Adaptive common mode bias for differential amplifier input circuits
a differential amplifier and input circuit technology, applied in differential amplifiers, amplifiers with semiconductor devices/discharge tubes, amplifier details, etc., can solve the problems of non-linear operation of differential amplifier stages, non-linear response, complex problems continue to rise to the forefront, etc., and achieve the effect of expanding the input common mode rang
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
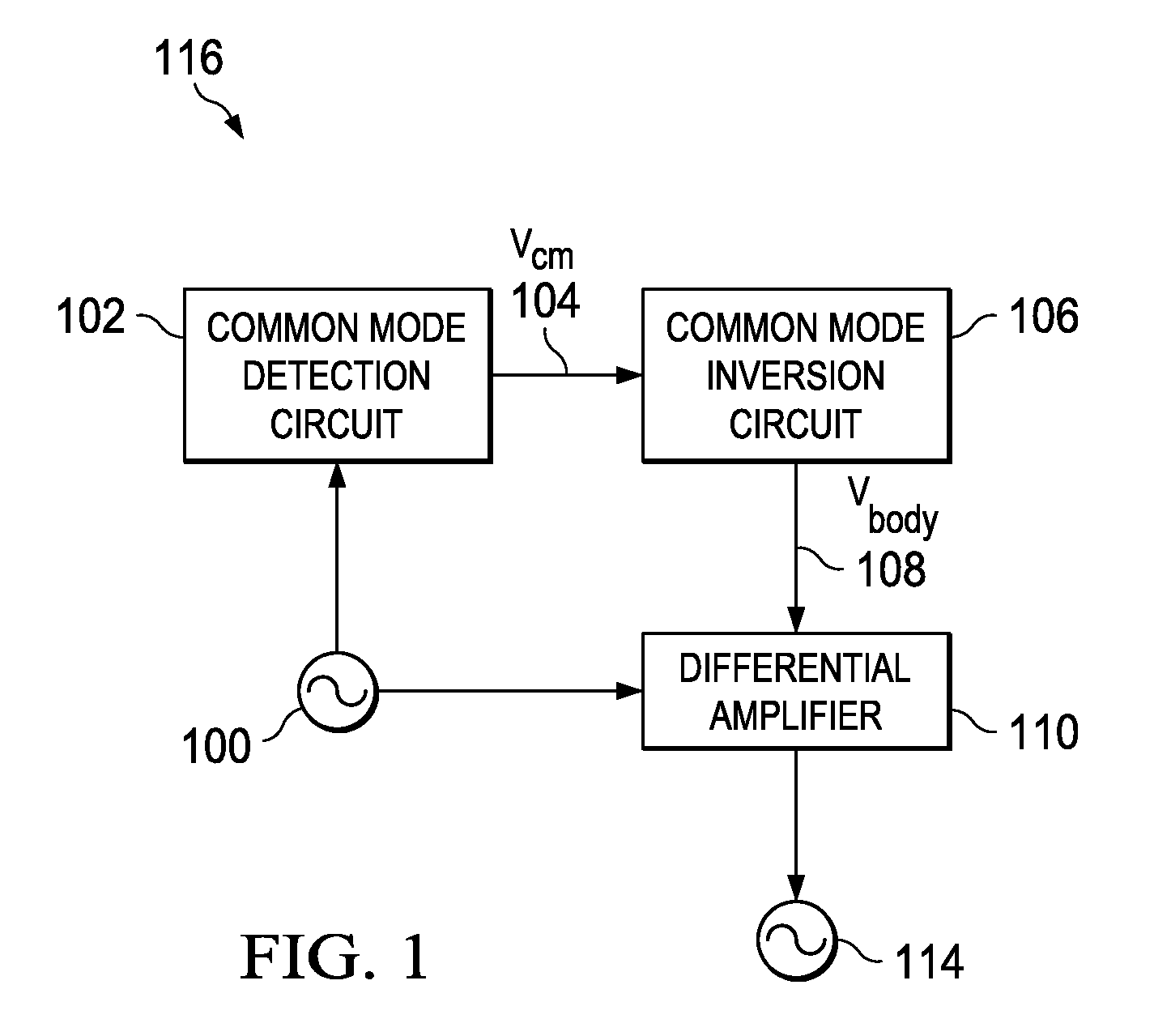
[0020]With reference now to the figures, and particularly with reference to FIG. 1, a block diagram of circuit system 116 is depicted in accordance with an illustrative embodiment. Differential signal 100 is received by both common mode detection circuit 102 and differential amplifier 110. Common mode detection circuit 102 monitors differential signal 100 to determine common mode voltage 104 of differential signal 100. Common mode voltage 104 passes through common mode inversion circuit 106 creating body voltage 108. Body voltage 108 bears an inverse relationship to common mode voltage 104, thereby extending the common mode range of differential amplifier 110. Differential amplifier 110 produces output signal 114. While circuit system 116 is comprised of common mode detection circuit 102, common mode inversion circuit 106, and differential amplifier 110 in this illustrative embodiment, additional circuitry may be added to circuit system 116.
