Knowledge Reasoning Method of Boolean Satisfiability (SAT)
a boolean satisfiability and knowledge reasoning technology, applied in knowledge based models, instruments, computing, etc., can solve the problems of solving algorithms that have been proposed and implemented, and none of them can reach a polynomial-time efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017]Elimination of OR Operator Method
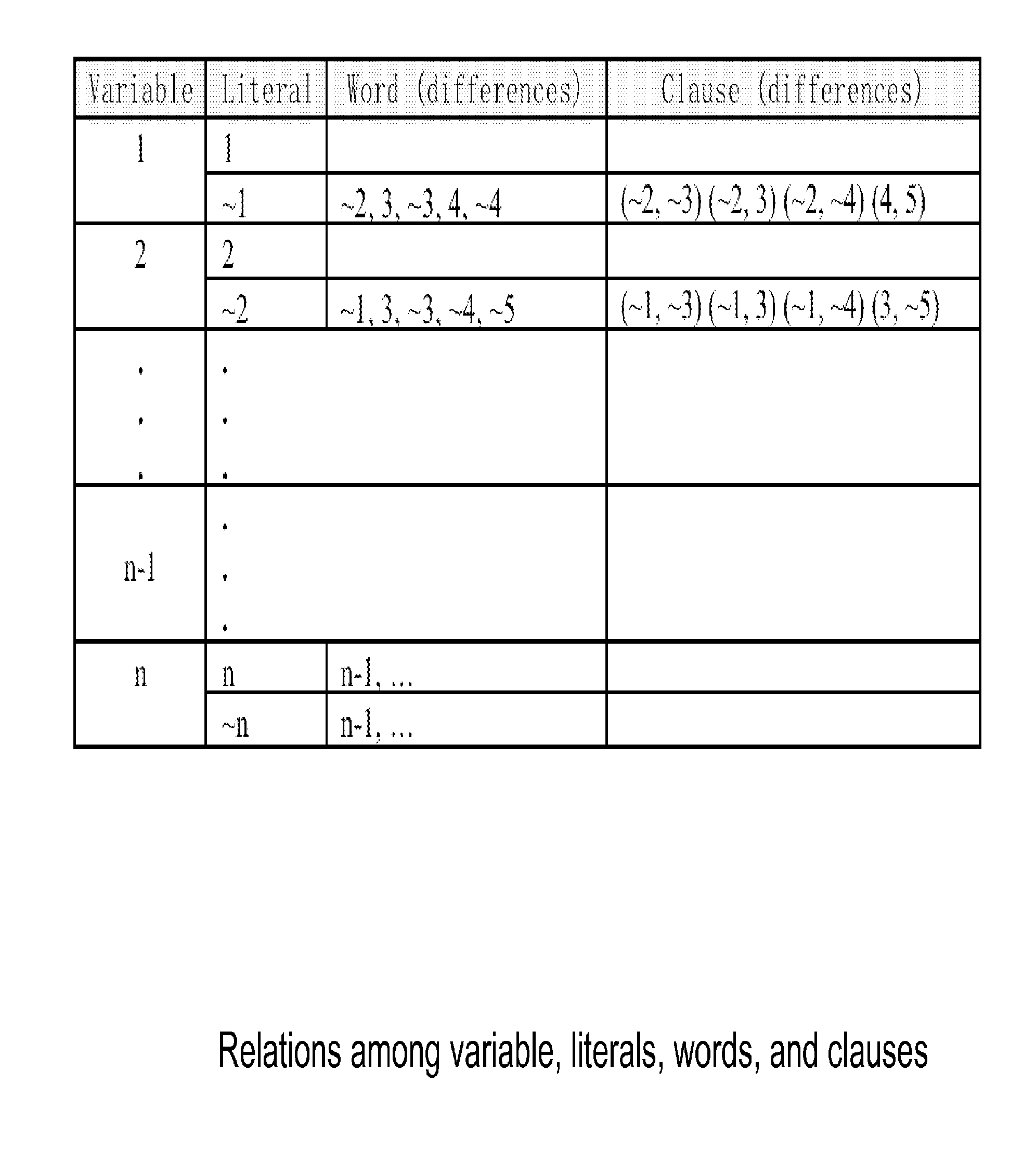
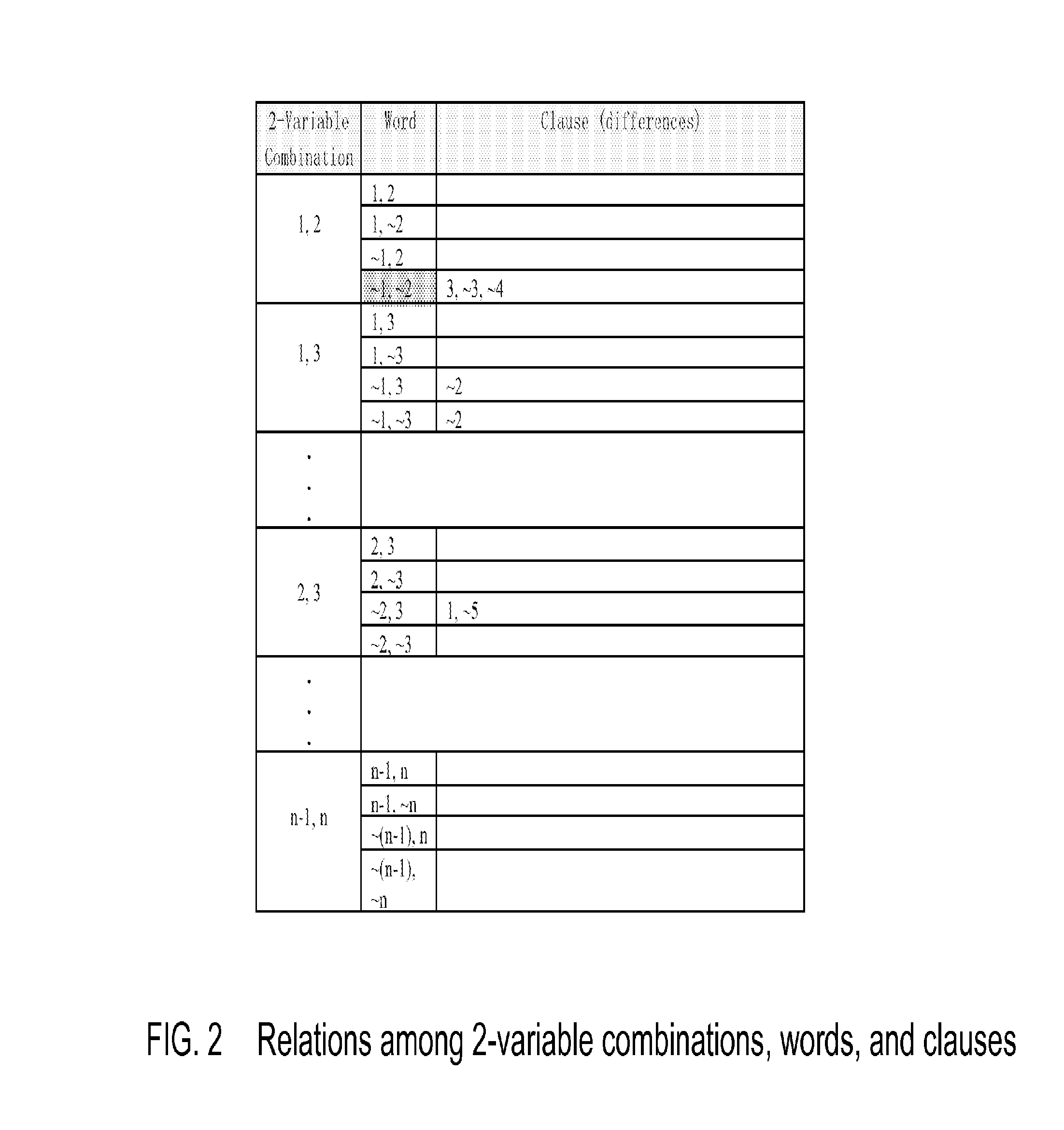
[0018]The present knowledge reasoning method applies a patented knowledge acquisition and retrieval method disclosed in the US patent “Knowledge Acquisition and Retrieval Apparatus and Method” (U.S. Pat. No. 6,611,841) by the same inventor Sherwin Han. Knowledge reasoning method converts the disjunction of the literals of the formula clauses to its semantic equivalent conjunction of literals, and eliminates OR operators. Each 3SAT formula contains m disjunctive clauses, and each disjunctive clause can be represented by a set of eight conjunctive clauses including one complement. For example, disjunctive clause (xxx2˜x3) can be presented by a set of eight conjunctive clauses {(x1x2x3), (x1x2˜x3), x1˜x2x3), (x1˜x2˜x3), (˜x1x2x3), (˜x1x2˜x3), (˜x1˜x2x3), (˜x1˜x2˜x3)} in which (˜x1˜x2x3) is a complement of (x1x2˜x3). Clause (x1x2˜x3) means that (˜x1˜x2x3) is not satisfiable, and the rest of conjunctive clauses are satisfiable. Elimination of OR ope...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com