STRUCTURE OF THE C-TERMINAL REGION OF THE INSULIN RECEPTOR a-CHAIN AND OF THE INSULIN-LIKE GROWTH FACTOR RECEPTOR a-CHAIN
a technology of c-terminal region and insulin receptor, which is applied in the direction of instruments, molecular structures, metabolism disorders, etc., can solve the problems of infertility, impaired postnatal growth, and embryonic growth deficiency, and the conclusions of these studies have been questioned
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Solving the crystal structure of the C-terminal region of the α-chain of IR
2.1 Introduction: Ambiguous Electron Density
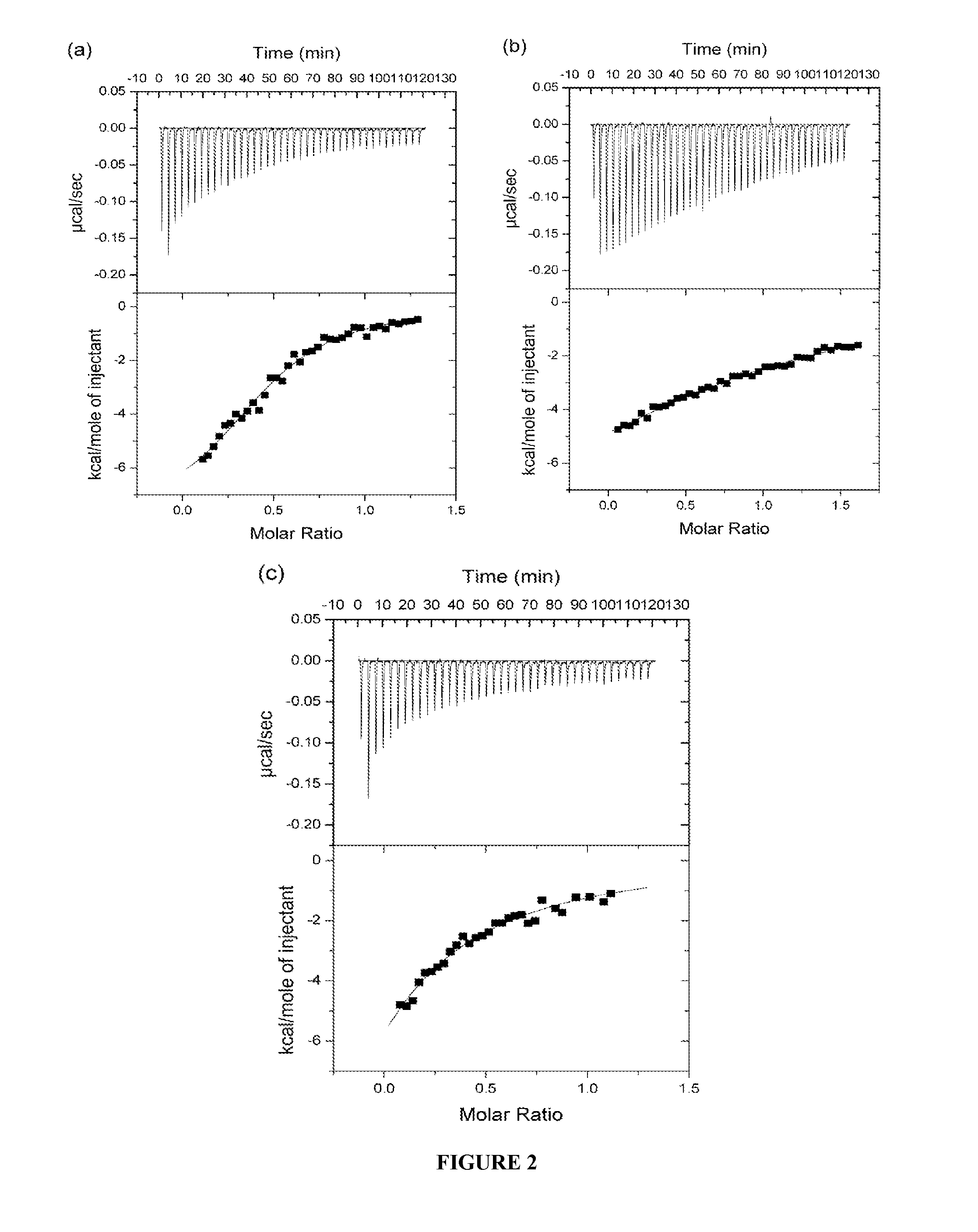
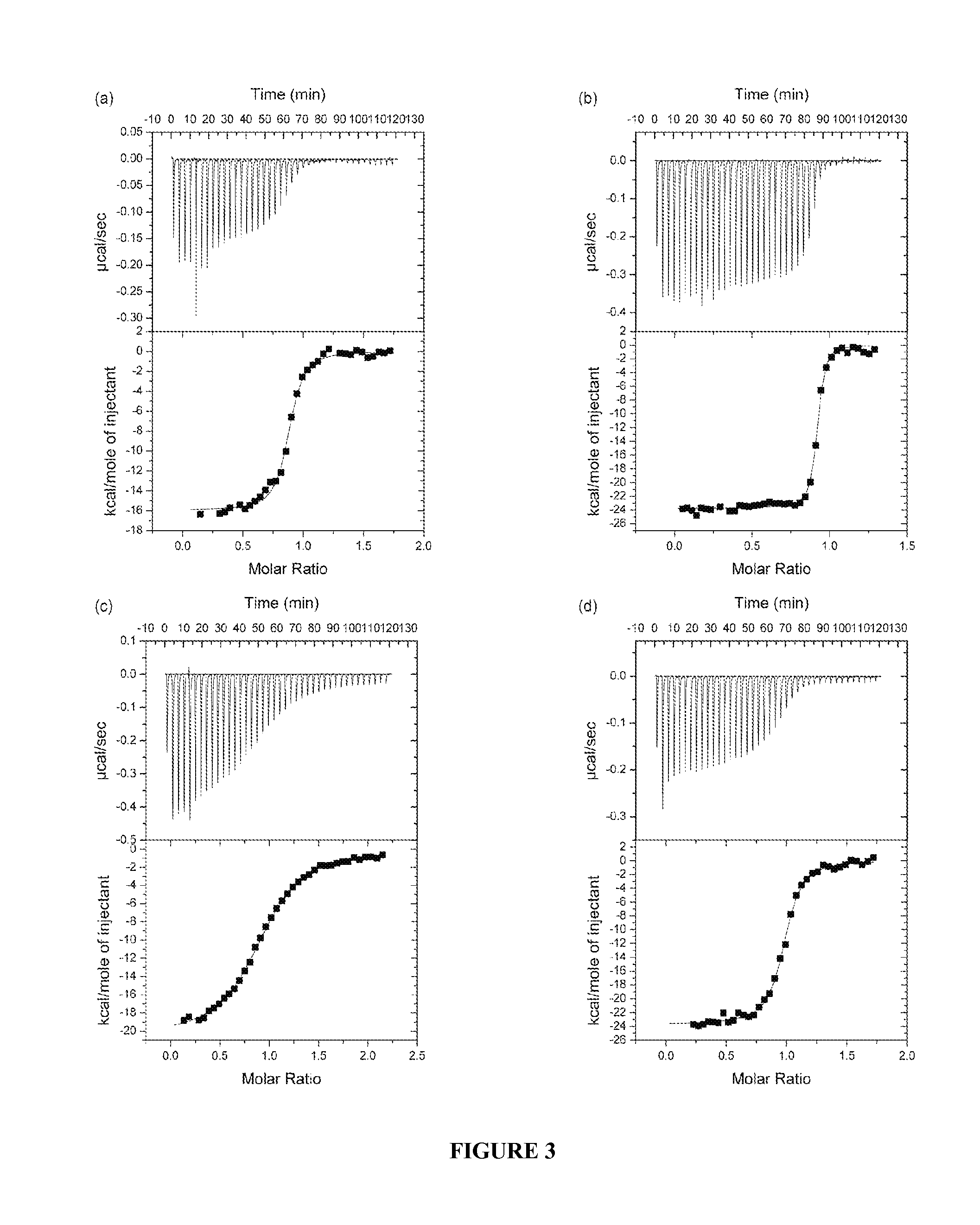
[0330]As described previously (WO 07 / 147,213), an area of strand-like ambiguous electron density was present near the L1-β2 face of IR. However, despite numerous different processing and refinement protocols, the density was impossible to interpret in terms of any peptide sequence. The data described in Example 1 above implied a surprising and previously unexpected sequence relationship between the S519C16 peptide (SEQ ID NO: 18) and the ‘classical’αCT peptide region (residues 704-719; SEQ ID NO: 11) described previously in the literature (Kurose et al., 1994). X-ray data obtained in WO 07 / 147,213 were revisited and further reviewed with the possibility then in mind that the ambiguous electron density near the L1-β2 face of IR could have been due to the ‘classical’αCT peptide region of the IR α-chain.
2.2 Protein Production, Crystallisation and Data Collection from I...
example 3
Molecular modelling
3.1 Introduction