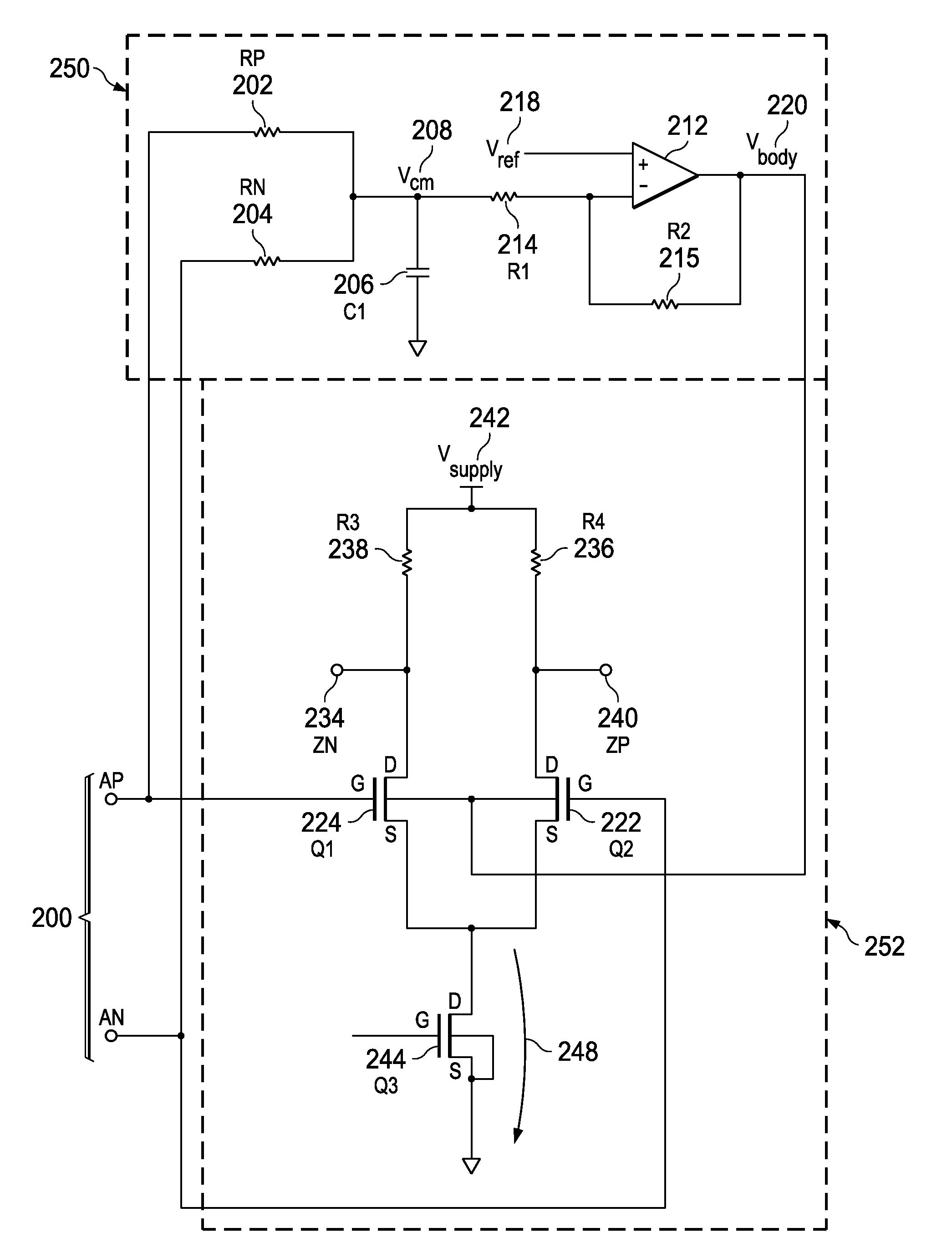
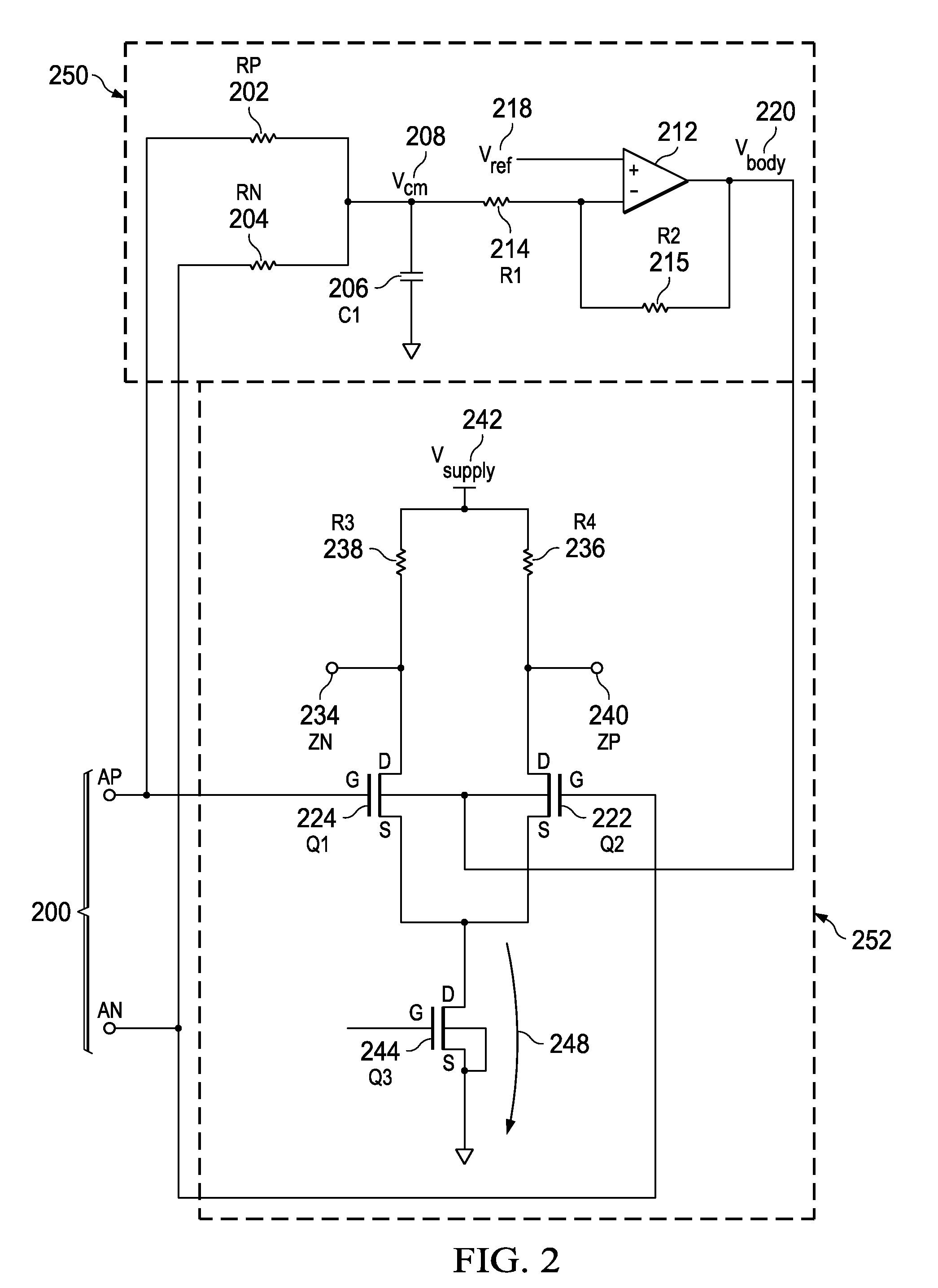
[0021]Turning now to FIG. 2, a circuit dia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com