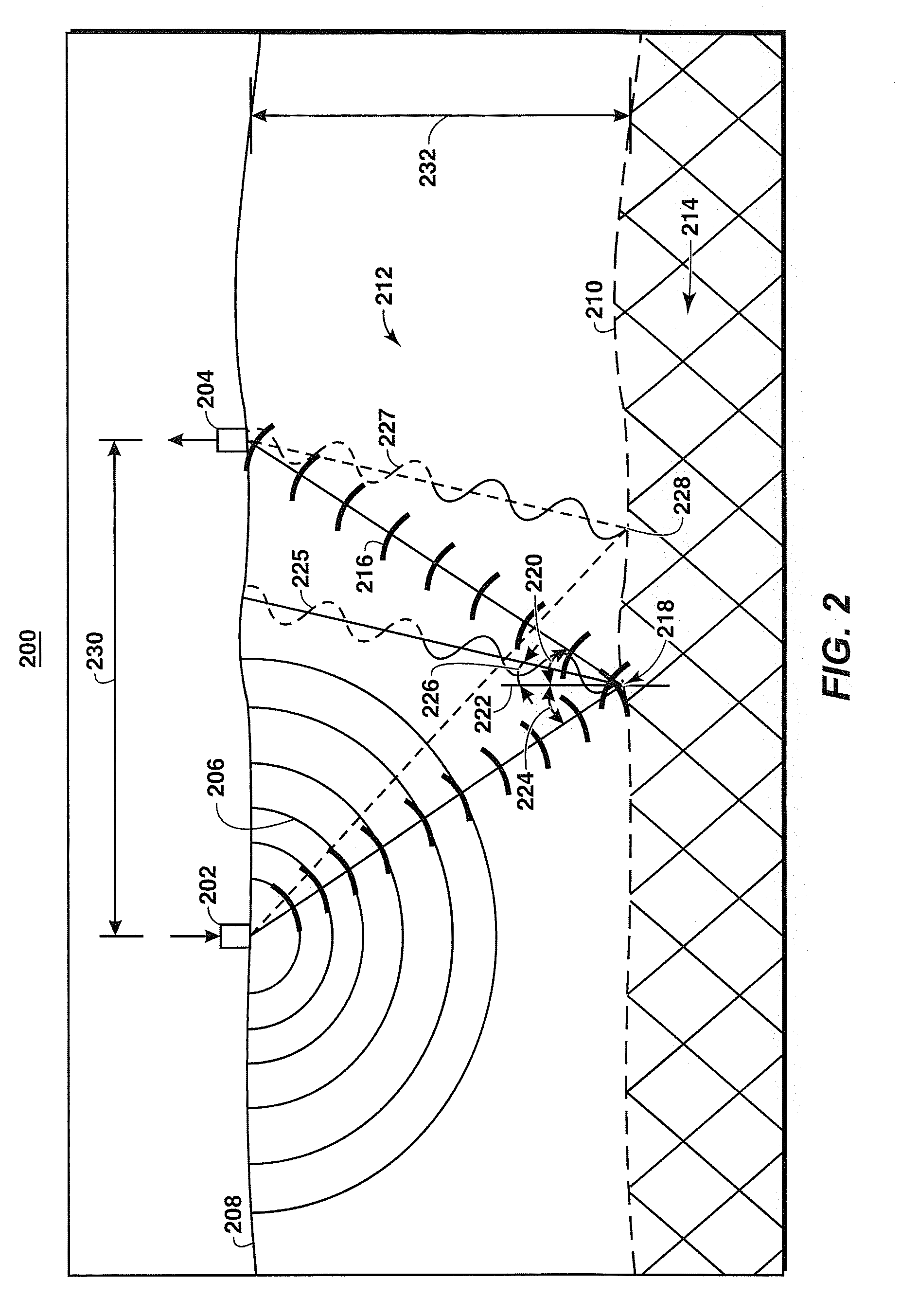
Using Seismic Attributes for Data Alignment and Seismic Inversion In Joint PP/PS Seismic Analysis
a technology of which is applied in the field of using seismic attributes for data alignment and seismic inversion in joint pp/ps seismic analysis, can solve the problems of difficult combining data collected in the different modes in a joint pp/ps analysis, affecting the strength of reflected elastic waves, and affecting the accuracy of seismic image obtained by analyzing seismic signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0128]Simulated seismic data (e.g., simulated or synthesized data) obtained from well log data were used to test the method for aligning PP mode data and PS mode data described herein, in two scenarios, the first assuming a constant Vp / Vs, and the second assuming a variable Vp / Vs. In the first scenario, wherein the value for Vp / Vs was assumed to be constant, the AVA attributes in the attribute volume were derived from well log data that had measured compressional wave velocity, Vp, and density, ρ. The shear wave velocity, Vs was calculated from Vp assuming a constant ratio of Vp / Vs=2. The AVA attributes A, B, and D were calculated in depth (time) volumes from equations (3), (4) and (6) from a combination of the available seismic data, e.g., from the well log data. For this simple Vp / Vs scenario, equation (8) provides the relation 3A−B+2D=0, which is equal to a plane in A, B, and D attribute space, as shown in FIG. 5.
[0129]As such, points in the A, B, and D attribute space should the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com