[0338]There is a high level of sequence identity between, on the one hand, the L1 domains of IGF-1R and IR, and, on the other hand, between the C-terminal regions of the α-chain of IGF-1R and IR (FIG. 1 and FIG. 6c). Accordingly, models of IR in complex with S519C16 and the IGF-1R α-chain residues 681-697, respectively, were constructed using the MODELLER program (SalI and Blundell, 1993) with the crystallographic structure of IR ectodomain presented in the main text as a template. Models of theectodomain of IGF-1R in complex, respectively, with the IGF-1R α-chain residues 681-697 (SEQ ID NO: 15), S519C16 (SEQ ID NO: 18) and the IR α-chain residues 693-710 (SEQ ID NO: 13) were constructed employing the crystal structure of the first three domains of IGF-1R (Garrett et al., 1998), the structure of the IR ectodomain presented here and the known sequence relationship between IR and IGF-1R (Adams et al., 2000).
3.2 Materials and Methods for Modelling
[03...
example 4
Binding of Mutant αCT Peptides to an Insulin Mini-Receptor (1R485 Construct)
4.1 Introduction
[0358]Insulin-mimetic peptides have been discovered by phage display technology and classified as “Site” 1, 2 or 3 on the basis of competition of binding to insulin receptor (Pillutla et al., 2002). The affinity-matured Site 1 peptides are characterized by a FYXWF motif (SEQ ID NO: 19) (Pillutla et al., 2002); selected Site 1 and 2 peptides have been covalently tethered to yield agonists with up to picomolar affinity for insulin receptor (Schaffer et al., 2003). A sequence relationship has been shown (see FIG. 6c) between the αCT region and the prototypic Site 1 mimetic peptide that places the αCT region residues Phe701 and Phe705 in respective alignment with the two flanking phenylalanine residues in the FYXWF motif This relationship was used to explain the competitive binding of the αCT peptide and the prototypic Site 1 mimetic peptide to the insulin mini-receptor IR485, a construct which c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com